Overview of Application Configuration and Extension
By default, the application provides robust functionality, tailored to support most of the business requirements an organization could have. But you can still make changes to your application to best fit your specific business or personal needs.
Types of Changes
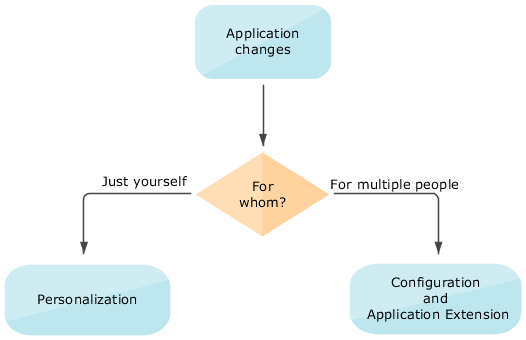
The types of change you can make depend on whether you're an administrator or a user, the pages you're changing, and who you're making the changes for.
-
Configuration: These changes are made by administrators, and such changes affect many users. For example, you might hide some menu items in the Navigator, or create a new page for all users.
-
Extensions: These are modifications applied to Oracle Fusion Cloud Applications at runtime using Visual Builder Studio. Extensions are made by one or more application developers and administrators, and such changes affect specific users based on the conditions defined for the extensions. These conditions are evaluated during runtime, determining which users can see the changes. For example, you may want to add a new field to a table or rearrange the fields in a form, but only when the user has a certain role. In most cases, the work for each product family (such as Oracle Fusion Cloud HCM, Oracle Fusion Cloud SCM, and so on) is separated into its own extensions, to which many people contribute.
-
Personalization: These changes are made by individual users, and they affect only the users who made the changes. As an administrator, you can't make personalizations for any specific user. Personalizations are also limited to certain types of changes, such as hiding infolets or resizing table columns.
Configurations, extensions, and personalizations are preserved when you move on to a newer release update.
What You Can Change
When you make a change to the data model, that change is available to other aspects of the application. For example, after you add an attribute to an object, you can use that attribute in these related artifacts:
-
Web-based view page
-
Associated mobile page
-
Associated reports
Generally, you use Application Composer to change the data model. You can then reflect those changes in the UI by using Visual Builder Studio, Page Composer, or Application Composer. If you see the Edit Page in Visual Builder Studio option in the Settings and Actions menu of a page, you know that you must use Visual Builder Studio to edit that page.
For information about configuring business intelligence, see the Creating and Editing Analytics and Reports guides relevant to your products.