Setting Up OCI Object Storage
A separate subscription to OCI Object Storage is required in order to use this feature. Note that a Bucket is a logical container in OCI Object Storage for storing objects. In the context of Account Reconciliation, your attachments are considered objects.
The high level steps in OCI Object Storage are listed here:
- Create a Bucket in OCI Object Storage to store your
Account Reconciliation attachments. For instructions, see
Creating a Bucket .
Note:
You can create a bucket in an existing compartment or create a new compartment for Account Reconciliation attachments.Here's an example of a set up Bucket.
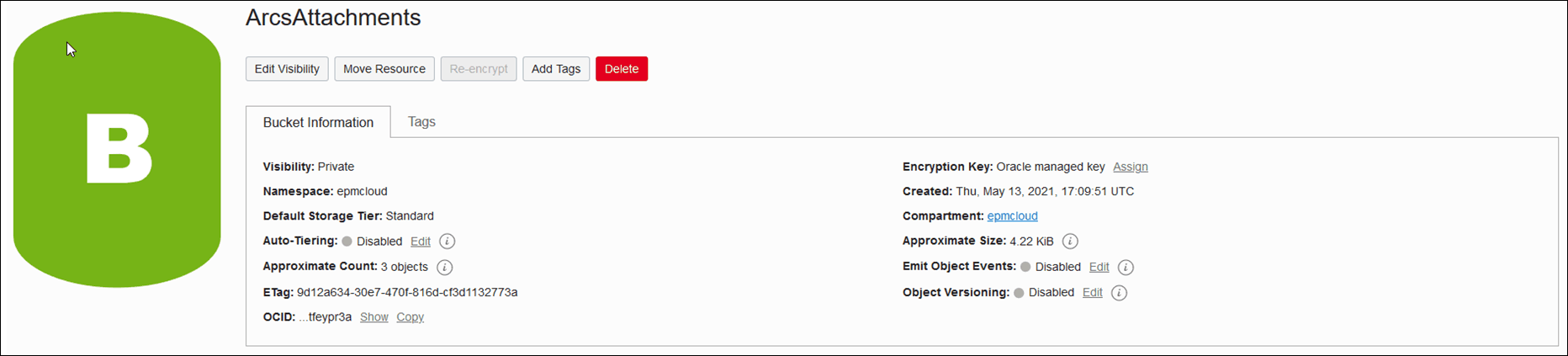
To enable you to test access to the bucket and to switch seamlessly from a test environment to a production environment, it is recommended that you create two folders within the bucket – one folder for the test environment and another folder for the production environment. For example, if you create a bucket named
account_rec_datato store your attachments, create folderstestandprodwithin this bucket. During the implementation phase, use thetestfolder by specifying the bucket URL as<bucket_url>/test. When moving to the production environment, switch the bucket configuration to<bucket_url>/prod. The foldertestcan subsequently be deleted without any impact in the production environment. - Ensure that Auto-Tiering is disabled for the bucket. See Managing Auto-Tiering for an Object Storage Bucket.
- You need to keep the Lifecycle Policy Rules as is in OCI Object Storage. Do not change this.
-
Optional: Retention Rules in OCI Object Storage follow your company's audit requirements (for example five to seven years).
- In Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI), you need to create a
user for Account Reconciliation and grant that user at least
READ and WRITE access but do not grant DELETE access. The user can be an
Identity and Access Management (IAM) user or a Federated
user.
We recommend a separate user be created for accessing Object Storage for Account Reconciliation. This user has to be granted privileges to access to the attachment storage bucket and to manage objects in the bucket.
-
You need to create a group to assign policies.
Access to Object Storage is managed by Identity and Access Management (IAM) policies. Common object storage policies can be found in Common Policies
To create IAM policies, refer to this guide Getting Started with Policies
Here is an example of the policy that is required.
-
Allow group ArcsAttachmentWriters to read buckets in compartment ABC -
Allow group ArcsAttachmentWriters to manage objects in compartment ABC where all {target.bucket.name='ArcsAttachments', any {request.permission='OBJECT_CREATE', request.permission='OBJECT_INSPECT', request.permission='OBJECT_READ'}}
-
- An auth token has to be created for the user. For details, see Managing User Credentials
Note:
The auth token will not be displayed after it has been created so make a note of the token since it ill be used later in the configuration process. - Once you have created the Bucket and created a user, you need to set up OCI Object Storage in Account Reconciliation so that the connection is made using the Bucket URL and the Username and Password. See Setting Up OCI Object Storage in Account Reconciliation.
Examples: Configuring Policies
When creating a policy, ensure that you select the compartment or tenancy where your bucket is stored. For example, if your bucket is created in the compartment ABC, then your policy must also be placed in the compartment ABC.
Bucket in the Root tenancy and user is created in Federated Identity Provider
If you bucket is in Root tenancy, you are using a group, and the user is created in Federated Identity Provider, the policy format must be as follows:
Allow group 'OracleIdentityCloudService'/'GROUP_NAME' to read buckets in tenancy
Allow group 'OracleIdentityCloudService'/'GROUP_NAME' to manage objects in tenancy where all {target.bucket.name='BUCKET_NAME', any {request.permission='OBJECT_CREATE', request.permission='OBJECT_INSPECT', request.permission='OBJECT_READ'}}
For example, when the group name is arcs_attachments and bucket name is arcs_bucket:
Allow group 'OracleIdentityCloudService'/'arcs_attachments' to read buckets in tenancy
Allow group 'OracleIdentityCloudService'/'arcs_attachments' to manage objects in tenancy where all {target.bucket.name='arcs_bucket', any {request.permission='OBJECT_CREATE', request.permission='OBJECT_INSPECT', request.permission='OBJECT_READ'}}
Bucket in the Root tenancy, regular (non-federated Identity Provide) group, and user
If your bucket is in Root tenancy and you are using a regular (non-federated Identity Provider) group and user, the policy format must be as follows:
Allow group GROUP_NAME to read buckets in tenancy
Allow group GROUP_NAME to manage objects in tenancy where all {target.bucket.name='BUCKET_NAME', any {request.permission='OBJECT_CREATE', request.permission='OBJECT_INSPECT', request.permission='OBJECT_READ'}}For example, when the group name is arcs_attachments and bucket name is arcs_bucket:
Allow group arcs_attachments to read buckets in tenancy
Allow group arcs_attachments to manage objects in tenancy where all {target.bucket.name='arcs_bucket', any {request.permission='OBJECT_CREATE', request.permission='OBJECT_INSPECT', request.permission='OBJECT_READ'}}Bucket is in the Compartment Level and the group and user are created in a Federated Identity Provider
If your bucket is in the compartment level and you are using a group and user that are created in the Federated Identity Provider, the policy format must be as follows:
Allow group 'OracleIdentityCloudService'/'GROUP_NAME' to read buckets in compartment COMPARTMENT_NAME
Allow group 'OracleIdentityCloudService'/'GROUP_NAME' to manage objects in compartment COMPARTMENT_NAME where all {target.bucket.name='BUCKET_NAME', any {request.permission='OBJECT_CREATE', request.permission='OBJECT_INSPECT', request.permission='OBJECT_READ'}}For example, when the group name is arcs_attachments and compartment name is arcs_compartment:
Allow group 'OracleIdentityCloudService'/arcs_attachments' to read buckets in compartment ABC
Allow group 'OracleIdentityCloudService'/arcs_attachments' to manage objects in compartment arcs_compartment where all {target.bucket.name='arcs_bucket', any {request.permission='OBJECT_CREATE', request.permission='OBJECT_INSPECT', request.permission='OBJECT_READ'}}Bucket in the Compartment level and regular (non-federated Identity Provider) group and user
If your bucket is in compartment level and you are using regular (non-federated Identity Provider) group and user, the policy format must be as follows:
Allow group GROUP_NAME to read buckets in compartment COMPARTMENT_NAME
Allow group GROUP_NAME to manage objects in compartment COMPARTMENT_NAME where all {target.bucket.name='BUCKET_NAME', any {request.permission='OBJECT_CREATE', request.permission='OBJECT_INSPECT', request.permission='OBJECT_READ'}}For example, when the group name is arcs_attachments and compartment name is arcs_compartment:
Allow group arcs_attachments to read buckets in compartment arcs_compartment
Allow group arcs_attachments to manage objects in compartment arcs_compartment where all {target.bucket.name='arcs_bucket', any {request.permission='OBJECT_CREATE', request.permission='OBJECT_INSPECT', request.permission='OBJECT_READ'}}