Start Using SQL Firewall
In order to begin using SQL Firewall you need to complete the following steps. Ensure you have already completed the prerequisites before starting these steps.
These steps will walk you through
Step 1: Enable SQL Firewall On Your Target Database
Step 2: Start SQL Collection for a Database User
Step 3: Monitor the Progress of SQL Collection with Insights
Step 4: Generate and Enforce SQL Firewall Policies
Step 5: View SQL Firewall Violation Reports
Step 6 (Optional): Create Audit and Alert Policies for SQL Firewall Violations
By completing these steps you will be taking steps to protect your database fleet against SQL injection attacks and compromised accounts.
Step 1: Enable SQL Firewall On Your Target Database
This steps ensures that SQL Firewall is enabled on your target database.
- Under Data Safe - Database Security, select SQL Firewall.
- Click the Target summary tab.
- From the Target summary tab, select
the name of a target database.
This will take you to the Configuration details page.
- Click Enable. This can be done through either the button under the name of the database security configuration or the Enable option under the Target database section of the Details tab.
- Wait for the resource to change to Active before continuing to the next step.
Step 2: Start SQL Collection for a Database User
This step starts the collection of expected SQL statements and expected database connection paths for the database user. Run the typical application workload from the trusted database connection paths.
- On the SQL Collections tab in the Database Security configuration page from the previous step, click Create and start SQL collection.
- Select the database user for which collection needs to be created.
- Select the SQL Collection Level:
- User issued SQL commands - These are SQL statements that were issued directly from the user to be executed on the database. This is the default.
-
User issued SQL commands and SQL commands issues from PL/SQL units - This includes SQL statements issued directly from the user as well as SQL statements within a PL/SQL unit which is invoked by the user.
Note: SQL collection will not record any internal recursive SQL statements.
- Click Create and start SQL collection.
- Perform typical daily tasks in your applications for the selected database user.
- Allow the SQL collection to run for some time. This is discussed further in Step 3: Monitor the Progress of SQL Collection with Insights.
Step 3: Monitor the Progress of SQL Collection with Insights
In this step you will monitor the collection of SQL statements and determine when collection can be stopped. Monitor the SQL collection until you see there are no new incoming unique SQL statements or trusted connection paths from the running workload.
- Under SQL Firewall, select SQL collections.
- Select the database user you want to view insights for.
- Click the SQL collection insights tab.
- The information on the SQL collection tab refreshes every hour, if necessary click Refresh Insights.
- (Optional) Select the time period for which you would like to review the SQL collection.
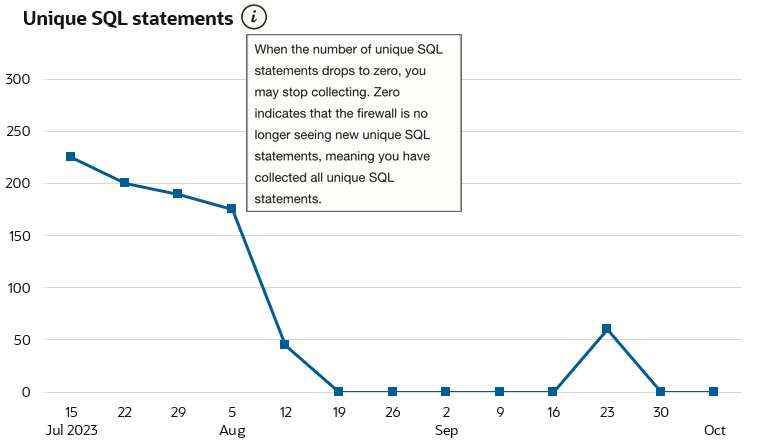
- Review the Unique SQL statements chart.
The collected SQL statements are analyzed to determine if they are unique over the span of the collection period and this chart displays the number of unique SQL statement on the selected time interval. Once there are no more new unique SQL statement being initiated, i.e. the chart remains steady at zero, it is recommended to stop the collection. Waiting until the number of unique SQL statements comes to zero ensures that you collect all statements that are typically executed on your target database and helps establish a status quo.
For example, if there are 250 SQL statements executed on the first day of the collection but only 225 of those are unique then the chart will show 225 for that day. In the following week if the same 250 statements and an additional 200 new and unique statements are executed then the chart will only show 200. This is because the 250 statements were already collected and observed in week one, thus they are not unique. The number of unique SQL statements will reach zero when there are no more unique SQL statements are observed. See Figure 8-1 for reference.
It may take several days to weeks for you to collect enough unique SQL statements to stabilize at zero.
Figure 8-1 Unique SQL Statements chart in SQL Collection Insights
- Review the Client IP, Client OS user, and Client program charts.
These charts show you the number of client IP addresses, OS users, and programs, respectively, that are executing SQL commands on your target database each day. The specific context information can be viewed in the table below the charts.
Since SQL statements should be coming from the same session contexts each day, it is recommended to stop the collection when the charts stabilize at a certain value day to day.
- Review the list of session context types and values.
Reviewing the list of client IP addresses, client OS users, and client programs allows you to determine where your traffic is coming from. With this information you can set up rules that log or block traffic from all other locations. This is further discussed in Step 4: Generate and Enforce SQL Firewall Policies.
- Once you have collected a sufficient amount of unique SQL statements,
click Stop to stop the collection.
Once you have stopped the collection you will see start time, stop time, and the elapsed time under Collection timeline of the Details tab.
Step 4: Generate and Enforce SQL Firewall Policies
In this step you will review the information gathered during the collection and create policies with allowlists based on the collected data. Policies will also be enforced to either observe and allow violations or block violations.
- In the SQL collection details page from the previous step, under the Actions menu, select Generate firewall policy. This will take you to the Firewall policy details page.
- Review the SQL session context on the Details
tab and the Unique allowed SQL statements tab.
If desired you can add, edit, or remove session context information to be included in the policy but you can't add, edit, or remove any of the collected unique SQL statements in the policy.
- (Optional) Update the allowed SQL session context values as
desired.
- Find the Session context section of the Details tab.
- Select Update for the respective row.
- To remove a value, select the X at the end of the row in the panel.
- To add a value, select Add and enter the new value in the empty field.
- Select Update client IP/client program/client OS user, depending on which context information you selected.
- (Optional) Download a PDF or XLS report of all Unique
allowed SQL statements.
- Click the Unique allowed SQL statements tab.
- Under the Actions menu in the
Unique allowed SQL statements table, select
Generate report.
A pop-up will appear.
- Select which format you want the report in, PDF or XLS.
- Enter a name for the report.
- Optionally, enter a description for the report.
- Select Generate report.
- Download the report. You have two options:
- In the Generate report window, select the here link. The document will begin downloading.
- Select Close to close the Generate report window. Then, select the Download report button. A dialog box is displayed providing you options to open or save the document.
- Select Deploy and Enforce.
- Select the enforcement scope:
- All (Session contexts and SQL statements)
- Session contexts only - This option enforces the checks only on the database connection paths.
- SQL statements only - This option enforces the checks only on the SQL statements.
- Select the action on violations:
- Observe (Allow) and log violations - This option will observe and allow all SQL statements and connections to the database while logging any violations.
- Block and log violations - This option will block any SQL statements and database connections not listed in the policy and log the violations. Consider this option when you want SQL Firewall to prevent unauthorized SQL traffic to the database.
- Audit for violations
- On - This option will write the violation records to the audit trail. It enables alerting and helps demonstrate compliance to your audit requirements. Ensure to start the audit trail in Oracle Data Safe to collect the audit events. These audit events contribute to the monthly free limit of 1 million audit records per month per target database.
- Off
- Select Deploy and enforce.
- Select the enforcement scope:
Step 5: View SQL Firewall Violation Reports
In this step you can view a report of violations for your enforced SQL Firewall policies. There are a variety of ways to navigate to the violations report, some of which will automatically apply filters for your selected SQL Firewall policies, target databases, time periods, and so on.
Note:
It is unlikely that you will see any violations immediately after enforcing a SQL Firewall policy.Complete these steps to view a report of all violations across your database fleet.
- Under Data Safe - Database Security, select SQL Firewall.
- Under SQL Firewall, select Violation reports.
- Select which report you would like to see from the
Predefined reports tab:
- All violations report - Both SQL and context violations
- SQL violations report - Violations on SQL statements
- Context violations report - Violations on database connection paths
- Once at the report you may perform all standard report actions in Oracle
Data Safe such as:
- Apply basic filters
- Apply advanced SCIM filters
- Create custom reports
- Schedule reports
- Generate and download reports
- Manage which columns to display
Complete these steps to view a report of all violations on a specific target database from the last week.
- Under Data Safe - Database Security, select SQL Firewall.
- Click the Violation summary tab.
- Select the name of a target database from the list.
This will take you to the violation report.
- The violation report will be automatically filtered to show only the violations for the selected target database from the selected time period.
- Once at the report you may perform all standard report actions in Oracle
Data Safe such as:
- Apply basic filters
- Apply advanced SCIM filters
- Create custom reports
- Schedule reports
- Generate and download reports
- Manage which columns to display
Complete these steps to view a report of violations specific to a selected SQL Firewall policy.
- Under Data Safe - Database Security, select SQL Firewall.
- Click the Target summary tab
- Select the name of a target database from the list.
This will take you to the Database Security Configuration details page.
- Click the SQL Firewall policies tab.
- Select a SQL Firewall policy from the list.
This will take you to the Firewall policy details page.
- Under Enforcement information, click View report next to Violation reports.
- The violation report will be automatically filtered to show
only the violations for the selected database user on the selected target
database.
This will take you to the violation report.
- Once at the report you may perform all standard report actions in Oracle
Data Safe such as:
- Apply basic filters
- Apply advanced SCIM filters
- Create custom reports
- Schedule reports
- Generate and download reports
- Manage which columns to display
Step 6 (Optional): Create Audit and Alert Policies for SQL Firewall Violations
In this step you will create audit and alerts policies for SQL Firewall violations so that you can better track and monitor activity on your database fleet. Though this step is optional, it is recommended as it enables alerting and helps demonstrate compliance to your audit requirements.
Complete the prerequisites for Activity Auditing and Alerts.
- Complete the Activity
Auditing workflow to audit SQL Firewall violations.
You need to have turned on Audit for violations when enforcing your SQL Firewall policies for the corresponding audit policies to show as enabled in Activity auditing. You can view and manage the audit policies for SQL Firewall listed under the SQL Firewall auditing section of the Audit policy details.
Tip:
You must turn on Audit for violations in your SQL Firewall policy before managing the SQL Firewall audit policies in the Activity Auditing workflow. See Update the Enforcement of SQL Firewall Policies for more information. - Complete the Alerts workflow to
receive alerts for SQL Firewall violations.
The alert policy for SQL Firewall is SQL Firewall violations.