Perform Text Analysis and Translation with a Language Action
You can use AI to perform in-depth text analysis and machine translation with a language action. Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Language enables you to process unstructured text for sentiment analysis, entity recognition, classification, translation, and more.
Capabilities
OCI Language is a cloud-based AI service that enables you to build intelligent applications by using REST APIs and SDKs to process unstructured text for language detection, text classification, recognition of named entities, key phrase extraction, sentiment analysis, text translation, and detection of personal identifiable information. OCI Language can identify more than 100 languages in text. It also automatically recognizes at least 18 entity types, including the names of organizations and products. It makes text analysis easier for large volumes of text data. Oracle Integration supports using OCI Language in an integration with the language action.
See AI Language.
Prerequisites
See Prerequisites for information on the prerequisites you must satisfy in the Oracle Cloud Console.
Invoke Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Language from an Integration
- Add a Language action to an integration in either of the following ways:
- On the side of the canvas, click Actions
 and drag the OCI Language action to the appropriate location.
and drag the OCI Language action to the appropriate location.
- Click
 at the location where you want to add the OCI Language action, then select OCI Language.
at the location where you want to add the OCI Language action, then select OCI Language.
- On the side of the canvas, click Actions
- Enter a name and optional description. Select the following information, then click Continue.
Element Description Select categories Select one of the following categories: - Actions
- Jobs
The Actions category lets you perform analysis and translation on unstructured text. You will need to provide the text to process in the mapper using the Text target element.
The Jobs category lets you perform analysis on unstructured text data at scale by enabling you to create asynchronous language jobs. It also enables you to get information about a language job or list language jobs. You will be able to process large volumes of textual information. You need to provide the documents to be processed in object storage. It also enables you to update, delete, or cancel a language job.
Action If you selected the Actions category, select one of the following actions to perform. You can enter the action name to filter the list.
-
Language detection: Detects languages based on the text provided, and includes a confidence score.
OCI Language detects the language and returns the detected language along with a related confidence score (between 0 and 1). You can also specify a batch of records.
-
Named entity recognition: Identifies common entities, people, places, locations, email, and so on.
OCI Language extracts the entities in the text records. It returns the type/subtype and confidence score (between 0 and 1) for each entity.
-
Key phrase extraction: Extracts an important set of phrases from a block of text.
OCI Language extracts the key phrases from the text. For each key phrase, it returns a score (between 0 and 1) that highlights the importance of the key phrase in the context of the text. -
Sentiment analysis: Identifies the tone of the text and classifies the expressions in the text into positive, negative, neutral, or mixed polarity.
OCI Language supports both aspect-based and sentence-based sentiment analysis. For example, opinions, appraisals, emotions, or attitudes toward a topic, person, or entity. After the analysis, it returns a confidence score for each of the classes (positive, negative, neutral, or mixed).
-
Personal identifiable information (PII)/ Private Health Information (PHI): Identifies, classifies, and de-identifies private information in unstructured text. It can also process healthcare records and detect private health information such as healthcare plan IDs, medical records numbers, and so on. OCI Language supports masking of PII.
You can configure masking for entities such as bank account number, telephone number, age, and so on. The entities that you can configure are available in the mapper under the MASKING element.
You can also specify masking options to specify the masking character, whether PII should be unmasked from the start/end, and the number of characters to leave unmasked.
OCI Language helps identify and classify personal identifiable information such as name, age, address, email, telephone number, and so on. It returns the information that was identified and classified.
-
Text classification: Identifies the document category and subcategory that the text belongs to.
OCI Language analyzes the text and automatically classifies it into a set of predetermined categories and sub-categories. It returns this information for each record that was classified.
-
Text translation: Translates text into the language of your choice.
OCI Language translates the text you provide from the source language to the specified language. It returns the translated text.
-
Health entity: Detects and extracts healthcare entities from healthcare records such as electronic healthcare records (EHR), progress notes, and clinical trial documents. See Healthcare NLP Models and Analyzing Healthcare Data Using Healthcare NLP Models.
- You need to create a project in the Oracle Cloud Console to host your model.
- You need to create a model.
- To access the model, you need to create an endpoint for the model in the Oracle Cloud Console.
If you selected the Jobs category, select one of the following jobs to perform.
- Create job: Creates a new asynchronous language job. It reads the documents from object storage and returns the results of the analysis along with the job ID.
- Get job: Gets the status of the language job using the job ID you specify. This action returns the status of the language job.
- List jobs: Returns a list of language jobs in the specified compartment.
- Update job: Updates the specified language job with details specified in the request payload.
- Delete job: Deletes the specified language job.
- Cancel job: Cancels the specified language job (including its tasks).
- If you selected the Actions category and an action, select the following information:
Element Description Compartment Select the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure compartment in which your Oracle Integration is installed.
This field is not applicable if you selected the Health entity action.
endpointid This field is available only if you selected the Health entity action.
Specify an endpoint ID to use for inferencing.
You need to specify the ID (OCID) of the model endpoint you created in the Oracle Cloud Console in Step 2.
Level This field is available only if you selected the Sentiment analysis action.
Select the level of sentiment analysis you want to perform from the Available Options list and move it to the Selected Options list.- Sentence: Enables you to perform sentence-level sentiment analysis with confidence scores for each sentence in the text.
- Aspect: Enables you to extract the individual aspects in the input document and classify each of the aspects into one of the polarity classes (positive, negative, mixed, or neutral). With the predicted sentiment for each aspect, it also provides a confidence score for each of the classes, and their corresponding offsets in the input. Confidence scores closer to 1 indicate higher confidence in the label's classification and lower scores indicate lower confidence. The range of the confidence score for each class is between 0 to 1, and the cumulative scores of all the four classes sum to 1. This option is available in the Selected Options list by default.
You can select one of the options or both the options, as needed.
You can also specify the "SENTENCE" or "ASPECT" option using the Basis target element in the mapper.
Entities to be detected This field is available only if you selected the Personal identifiable information (PII)/ Private Health Information (PHI) action.
Select an entity to detect from the list of entities (such as Person name, Address, Age, and so on) available in the drop-down list. If you want all the entities to be detected, you can select All from the drop-down list.
Masking configuration (optional) This field is available only if you selected the Personal identifiable information (PII)/ Private Health Information (PHI) action.
For PII masking, you can optionally select masking modes such as the following:- MASK: Masks (hides) PII with masking characters like '***', 'X', or by showing a portion of the information (for example: last four characters).
- Masking character (Optional): Enter a masking character to use.
- Number of characters to be left unmasked (Optional): Enter the number of characters to be left unmasked if you want to show only a portion of the information.
- Unmask options: Select From the start or From the end.
- REPLACE: If you select this option, then, in the Replace with field, specify the characters that will replaces PII.
- REMOVE: Removes the PII entities from the output text.
You can also specify masking modes and masking options in the request payload. The options specified in the request payload override the options specified in the wizard.
- If you selected the Jobs category and the Create job action, select the following information.
Element Description Compartment Select the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure compartment in which your Oracle Integration is installed.
Feature type Select one of the following feature types: - Pretrained language detection
- Pretrained sentiment analysis
- Pretrained keyphrase extraction
- Pretrained language pii entities
- Pretrained language translation
- Pretrained named entity recognition
- Pretrained text classification
- Text classification
- Named entity recognition
Pretrained models are ready-to-use AI models that perform the selected task (feature type) on the text you provide in the request payload.
Configuration This field is available only if you selected the Pretrained sentiment analysis feature type.
Select sentiment analysis options from the Available Options list and move them to the Selected Options list.- Sentence: Enables you to perform sentence-level sentiment analysis with confidence scores for each sentence in the text.
- Aspect: Enables you to extract the individual aspects in the input document and classify each of the aspects into one of the polarity classes (positive, negative, mixed, or neutral). With the predicted sentiment for each aspect, it also provides a confidence score for each of the classes, and their corresponding offsets in the input. Confidence scores closer to 1 indicate higher confidence in the label's classification and lower scores indicate lower confidence. The range of the confidence score for each class is between 0 to 1, and the cumulative scores of all the four classes sum to 1. This option is available in the Selected Options list by default.
Entities to be detected This field is available only if you selected the Pretrained language pii entities feature type.
Select All from the drop-down list.
Masking configuration (optional) This field is available only if you selected the Pretrained language pii entities feature type.
For PII masking, you can optionally select masking modes such as the following:- MASK: Masks (hides) PII with masking characters like '***', 'X', or by showing a portion of the information (for example: last four characters).
- Masking character (Optional): Enter a masking character to use.
- Number of characters to be left unmasked (Optional): Enter the number of characters to be left unmasked if you want to show only a portion of the information.
- Unmask options: Select From the start or From the end.
- REPLACE: Replaces PII with a designated sequence of characters.
- REMOVE: Removes the PII entities from the output text.
You can also specify masking modes and masking options in the request payload. The options specified in the request payload override the options specified in the wizard.
Source language This field is available only for the Pretrained language translation feature type.
Select the source language of the text to be translated from the drop-down list.
Target language This field is available only for the Pretrained language translation feature type.
Select one or more target languages from the Available Options list and move them to the Selected Options list to translate the text from the source language to the selected target language(s).
Document Type Select one of the following document types: - TXT: Use this option to provide text files as input files.
- CSV: Use this option to provide comma-separated value (CSV) files as input files.
This field is not available for the Pretrained language translation feature type.
Input bucket Select the input storage bucket that contains the document(s) to analyze.
Note:- For TXT document type, all the text files in the bucket are selected for processing.
- For CSV document type, you need to specify the particular CSV file to use in the request payload along with other parameters (such as row/column details). See DocumentsConfiguration Reference.
- For the Pretrained language translation feature type, you can specify a particular text or CSV file to use in the request payload.
Input prefix (Optional) This field is available only if you select the TXT document type.
Optionally, you can specify an input prefix (which is similar to a folder name).
This field is available for the Pretrained language translation feature type too.
Output bucket Select the output storage bucket to store the results.
Output prefix (Optional) Optionally, you can specify an output prefix (which is similar to a folder name).
If you selected the Jobs category and the List jobs action, select the following information.Element Description Compartment Select the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure compartment in which your Oracle Integration is installed.
Click Continue.
- On the Summary page, click Finish.
- Open the mapper and complete the configuration by mapping appropriate source elements to the target elements.
- If you selected the Actions category in Step 2:
For Language detection, Key phrase extraction, Sentiment analysis, Text classification, Text translation, and Named entity recognition actions, complete the following steps.
- Expand the topmost node in the Target section.
- Within that node, expand Request Wrapper, expand Body, and then expand Documents.
- Right-click Key, and select Create target node.
- Click Design View
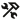 in the Expression Builder.
in the Expression Builder.
- In the Expression Builder, specify a value for Key.
Note:
A key is an identifier that is used to distinguish the documents within a request. It should be unique within that request. - In the Target section, within Documents, right-click Text, and select Create target node.
- In the Expression Builder, specify the text on which you want to perform the action you selected in Step 2.
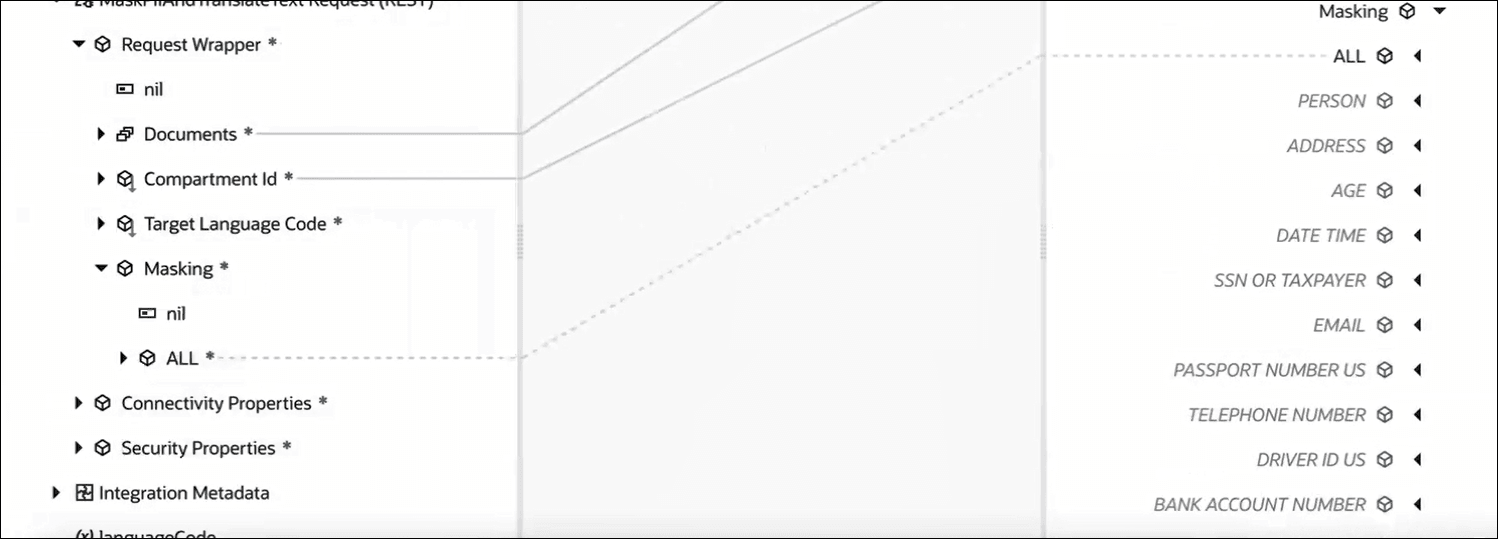
 If you selected the Personal identifiable information (PII)/ Private Health Information (PHI) action in Step 2, then map the appropriate source element to the Documents target element. You also need to map the appropriate source element to the Profile target element. Using the Expression Builder, specify values for attributes of the Profile element. See Profile Reference. For specific masking entities (such as BANK ACCOUNT NUMBER, AGE, EMAIL, and so on), complete the mappings for target elements such as Mode, Is Unmasked From End, Leave Characters Unmasked, Masking Character, and Replace With as needed. Or, to configure all the entities, map the appropriate source element to the All target element within Masking in the Target section, and complete one of the following mappings as needed:
If you selected the Personal identifiable information (PII)/ Private Health Information (PHI) action in Step 2, then map the appropriate source element to the Documents target element. You also need to map the appropriate source element to the Profile target element. Using the Expression Builder, specify values for attributes of the Profile element. See Profile Reference. For specific masking entities (such as BANK ACCOUNT NUMBER, AGE, EMAIL, and so on), complete the mappings for target elements such as Mode, Is Unmasked From End, Leave Characters Unmasked, Masking Character, and Replace With as needed. Or, to configure all the entities, map the appropriate source element to the All target element within Masking in the Target section, and complete one of the following mappings as needed:- Mapping for Mode, Is Unmasked From End, and Leave Characters Unmasked target elements.
- Mapping for Mode and Replace With target elements.
- Mapping for Mode target element.
If you selected the Health entity action in Step 2, then map the appropriate source elements to the Documents and Endpoint Id target elements. Optionally, you can also perform mappings for the other target elements such as Is Detect Assertions and Is Detect Relationships. See BatchDetectHealthEntityDetails Reference.
Note:
You can optionally specify Compartment Id in the mapper to override the value you selected initially for Compartment in Step 4. - If you selected the Jobs category, then complete the following steps.
If you selected the Create job action, then map the appropriate source elements to the Compartment Id, Input Location, Model Metadata Details, and Output Location target elements. See CreateJobDetails Reference.
If you selected the List jobs action, then map the appropriate source element to the Compartment Id target element.
If you selected the Get job, Delete job, Cancel job, or Update job action, then map the appropriate source element to the Job Id target element.
Note:
- If you selected the Get job, Delete job, or Cancel job action, then you need to specify the job ID (on which to perform the action) as a path parameter.
- If you selected the Jobs category and the Update job action, then you need to specify the job ID as a path parameter, and specify the updates in the request payload.
See Job Reference, CreateJob, UpdateJob, GetJob, ListJobs, DeleteJob, and CancelJob.
- If you selected the Actions category in Step 2:
- Exit the mapper.
The language action is now configured.
Example
- Send the following text, masking configuration, and profile domain value in the request payload.
Text: User passport is A123456789, email example@example.com, age is 25 years, IFSC_CODE is I12345.
Request payload:{ "compartmentId": "ocid1.compartment.oc1..aaaaakxpkqgmdmspdcf2smlvkph7memlu3gwe5c7aj7pqozyndlwy5a", "documents": [ { "key": "doc1", "text": "User passport is A123456789, email example@example.com, age is 25 years, IFSC_CODE is I12345.", "languageCode": "en" } ], "masking": { "PASSPORT_NUMBER_US": { "mode": "MASK", "maskingCharacter": "*", "leaveCharactersUnmasked": 3, "isUnmaskedFromEnd": true }, "EMAIL": { "mode": "REMOVE" }, "AGE": { "mode": "REPLACE", "replaceWith": "30 years" } }, "profile": { "domain": "ALL" } } - Select the Personal identifiable information (PII)/ Private Health Information (PHI) action.
- Complete the mapper configuration as needed.
The language action returns the text with passport number partially masked (showing only the last 3 characters), email removed, and age replaced with the text specified.