Connect to Other Processes and Services
More likely than not, you’ll need to define interactions across business processes within a process-oriented application. For example, your business process may need to invoke an external service, call another process from within the current process, or pass a message to a process outside of the current process. Use the following System activities to model communication between processes and services.
Processes can communicate with each other either synchronously or asynchronously. Processes interact synchronously when one process starts another and waits for a response. Processes interact asynchronously when one process starts another and both processes run independently.
| Activity | Description |
|---|---|
|
Service |
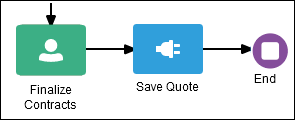
Use the service activity to communicate with other processes and services. Add the service activity when you know that your business process must invoke an external service or process. For example, the following process uses the service activity to save the finalized sales quote to a database.
When the service activity invokes a service, the token waits at the service activity until a response is returned. After the response is received, the token continues to the next sequence flow in the process. Note that multiple service activities can also execute at any given point of time depending on the way the user has modeled the application. In case a service activity fails to execute (for example, due to REST endpoint timeout), you get an error message with details about the failure in the process Tracking page in runtime. You can manually retry the service activity from the process Tracking page by clicking the Retry button. |
|
Notify |
Use the notify activity to generate and send notifications. The notify activity, which is similar to the service activity, uses a predefined service to perform notifications. You use expressions to determine which users receive the notifications generated by the notify activity. Currently, email is the only type of notification supported in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Process Automation. This type of notification sends an email to the users you specify. See Send Notifications. |
|
Call |
Use the call activity to call a reusable process from within the current process. The process being called becomes a child process of the calling process. When calling a reusable process, the call activity of the parent process waits until the child process completes before continuing. Data objects of the parent process aren’t automatically available to the reusable process. Data objects must be passed to and from the child process using argument mapping of the call activity. |
|
Decision |
Use the decision activity to add decision services to your process applications. You can use different types of decision logic, such as decision tables, simple expressions, and so on, to create an executable decision model, then expose it as services. These decision services can be incorporated into your business process to facilitate automated decision-making. Want to know more about working with decision models? See Model Decisions. |
|
Upload Form |
Use the upload form activity to capture snapshot of a form (with its payload) during execution of a process instance and store the form in a database or service for archiving or auditing purposes. For example, you can capture snapshots of a form after a user submits the form and then again after a manager approves the form during a process execution and upload the form snapshots to an external database for auditing purpose. |
|
Subprocess |
Use the subprocess activity to model a subprocess within a business process. The subprocess becomes a child process of the parent process and is always a part of the parent process. A subprocess activity lets you hide the complex details of a part of a process to make the overall process more readable. See About Subprocesses. |
|
Event Subprocess |
Use the event subprocess activity to catch system exceptions that occur in the runtime life cycle of a process and cause it to fail. |
|
Send |
Use the send activity to start another process from within the current process. The send activity doesn't wait for the process that it starts to complete. Once the called process is started, the main process continues to the next activity in the process flow. The called process and the main process runs asynchronously. See Use a Send Activity. A send activity can also be used to send a message to a receive activity in another process. See Use Send and Receive. |
|
Receive |
Use the receive activity to receive messages from another process or external system. It waits for the message to arrive from a process or external system. Once the message is received, the receive activity completes and the process continues to the next activity in the flow. A receive activity is usually paired with a send activity to interact between asynchronous processes. See Use Send and Receive. Receive activities paired with send activities can also be used to set up correlation to communicate between asynchronous processes. See Example of Using Correlation with Send and Receive. |