Global Location Number
Global location numbers (GLNs) are a key component in electronic transactions such as Electronic Data Interchange (EDI). They provide a unique and efficient identification of all locations relevant to EDI transactions. The advantage to using GLNs is that every EDI transaction does not have to communicate information about particular locations such as names and addresses. Organizations can communicate this information only once, enter it onto computer files, and subsequently retrieve it by referring to a unique GLN.
Companies involved in a variety of business activities such as life sciences, chemicals, electronics, and pharmaceuticals, are using GLNs. The United Nations, Electronic Data Interchange for Administration, Commerce and Transport (UN/EDIFACT) and the International Standard Organization (ISO 6523) recognize GLNs as a viable part of the international community in more than 100 countries
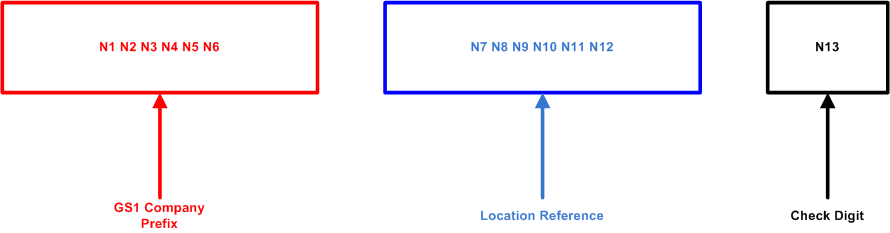
The GLN is a standard means to identify physical locations, business units, cost centers, and so on. It is a 13-digit number composed of:
GS1 Company Prefix
The first six digits of the GLN is the GS1 company prefix. The GS1 member organization assigns the company prefix to ensure uniqueness of the number.
Note: You can set up your GS1 prefix in UDC table 47/LN.Location Reference
The following six digits represents entities within the company. Each company or organization holding a GS1 company prefix can assign GLNs to their own locations. The company can assign a location reference to business units within the company.
Check Digit
This is the final digit of the GLN number. This single digit number is calculated according to a standard algorithm to ensure data integrity.
With JD Edwards EnterpriseOne, you can use GLNs to improve efficiency of integrated logistics and to provide value to partners and customers. You can use a GLN to identify:
Functional entities such as a customer service or billing department within a company.
Physical entities such as a branch/plant, warehouse, or a delivery location.
External organizations such as trading partners, customers, and suppliers.
Additionally, the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne system uses GLNs for real-time events (RTE), business services (BSSV), and EDI transactions within distribution systems such as Sales, Procurement, and Transportation.
You can only associate a GLN with an address book number. For internal business units you can dynamically generate GLNs by clicking a button. Additionally, you can provide external support by manually entering GLNs to update the address book record of the respective vendor or customer.