Working with Valid Intersections in Page Drop-down Lists
To select members when valid intersections are enabled in a form:
Example 9-1 Working with Valid Intersections in Page Drop-down Lists
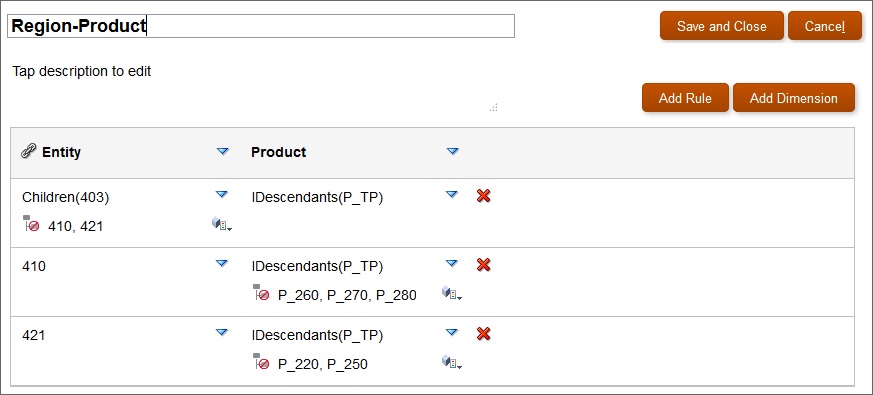
Valid intersection rules are set up by Planning administrators in the Planning web application. In Figure 9-6, valid intersection rules are set up as follows.
-
When the 403:Sales member is selected in the Entity dimension, all products in the Product dimension are available for selection.
-
When the 410:International Sales member is selected in the Entity dimension, then the members P_260:Game, P_270:Camera, and P_280:Television are not available for selection. All other members are available for selection.
-
When the 421:Sales NorthEast member is selected in the Entity dimension, then the members P_220:Software Suite and P_250:Network Card are not available for selection. All other members are available for selection.
Figure 9-6 Valid Intersections Rules Constructed in Planning Web Application
Now let's see how the rules set up in Figure 9-6 are exposed in Oracle Smart View for Office.
In the following examples, we'll demonstrate the valid intersection rules noted above. We'll select members in Entity and Product to change the point of view of the form, within the scope of the valid intersection rules.
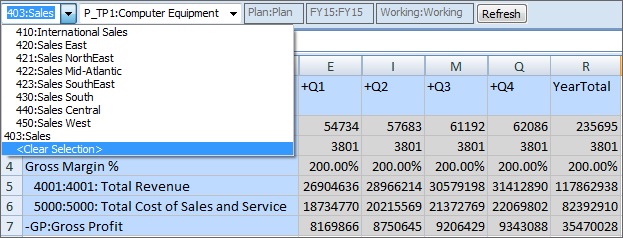
Figure 9-7 shows a newly opened form. The form has five dimensions. We can change the Page member on two of the dimensions.
Figure 9-7 Planning Form with Access to Member Selection on Two Dimensions
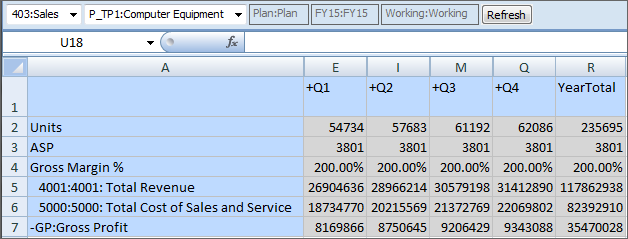
According to the valid intersection rules:
-
When the 403:Sales member is selected in the Entity dimension, all products in the Product dimension are available for selection. For example:
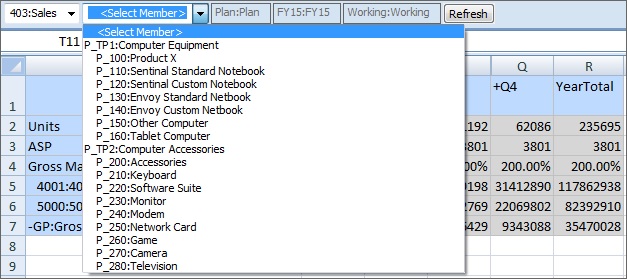
-
When the 410:International Sales member is selected in the Entity dimension, then the members P_260:Game, P_270:Camera, and P_280:Television are not available for selection. All other members are available for selection. For example:
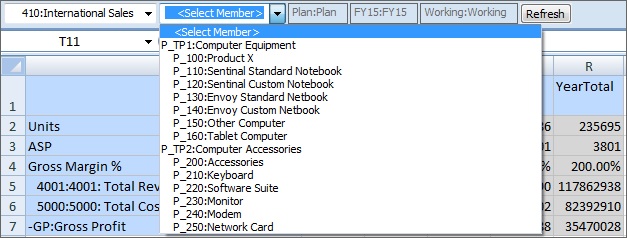
-
When the 421:Sales NorthEast member is selected in the Entity dimension, then the members P_220:Software Suite and P_250:Network Card are not available for selection. All other members are available for selection. For example:
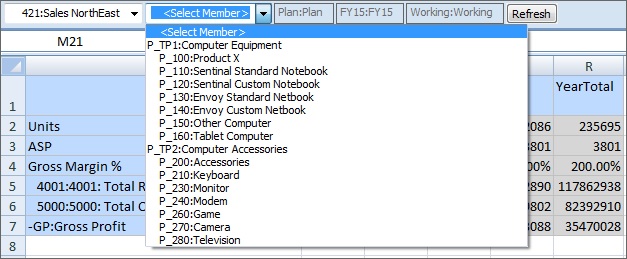
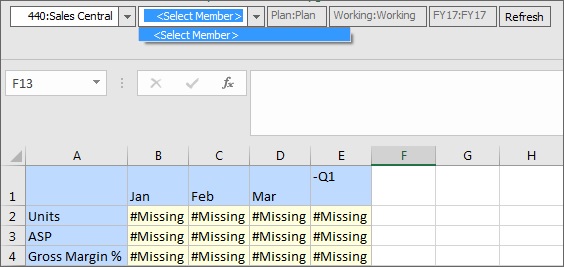
Example 9-2 Working with No Members in Page Drop-down Lists
The scenario shown in Figure 9-8, where there are no members to select from in the Product dimension Page drop-down list, might come about in at least a couple of different ways. For example, the Planning administrator may have configured any of the following:
-
Defined a valid intersection rule that excludes members of the Product dimension when 440:Sales Central is selected for the Entity dimension.
-
Defined a valid intersection rule that excludes P_260:Game, P_270:Camera, and P_280:Television when 440:Sales Central is selected for the Entity dimension, but the form is designed for only those three members.
In either case, when 440:Sales Central is selected for Entity, there are no Product members to select from in the Page drop-down list, and only <Select Member> is displayed.
Figure 9-8 Page Drop-down List with No Available Members to Select