About Selecting the Method to Connect Devices
You have several options to connect devices to Oracle Fusion Cloud IoT Intelligent Applications. You select the method based on the types of devices, protocols, and existing environment.
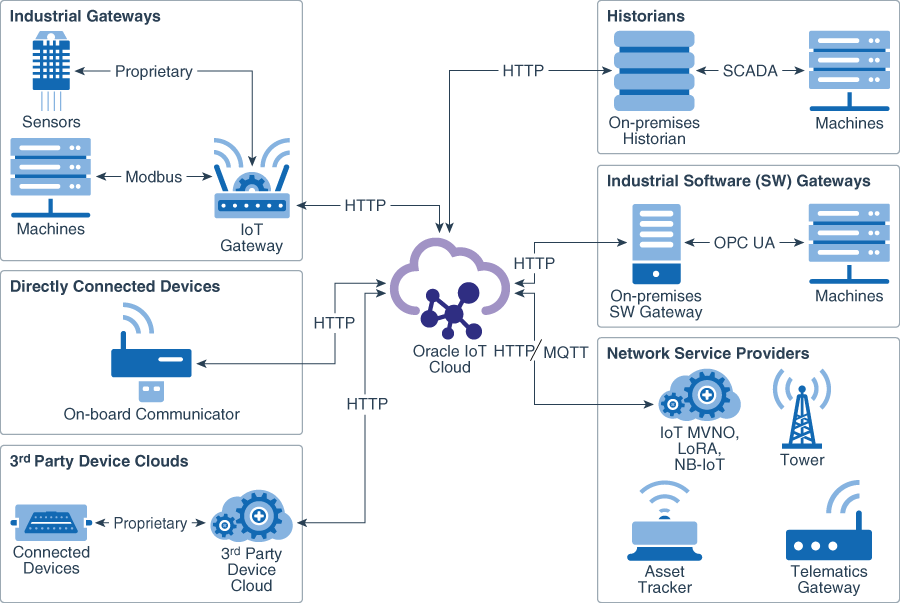
The diagram and the comparison table help you to select the best option for you to connect your devices toOracle Fusion Cloud IoT Intelligent Applications based on your setup and protocols.
Device Integration Models
Options to Select the Method
| Scenario | Option to Connect the Devices | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Devices that support proprietary protocols. | Sensors and machines connect indirectly to Oracle Fusion Cloud IoT Intelligent Applications through a standardized industrial gateway using proprietary protocols. | A device uses the MODBUS protocol to connect with an industrial IoT gateway from vendors such as Cisco, Dell, Bosch, Intel, or Multitech which, in turn, connects to Oracle Fusion Cloud IoT Intelligent Applications using the HTTP protocol |
| Machine with a powerful in-built sensor that supports HTTP protocol. | Directly connect with Oracle Fusion Cloud IoT Intelligent Applications using HTTP. | A device such as an on-board communicator directly exchanges messages with Oracle Fusion Cloud IoT Intelligent Applications by using the HTTP protocol. |
| Devices that are already connected to an existing third-party cloud service using proprietary protocols. | Third-party clouds can connect with Oracle Fusion Cloud IoT Intelligent Applications using HTTP. This results in the devices getting indirectly connected to Oracle Fusion Cloud IoT Intelligent Applications. | A device such as an OBD II data logger connects to a third-party cloud service using its proprietary protocol. The third-party device cloud connects to Oracle Fusion Cloud IoT Intelligent Applications using the HTTP protocol. |
| Devices and gateways that are already connected to existing network providers that provide wireless connectivity to the devices. | The network providers can transmit the device data to Oracle Fusion Cloud IoT Intelligent Applications using HTTP or MQTT. | Network providers use LoRA, NB-IoT, or IoT MVNO for wireless connectivity with devices such as an asset tracker or a telematics gateway. The network provider can transmit the device messages to Oracle Fusion Cloud IoT Intelligent Applications using HTTP or MQTT. |
| Existing database with device data on events, time stamps, and alarms. | The on-premises database can connect to Oracle Fusion Cloud IoT Intelligent Applications using HTTP and transfer the device messages. | Machines using the Historian service save and store messages in a database or multiple databases over the supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) network. An on-premises Historian service such as Pi from OSI Soft connects to Oracle Fusion Cloud IoT Intelligent Applications and provides the machine data for analysis. |
| Existing on-premises industrial gateway software | On-premises industrial gateway software applications manage machine data. Oracle Fusion Cloud IoT Intelligent Applications can connect to these gateway applications using HTTP to obtain the machine data. | Machines that use OPC Unified Architecture ( UA), a machine-to -machine protocol to transfer machine data to industrial gateway software such as Metrikon or Kepware and that, in turn, can connect to Oracle Fusion Cloud IoT Intelligent Applications and send device messages received from the machines. |