About Search Indexing
Administrators can use the Search Index page in Console to control which content is indexed and searchable.
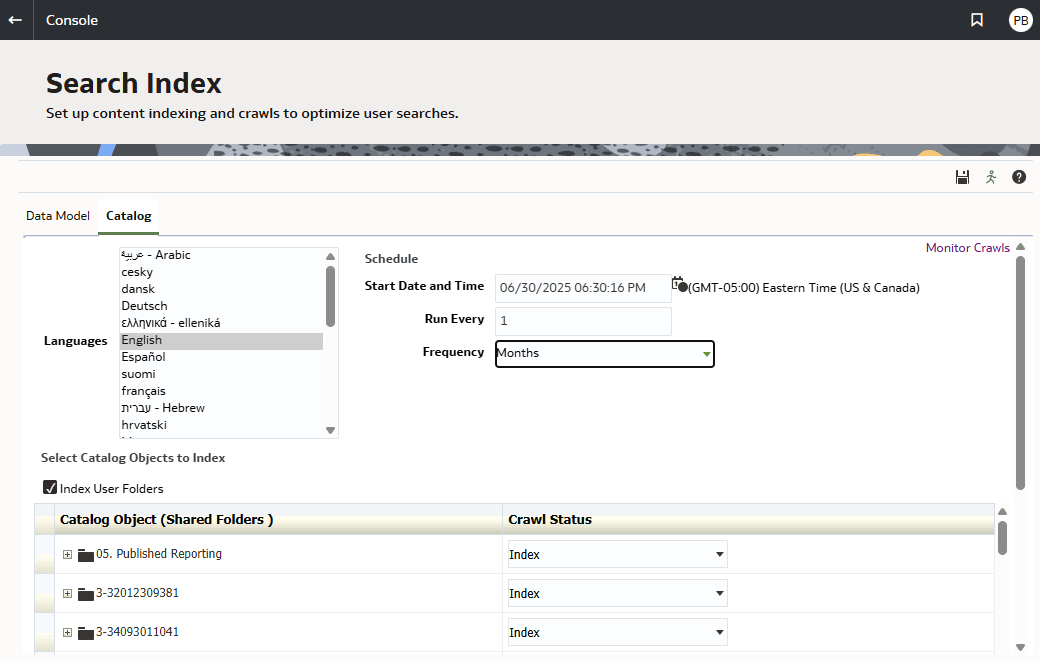
Description of the illustration search-index-dialog.png
-
Data model - Use the Data Model tab to configure which columns to include in the search index. See Configure Data Model Search Indexing.
You can also control whether the Oracle Analytics AI Assistants and home page searches can use the indexed data in their search results. See About Indexing Subject Areas for Oracle Analytics AI Assistants and Home Page Search.
-
Catalog content - Use the Catalog tab to configure which objects to include in the search index.
Oracle Analytics performs an automatic catalog crawl once per month that indexes everything (that is, both user folders and shared folders). You can change the frequency of this schedule and specify what content to index.
Here're some tips to optimize catalog crawls:
- Before you start indexing, remove any redundant duplicates or copies and older unused content in the catalog to avoid unnecessary processing.
- Exclude user folder indexing from the catalog crawl to reduce the size of the catalog. On the Search Index dialog, Catalog tab, clear the Index User Folders check box.
- Keep the crawling frequency to Monthly (the default) unless your catalog is updated more rapidly and you require full crawls more often. Frequent crawling uses significant resources, so avoid increasing the crawl schedule frequency more than necessary—adjust it only if user activity patterns clearly require it. On the Search Index dialog, Catalog tab, set Run Every to 1 and set Frequency to Months.
Note:
File-based datasets are indexed differently. Users who upload datasets decide how and when they're indexed through the dataset's Inspect dialog. See Make a Dataset's Data Available for Search.Crawl results are added to the index in the languages that you specify. For example, if your company's headquarters are in the United States, and you have offices in Italy, then you can choose English and Italiano to create an index in both English and Italian.
Indexing Data Model content
When you select to index items in the data model, you can specify how the content is crawled using one of the following options for Crawl Status:
-
Index Metadata Only: Indexes only dimension and measure names. This is the default selection. For example, column names such as Product or Order, and metric names such as # of Orders. Always use this option if the column contains sensitive data values that you don’t want to expose to users when they search on the home page.
-
Index: Indexes metadata (dimension names and measure names) and data values. Applies only to dimension or attribute columns. For example, if you select this on a Product column, both the metadata for the Product column and its data values (such as iPad, iPod, iPhone ) are indexed.
Indexing data values provides additional functionality for users who want to visualize data values from the search bar on the home page. Be aware that selecting this option can be costly because it indexes values for all of the columns in all subject areas of the semantic model.
Note:
When you index data, it's visible to all users who have access to that column. Take care not to index data for columns that contain sensitive data, as this will expose the sensitive data values on the home page. -
Don’t Index: Use this selection to completely exclude subject areas, tables, or columns from the index.
Indexing Catalog Content
When you select to index objects in the catalog, you can specify how the content is crawled using one of the following options for Crawl Status:
-
Index: Use this option to include folders and items in the index.
-
Don’t Index: Use this selection to exclude folders and items from the index.
Oracle recommends that you don't set the Crawl Status field to Don't Index as a way of hiding an item from users. Users won't see the item in search results or on the home page, but are still able to access the item. Instead, use permissions to apply the proper security to the item.