Import and Export File Format for User Defined Dimensions
When you import and export data for user-defined dimensions, you must use a comma-delimited (.csv) file.
The following list describes the format and other considerations for import and export files:
- The file must have the following columns:
- Name: The name of the node.
- Parent. The name of the parent node, if the dimension is a hierarchy. If the node does not have a parent node, this field must be empty.
Note:
The column header for Name defaults to Node. Column headers for Name and Parent can be customized during registration.
- If the dimension has properties, the file contains a column for each property. The column header is the value specified when the property was created, see Adding an Existing Property to a Node Type for a User Defined Dimension and Creating a Custom Property.
- You can create, edit, and delete constant columns in your export file. See Managing Constant Keys for Universal Applications in Editing Binding Keys.
- The way in which the dimension is configured determines whether there are columns for node types and how top nodes are indicated, see User Defined Dimension Import and Export Settings.
- Data is imported in row order. Rows for parent nodes must precede rows for child nodes. If a row for a child node precedes the row of its parent node, an error occurs when the file is imported.
- You can place the columns in any order in the import file.
- If a column header does not match those described above, the import ignores the column.
Tip:
This means that an import file can contain information that will not be imported. For example, an import file can include a column for comments. - The import ignores duplicate rows.
-
Strings that contain the delimiter, quote, or line terminator (
CR/LF) character for the file or that start with characters from ASCII 35 and below (such asTab,!or#) will be surrounded by quotes. (For example,"# Children","Accumulated Depreciation, Equipment".) - Dates and timestamps for supported locales must be in one of these Java date format patterns:
-
Short
-
Default
-
Long
-
Medium
Note:
For information on Java date and time formats, see Using Predefined Formats. -
Example 38-1 Import File for a Dimension
Suppose you have a Departments dimension defined as follows:
- There are two node types, which are named Department and Department Rollup.
- Both node types use the
Descriptionproperty. - The Department Rollup node type had a property named
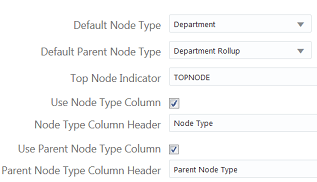
Company, which has been configured to use the abbreviation CO as the column header. - The dimension has been configured with the following import and export settings:
TOPNODErepresents top nodes.- The files can have a column for node types. The column header is Node Type.
- The files can have a column for parent node types. The column header is Parent Node Type.
- If the import file does not contain the Node Type and Parent Node Type columns, imports will assign bottom nodes to the Department node type and parent nodes to the Department Rollup node type.
The following table shows the first few rows of an import file for the dimension in this example:
| Name | Description | Node Type | Parent | Parent Node Type | CO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TD | Total Department | Department Rollup | TOPNODE |
1 | |
| 100 | Resources | Department | TD | Department Rollup | |
| 110 | Facilities Resources | Department | 100 | Department | |
| 111 | West Region Resources | Department | 100 | Department |
Note:
TheTOPNODE value in the Parent column indicates that TD is the root node. The column header for the Company property is CO.