Creating DB Systems in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure
This section shows you how to create DB systems in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure.
If you are implementing your database in Compute, you should be using the Learning Path entitled: "Deploying JD Edwards EnterpriseOne on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure on Linux with Compute Database".
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure offers 1-node DB systems on either bare metal or virtual machines, and 2-node RAC DB systems on virtual machines. The Oracle Database environment that your deployed database provides in either type of infrastructure is nearly the same. A few differences exist in the underlying infrastructure components and in the supported capabilities. Awareness of these differences will help you choose an appropriate infrastructure when deploying a database. For further details, refer to About Database Deployments in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure.
Prerequisites
- Refer to Prerequisites in this Oracle Cloud Infrastructure documentation: Creating Bare Metal and Virtual Machine DB Systems.
- The user interface for the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Console is constantly evolving. For the most up-to-date descriptions and navigation, refer to Using the Console.
- You should have a fundamental understanding of Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. It is highly recommended that you review the extensive collateral information, including training, at this site:
- You must have a subscription to the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure and an Administrator account in the platform. For more information, refer to:
- To access the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Console, you must use a supported browser.
Create DB Systems
Use this procedure if you choose to use DB systems for your Oracle database instead of creating an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Compute instance for your Oracle database.
For additional information on completing the fields for creating a DB System, refer to the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure documented for Creating Bare Metal and Virtual Machine DB Systems.
With DB systems, you can choose either of these licensing models:
- License Included (subscription service)
- Bring Your Own License (BYOL)
- On the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Console Home page, click the navigation menu in the upper-left corner.
- From the navigation menu, in the Oracle Database section, select Bare
Metal, VM, and Exadata.
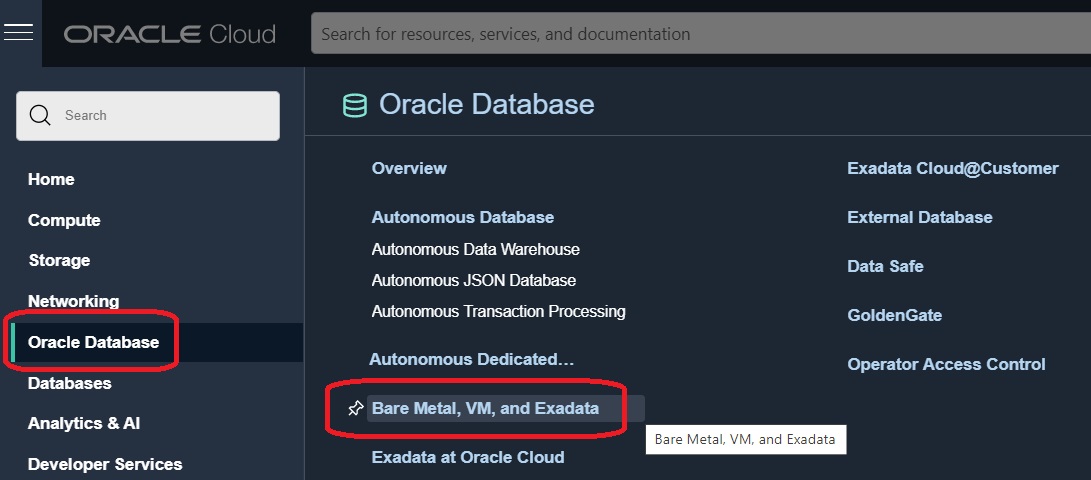
- On the Bare Metal, VM, and Exadata page, in the left pane, ensure that DB Systems is selected.
- By default, the DB System launches in your current compartment and you can use the network and subnet resources in that compartment. Otherwise you can use the pull-down menu in the List Scope section to choose the compartment into which you want to create a DB System. Otherwise you can change the Compartment and assign network resources when you define DB System Information in the following steps.
Click the Create DB System button.
-
The following steps describe the fields on these major sections of the Launch DB System form:
- DB System Information
- Database Information
Note: Refer to Default Options for the Initial Database in this Oracle Cloud Infrastructure documentation: Creating Bare Metal and Virtual Machine DB Systems.
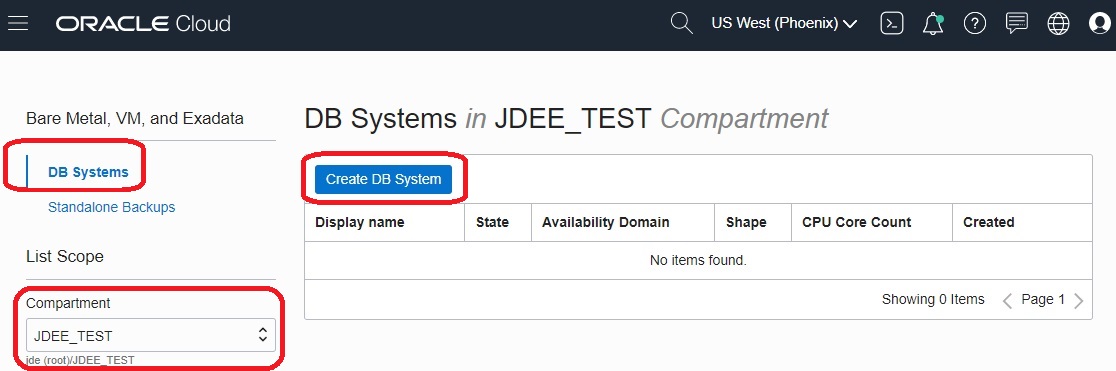
On the Create DB System pane in the DB System Information section, complete the fields to provide basic information for the DB System.
Important: For use with JD Edwards EnterpriseOne, the following conditions apply:-
Select a shape type
The supported shape type for a DB System is Virtual Machine.
-
Shape
Supported shapes are those which meet the OCPU and memory requirements listed in the section of this Learning Path entitled: Minimum Resource Requirements.
-
Oracle Database software edition
Single (1) Node Database
- Standard Edition
- Enterprise Edition
- Enterprise Edition High Performance
-
Enterprise Edition Extreme Performance
- Enterprise Edition Extreme Performance
-
Available Storage (GB)
The minimum recommended size for a JD Edwards EnterpriseOne database is shown in the resource table in the "Before You Begin" section of this Learning Path.
-
Hostname Prefix
Important: For JD Edwards Enterprise One-Click Provisioning, this host name can have a maximum of 15 alphanumeric lowercase characters (special characters such as hyphen (-) are not supported.) You must use this same DNS Hostname Prefix when creating an Orchestration using the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Provisioning Console.
-
-
On the Create DB System page in the Database Information section, complete all required fields. The following are required values for JD Edwards EnterpriseOne:
-
Database Name
Enter the value: orcl
-
Database Version
Select the latest supported database version as listed in the Supported Software Versions section of this Learning Path. For example, 19c.
-
PDB Name
The PDB name can be any value. This can be the same or different than the service name that you set in the tnsnames.ora as prerequisite. That is, the service name must be set as JDEORCL for shared DB in tnsnames.ora.
For example, JDEORCL
Note: Other than the values specified above, there are no additional special requirements to support JD Edwards EnterpriseOne.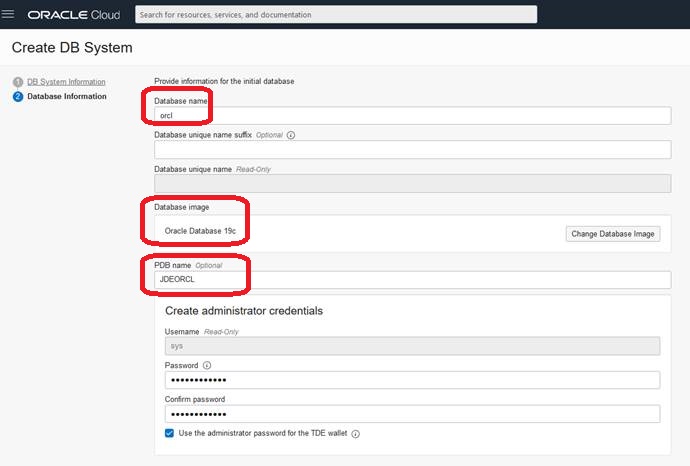
-
- If all the required fields are completed with valid values, click the Next button to create the defined DB System.