Enrich and Transform Reference
Use this reference information to help you enrich and transform your data.
Transform Reference
Find out about the data transform options that you can access in the transform editor. For example, to categorize racing lap times in a dataset column, you might use the Bin option.
To select transform options in the transform editor, open your dataset, then click Options (the ellipsis top-right of the data column ![]() ), and select an option (for example, Bin, Rename or Convert to Text).
), and select an option (for example, Bin, Rename or Convert to Text).
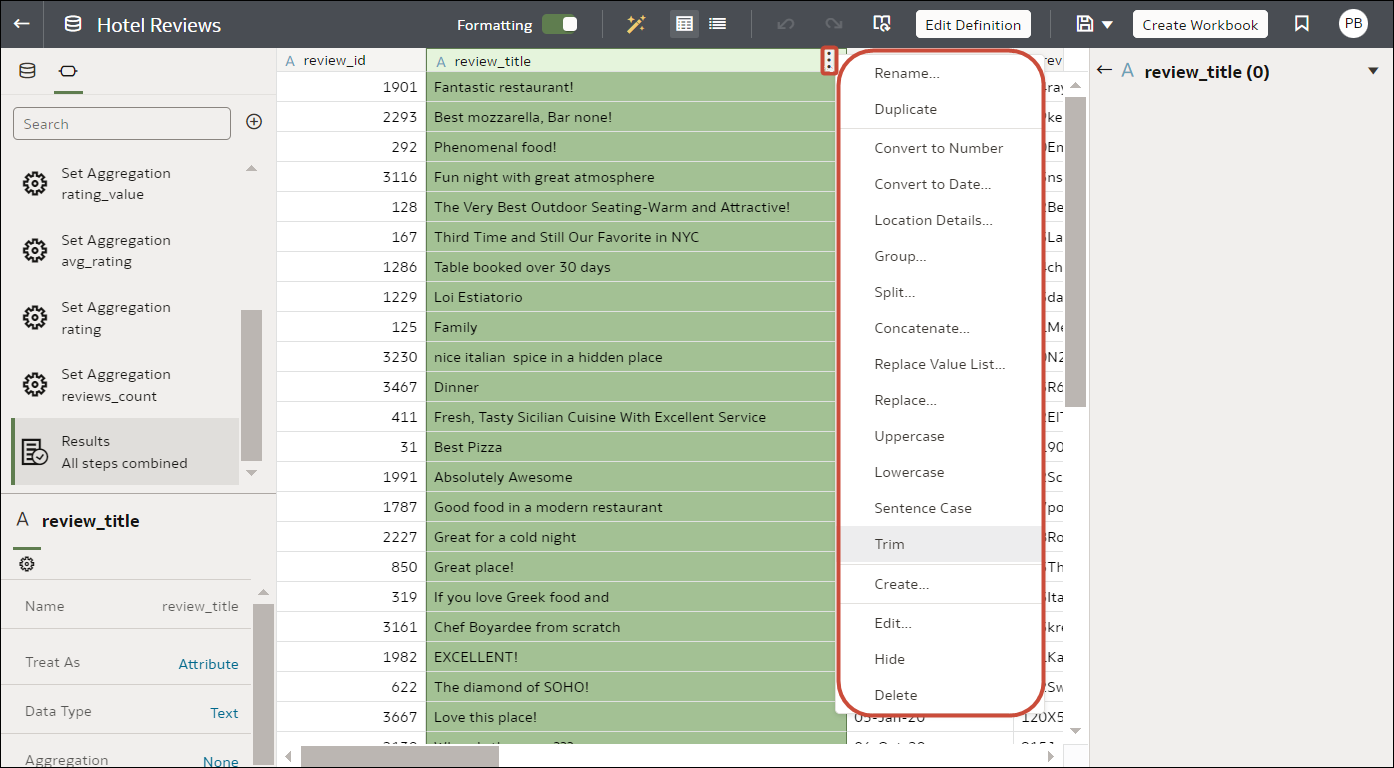
Description of the illustration prepare-data-using-column-options.png
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Bin | Create your own custom groups for number ranges. For example, you can create bins for an Age column with age ranges binned into Pre-Teen, Young Adult, Adult, or Senior based on custom requirements. |
| Calculate Duration | Calculate the duration between two dates or times. For example, to analyze order delivery times, you might calculate the number of days between ORDER_DATE and DELIVERY_DATE. |
| Convert to Date | Change the data type of the column to date and deletes any values that aren’t dates from the column. |
| Convert to Number | Change the data type of the column to number, which deletes any values that aren't numbers from the column. |
| Convert to Text | Change the data type of a column to text. |
| Create | Create a column based on a function. |
| Delete | Remove the column from the dataset. |
| Duplicate | Create a column with identical content of the selected column. |
| Edit | Change the column details. For example, you can change the name, select another column, or update functions. |
| Extract Date | Extract a range of date and time information from timestamps. For example, you might extract Year as 2024, Day of the Month as 23, or Hour of the Day as 03 PM. |
| Group, Conditional Group | Select Group to create your own custom groups. For example, you can group States together with custom regions, and you can categorize dollar amounts into groups indicating small, medium, and large. |
| Hide | Hide the column in visualizations. If you want to see which columns are hidden, click Hidden columns (ghost icon) on the page footer. To unhide a single column, remove the Hide step in the Preparation Scipt pane. To unhide all columns click Hidden columns (ghost icon) on the page footer and select Unhide All. |
| Log | Calculate the natural logarithm of an expression. |
| Lowercase | Update the contents of a column with the values all in lowercase letters. |
| Power | Raise the values of a column to the power that you specify. The default power is 2. |
| Rename | Change the name of a column. |
| Replace | Change specific text in the selected column to any value that you specify. For example, you can change all instances of Mister to Mr.. |
| Sentence Case | Update the contents of a column to make the first letter of the first word of a sentence uppercase. |
| Split | Split a column value into parts. For example, you can split a column called, Name, into first name and last name. |
| Square Root | Create a column populated with the square root of the value in the column selected. |
| Update Description | Add a user-friendly description for the selected column that's displayed in the Tile visualization when you add this column to a canvas. |
| Uppercase | Update the contents of a column with the values in all uppercase letters. |
General Custom Format Strings
You can use general custom format strings to create custom time or date formats.
The table shows the general custom format strings and the results that they display. These allow the display of date and time fields in the user's locale.
| General Format String | Result |
|---|---|
|
[FMT:dateShort] |
Formats the date in the locale's short date format. You can also type [FMT:date]. |
|
[FMT:dateLong] |
Formats the date in the locale's long date format. |
|
[FMT:dateInput] |
Formats the date in a format acceptable for input back into the system. |
|
[FMT:time] |
Formats the time in the locale's time format. |
|
[FMT:timeHourMin] |
Formats the time in the locale's time format but omits the seconds. |
|
[FMT:timeInput] |
Formats the time in a format acceptable for input back into the system. |
|
[FMT:timeInputHourMin] |
Formats the time in a format acceptable for input back into the system, but omits the seconds. |
|
[FMT:timeStampShort] |
Equivalent to typing [FMT:dateShort] [FMT:time]. Formats the date in the locale's short date format and the time in the locale's time format. You can also type [FMT:timeStamp]. |
|
[FMT:timeStampLong] |
Equivalent to typing [FMT:dateLong] [FMT:time]. Formats the date in the locale's long date format and the time in the locale's time format. |
|
[FMT:timeStampInput] |
Equivalent to [FMT:dateInput] [FMT:timeInput]. Formats the date and the time in a format acceptable for input back into the system. |
|
[FMT:timeHour] |
Formats the hour field only in the locale's format, such as 8 PM. |
|
YY or yy |
Displays the last two digits of the year, for example 11 for 2011. |
|
YYY or yyy |
Displays the last three digits of the year, for example, 011 for 2011. |
|
YYYY or yyyy |
Displays the four-digit year, for example, 2011. |
|
M |
Displays the numeric month, for example, 2 for February. |
|
MM |
Displays the numeric month, padded to the left with zero for single-digit months, for example, 02 for February. |
|
MMM |
Displays the abbreviated name of the month in the user's locale, for example, Feb. |
|
MMMM |
Displays the full name of the month in the user's locale, for example, February. |
|
D or d |
Displays the day of the month, for example, 1. |
|
DD or dd |
Displays the day of the month, padded to the left with zero for single-digit days, for example, 01. |
|
DDD or ddd |
Displays the abbreviated name of the day of the week in the user's locale, for example, Thu for Thursday. |
|
DDDD or dddd |
Displays the full name of the day of the week in the user's locale, for example, Thursday. |
|
DDDDD or ddddd |
Displays the first letter of the name of the day of the week in the user's locale, for example, T for Thursday. |
|
r |
Displays the day of year, for example, 1. |
|
rr |
Displays the day of year, padded to the left with zero for single-digit day of year, for example, 01. |
|
rrr |
Displays the day of year, padded to the left with zero for single-digit day of year, for example, 001. |
|
w |
Displays the week of year, for example, 1. |
|
ww |
Displays the week of year, padded to the left with zero for single-digit weeks, for example, 01. |
|
q |
Displays the quarter of year, for example, 4. |
|
h |
Displays the hour in 12-hour time, for example 2. |
|
H |
Displays the hour in 24-hour time, for example, 23. |
|
hh |
Displays the hour in 12-hour time, padded to the left with zero for single-digit hours, for example, 01. |
|
HH |
Displays the hour in 24-hour time, padded to the left with zero for single digit hours, for example, 23. |
|
m |
Displays the minute, for example, 7. |
|
mm |
Displays the minute, padded to the left with zero for single-digit minutes, for example, 07. |
|
s |
Displays the second, for example, 2. You can also include decimals in the string, such as s.# or s.00 (where # means an optional digit, and 0 means a required digit). |
|
ss |
Displays the second, padded to the left with zero for single-digit seconds, for example, 02. You can also include decimals in the string, such as ss.# or ss.00 (where # means an optional digit, and 0 means a required digit). |
|
S |
Displays the millisecond, for example, 2. |
|
SS |
Displays the millisecond, padded to the left with zero for single-digit milliseconds, for example, 02. |
|
SSS |
Displays the millisecond, padded to the left with zero for single-digit milliseconds, for example, 002. |
|
tt |
Displays the abbreviation for ante meridiem or post meridiem in the user's locale, for example, pm. |
|
gg |
Displays the era in the user's locale. |