Understand Oracle SOA Suite on Marketplace Topologies
You can create a virtual cloud network (VCN) with a public subnet or a private subnet to extend your on-premises network into the cloud.
- Public subnet: Instances created in a public subnet have both a public IP address and a private IP address. These instances have direct access to the internet through an internet gateway. Traffic can initiate from both the internet and public subnet instances.
- Private subnet: Instances created in a private subnet need only a private IP address with no internet access. These instances can initiate connections to the internet through a NAT gateway (for example, to get software updates), but cannot receive inbound connections from the internet through that gateway. When you provision an Oracle SOA Suite on Marketplace instance with a private subnet, you must select to create or use an existing private endpoint or to create or use an existing Bastion VM.
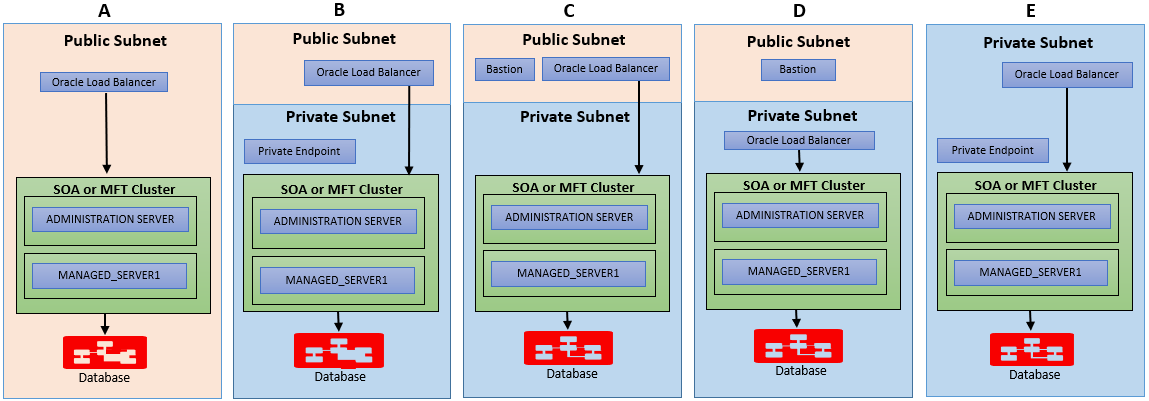
You can configure Oracle SOA Suite on Marketplace across a public and private subnet in several ways. As illustrated in the figure below, the scenarios for an Oracle SOA Suite on Marketplace topology are:
- Scenario A: All components in a public subnet.
- Scenario B: Load balancer in a public subnet, and remaining components in a private subnet.
- Scenario C: Bastion VM and load balancer in a public subnet, and remaining components in a private subnet.
- Scenario D: Bastion VM in a public subnet, and remaining components in a private subnet.
- Scenario E: All components in a private subnet.
Scenario A: Public Subnet
In this scenario, the VCN is directly connected to the internet through an internet gateway. The gateway is also used for connectivity to your on-premises network. Any resource in the on-premises network that needs to communicate with resources in the VCN must have access to the internet. A SOA server, Database server, and optional load balancers are created in a public subnet. All these resources are assigned a public IP address and can be accessible from the internet. Your on-premises resources will communicate to cloud resources over the public internet. After creating an instance, you can use SSH to connect to it over the internet from your on-premises network or other location on the internet. This setup has default routing rules that are designed to make it easy to get started with Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. When you set up a load balancer or SOA server in a public subnet, you allow SOA runtime traffic from the internet.
Scenario B, C, and D: Public and Private Subnet
This scenario consists of a virtual cloud network (VCN) with a regional public subnet to hold public servers (such as load balancers) and a regional private subnet to hold private servers (such as a SOA server and Database server). Optionally, you can set up a load balancer and a SOA server on a public subnet and a Database server on a private subnet. Your on-premises resources communicate to cloud resources over the public internet. After creating an instance, you can connect to instances in a public subnet over the internet. The VCN has a dynamic routing gateway (DRG) and IPSec VPN for connectivity to your on-premises network. After creating an instance, you can use SSH to connect to instances in a private subnet over a DRG/IPSecVPN. You cannot connect to instances in a private subnet over the internet. You need to set up additional routing rules to route traffic from a private subnet to a DRG that allows communication with an on-premises network. When you set up a load balancer or a SOA server in a public subnet, you allow SOA runtime traffic from the internet.
Scenario E: Private Subnet
This scenario consists of a virtual cloud network (VCN) with a regional private subnet to hold private servers (such as a SOA server, Database server, and load balancers). The VCN has a dynamic routing gateway (DRG) and IPSec VPN for connectivity to your on-premises network. The VCN has no direct connection to the internet. Any connection to the internet would need to come indirectly through the on-premises network. You cannot connect to instances in a private subnet over the internet. After creating an instance, you can use SSH to connect to instances in a private subnet over a DRG/IPSecVPN. You need to set up additional routing rules to route traffic from a private subnet to a DRG that allows communication with an on-premises network. When you set up a load balancer or SOA server in a private subnet, you allow SOA runtime traffic from your on-premises network only and not from the internet.