Setting Up a DB System with RAC
This section shows you how to set up a DB System on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure with an Oracle Real Application Cluster (RAC).
This section describes the general setup tasks that must be performed on the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure database service called DB System (DBS). If you are using a Linux-based VM in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Compute for the Database Server, refer to the Learning Path "Deploying JD Edwards EnterpriseOne on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure on Linux with Compute Database".
You will need to perform setup on the primary and secondary nodes of DBS as described by following the steps described in these sections:
- Setting Up the Primary Node
- Setting Up the Secondary Node
- Stopping the Database in the Secondary Node
Prerequisites
- You must have previously created a DB System by following the process described in the preceding module "Creating a DB System in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure" of this Learning Path .
- You must have specified more than one node when you created the DB System by following the process described in the preceding module "Creating a DB System in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure" of this Learning Path.
- You must have set up a DB System by following the process described in the preceding module "Setting up a DB System".
- You should have a fundamental understanding of the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. It is highly recommended that you review the extensive collateral information, including training, at this site:
- You must have a subscription to Oracle Cloud Infrastructure and an Administrator account in the platform. For more information, refer to this site:
- To access the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Console, you must use a supported browser.
Setting Up the Primary Node
To use a RAC in your DB System (also called DBaaS in industry terms), you must have enabled DNS in your VCN and therefore have DNS subnets. This step is necessary because VM shapes must be used for DB Systems and are not supported on non-DNS subnets.
The deployment of an RAC instance using the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure console creates a primary node and a secondary node in the cluster. Consider the node that has the instance name as its name with the suffix 1 as the primary node and the node with the suffix 2 as the secondary node.
To set up a DB System with a RAC, ensure that you have completed the following tasks which are described in the module "Setting up a DB System", which applies to setting up the primary node.
- Created the requisite groups and users and set permissions and ownership on /u01
-
Opened the required ports in the firewall
- Edited the .bash_profile file
-
Edited the /etc/resolv.conf file
- Edited the tnsnames.ora file
- Allocated recovery space for archive logging
- Set the number of processes
- Set the PGA_AGGREGATE_LIMIT
Setting Up the Secondary Node
The deployment of an RAC instance using the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure console creates a primary node and a secondary node in the cluster. This procedure describes how to set up the secondary node. Consider the node that has the instance name as its name with the suffix 1 as the primary node and the node with the suffix 2 as the secondary node.
After you complete the configuration described in this procedure, you must shut down the secondary node (node 2) prior to deploying One-Click Provisioning for Oracle Cloud Infrastructure by following the procedure described in the next section "Stopping the Database in the Secondary Node".
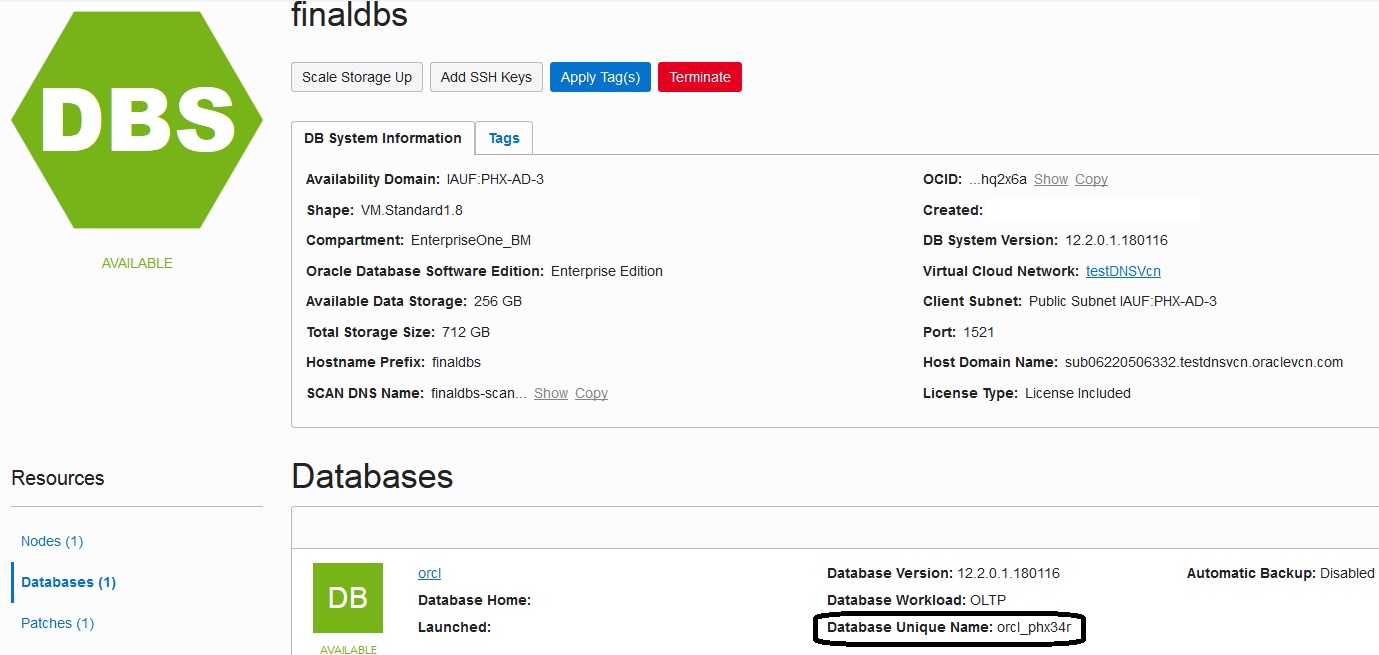
Determine the Database Unique Name by navigating to the DB Systems instance summary screen of the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure console.
 Note:
Note:In the above example, the value orcl_phx34r is the Database Unique Name. In subsequent examples, this value is referred to as the site variable <DB_UNIQUE_NAME>.
-
Add environment variables for the oracle user by editing /home/oracle/.bash_profile using these commands:
$ sudo su - oracle$ vi /home/oracle/.bash_profile -
Use this command to execute the .bash_profile file for the variables to take effect:
$ source /home/oracle/.bash_profileTypically, a properly completed .bash_profile will look like this:
export ORACLE_HOME=/u01/app/oracle/product/dbhome_1export ORACLE_UNQNAME=ORCL_phx1mkPATH=$ORACLE_HOME/bin:$PATHexport PATHValue Description ORACLE_HOME The ORACLE_HOME environment variable value is typically the software installation directory of your Oracle database. By default, the directory structure is: /u01/app/oracle/product/12.2.0.1/dbhome_1DB_UNIQUE_NAME Refer to Step 1. -
Make a TNS entry for the pluggable database in the tnsnames.ora file located in the $ORACLE_HOME/network/admin directory of the DB System. This entry is in addition to the existing entries in the tnsnames.ora file.
Copy the tnsnames.ora entry you had made for the pluggable database in the primary node into the tnsnames.ora of this node.
In the preceding example in this document, the TNS entry for the pluggable database in the tnsnames.ora file was:
JDEORCL =(DESCRIPTION =(ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = dbsrc14-scan.sub06220506330.testdnsvcn.oraclevcn.com)(PORT = 1521))(CONNECT_DATA =(SERVER = DEDICATED)(SERVICE_NAME = JDEORCL.sub06220506332.testdnsvcn.oraclevcn.com))) You must ensure that the search setting in the /etc/resolv.conf file specifies the DNS domain name of the Availability Domain to which all the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne servers belong. While logged in as the opc user, you must edit the file and add a line with this syntax:
$ vi /etc/resolv.confsearch <DNS_Domain_Name> <subnet>.<DNS_Domain_Name>Because each region has at least three subnets, you must specify the exact subnet in which your JD Edwards EnterpriseOne servers are running. For example, your subnets can look like this:
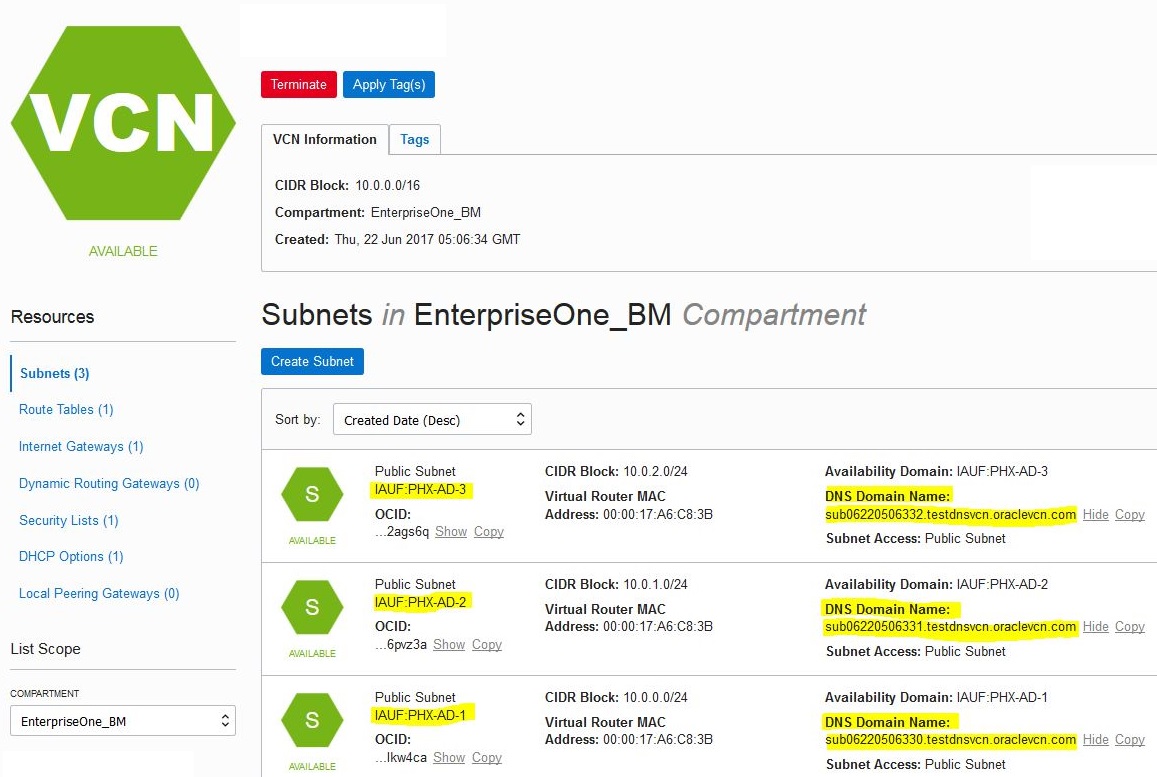
Using the above example, assuming that your JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Servers are running in the Phoenix Availability Domain 2 (labeled as IAUF:PHX-AD-2), you would edit your /etc/resolve.conf file to add a line with a search setting similar to the setting below:
search testdnsvcn.oraclevcn.com
sub06220506331.testdnsvcn.oraclevcn.com
- Run the hostname command and note the output.
-
Run the nslookup command using the output of Step 1 as the first argument.
The host name is specified in the Name field of the output from the nslookup command.
For example:
root@my_machine share]# hostnamemymachine[root@my_machine share]# nslookup mymachineServer: 11.111.11.111Address: 11.111.11.111#11Non-authoritative answer:
Name: mymachine.us.oraclex.comAddress: 11.111.111.111
Stopping the Database in the Secondary Node
At this point, prior to deploying One-Click Provisioning for Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, you must stop the database that is running in the secondary node for the RAC.
It is not recommended to use the user interface in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure to shut down the secondary node because this can cause a delay in synchronization between the nodes upon deployment and during fail over scenarios.
The recommended procedure to stop the database is to use this line command:
srvctl stop instance -d <DB_UNIQUE_NAME> -i <DB_NAME>
Where
<DB_UNIQUE_NAME>is the name you determined in the preceding section in this OBE "Setting Up the Secondary Node".
-
<DB_NAME>is the name you have given the database and which is appended with the number 2. For example, if you gave the database the name ORCL, then the database in the secondary node is named ORCL2.
After One-Click Provisioning completes the deployment of JD Edwards EnterpriseOne, you will need to start the secondary node by following the process documented in the OBE "Performing Post-Provisioning Tasks", in the section "Accessing the Provisioned Servers".
To view details of the secondary node in the RAC:
On the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Console Home page, click the navigation menu in the upper-left corner.
- From the navigation menu, in the Database section, select Bare Metal, VM, and Exadata.
- In the left panel, ensure that DB Systems is selected,and under List Scope, the applicable COMPARTMENT is selected which contains the DB System with RAC that you created contains the DB System that you created with a RAC.
- Click the link for your DB System with a RAC.
-
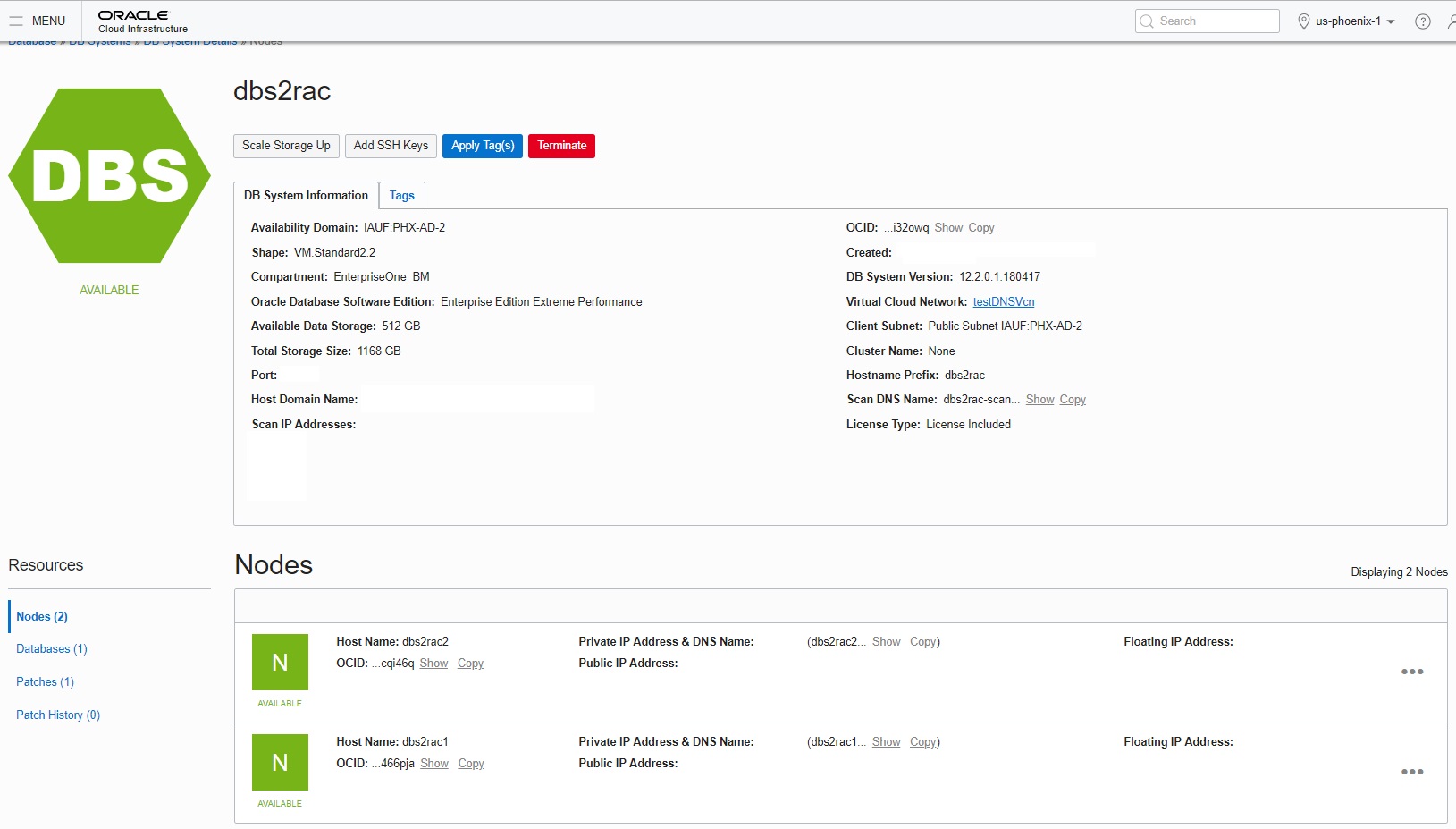
In the Resources section in the left pane, click Nodes.
The details for the two nodes are displayed as shown below:
-
As previously mentioned, the secondary node is identified with the suffix 2.