Embed a Web Application
Your web application can be embedded in sites in domains associated with your Identity Domain as well as external sites.
You must explicitly allow embedding in your web application’s settings if you want to allow other applications to embed your application. For example, if you know that another site wants to use pages and data from your web app in their site, and they don't want to or can't link to your app, you can allow your app to be embedded in their app.
For security reasons, all embedding is denied by default. You can use the app-level Settings editor to change this setting: 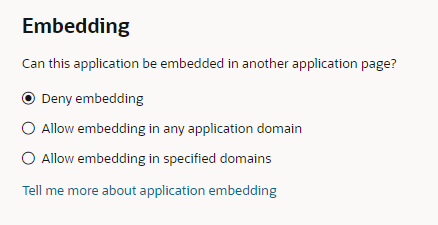
Description of the illustration settings-embedding.png
The web application’s security settings are stored in the configuration.json file, which is located in the application’s settings folder when you browse the application’s sources.
To allow your web app to be embedded in another app:
-
Open the web application in the Navigator.
-
Select the application artifact.
-
Click Settings, then Security.
- In the Embedding section, select Allow embedding in any application domain.
When your app is embedded within another app, the preferred method is for the other app to only embed the content of the page and not display the elements that wrap the content. For example, you might want to prevent a user from opening your app's user menu and logging out when it is embedded in another app. You can edit the shell template page to remove content such as the header and footer elements that you don’t want to appear when the page is embedded.
You can also embed a web app in an Oracle Cloud Application, but there's more to it than just allowing access. See Embed a Web App in an Oracle Cloud Application for details.