Permission Cascading
Best Practice
A best practice is to assign permissions at the most general level first (for example, at the application or dimension level), and then to assign permissions at more specific levels (such as hierarchy sets or node types) only if there are specific business requirements that must be met.
Considerations
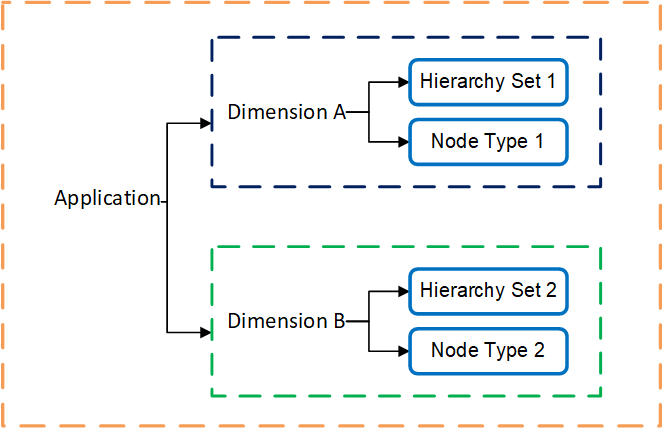
- Permissions assigned to an application will be applied to all dimensions in that application. For example, in the following image, if you assign Data Manager permission to a user on the application, that user will have Data Manager permission on Dimension A and Dimension B as well.
- Permissions assigned to a dimension will be applied to all node types and hierarchy sets in that dimension. For example, in the following image, if you assign a user Participant (Write) permission on Dimension A, that user will have Participant (Write) permission on both Hierarchy Set 1 and Node Type 1.
The following diagram illustrates these concepts:
Note:
You can also assign the Owner permission to a view. However, data access is controlled at the data object (application, dimension, hierarchy set, and node type) level. The Owner permission on a view enables a user to configure the view and to assign the Owner permission to other users and groups for that view, but it does not grant access to the data objects in that view.