Extend the Semantic Model Using the Sandbox Framework
The Sandbox framework enhances the development process with its intuitive graphical modeling capabilities. It enhances the user experience by visually organizing related elements within each logical star and subject area. The logical task organization and minimal steps make customization easy and efficient.
The Sandbox framework streamlines development by allowing changes to be made without requiring chronological order, eliminating the need to wait for compilation until all modifications are complete. This framework promotes greater consistency in the semantic model, supporting adherence to best practices.
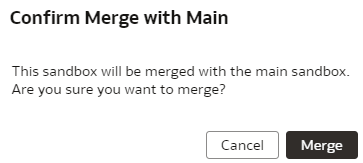
Multiple users can work concurrently in separate customization sandboxes. To ensure your work incorporates the latest changes, compare the update date of your sandbox with the main sandbox. If your sandbox was updated before the main sandbox, create a new customization sandbox and transfer your changes, then delete the old one, as changes merged to the main sandbox after your sandbox's creation won't be included. Before merging changes to the main sandbox, coordinate with other applicable users to prevent conflicts. Publish only one sandbox at a time. Publishing a sandbox removes any sandbox already published. If you've merged a sandbox, then the system preserves the changes that you published prior to merging with the main sandbox.
- Create a sandbox.
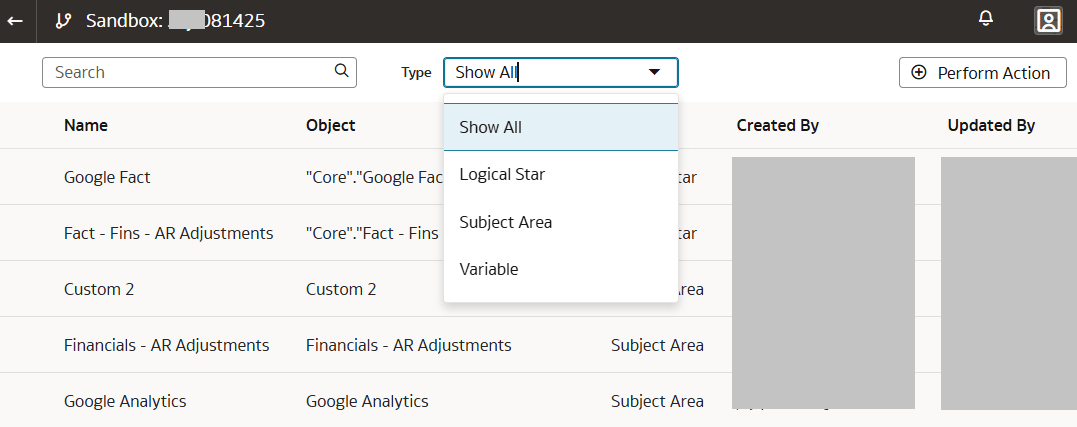
- Select Perform Action and then select Create or Manage a Star .
- Make changes as required (the changes are done to the logical model).
- Select Perform Action and then select Manage Subject Areas.
- Incorporate logical changes in the desired subject areas.
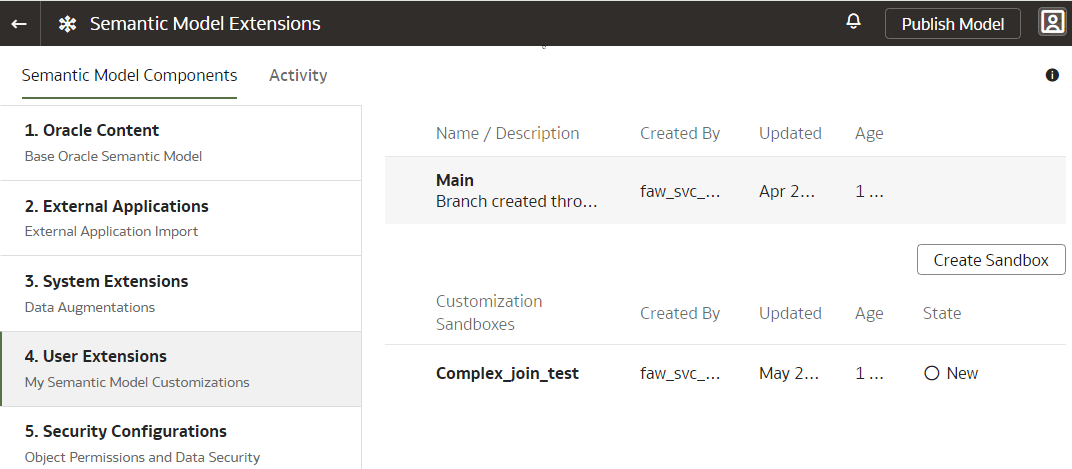
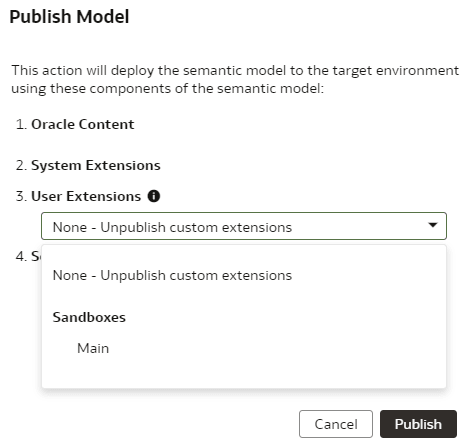
- Go back to Semantic Model Extensions page, select User Extensions, select Publish Model, and then select the sandbox to publish.
- In Oracle Analytics Cloud associated with your Oracle Fusion Data Intelligence instance, verify if the changes are reflected in the subject area.
Create Sandbox
To begin customizing your semantic model, create a sandbox.
You add customizations to the production environment. After you have added and tested your customizations, you can publish them to the model in the production environment.
Manage Subject Areas
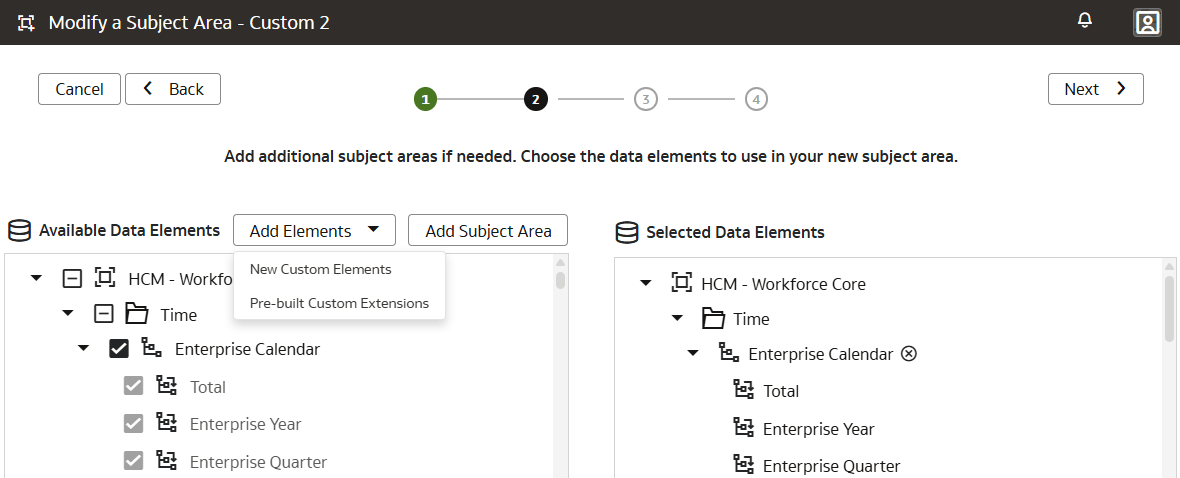
The Manage Subject Areas action enables you to organize all entities and attributes available for reporting in subject areas.
You can create business-friendly names and organize them in a desired order within folders to make it easier to find and include in the reports. The typical organization is to have each dimension organized in a folder with all its attributes within it, followed by folder for facts and calculations. You can rearrange columns based on your organizational preferences. You can reorder, rename, remove columns, and add folders to the custom dimensions and facts in the custom and prebuilt subject areas.
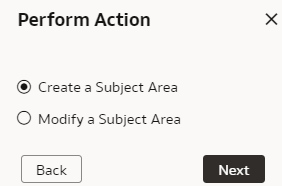
You can create a subject area or modify a subject area.
Create Subject Area
You can create a subject area as a container and later add facts and dimensions to your new subject area or create a subject area based on an existing one. The subject area enables you to organize all entities and attributes available for reporting.
Modify Subject Area
You can modify custom and prebuilt subject areas. Modify a custom subject area to change the previously selected data elements or add more data elements and modify a prebuilt subject area to add more data elements.
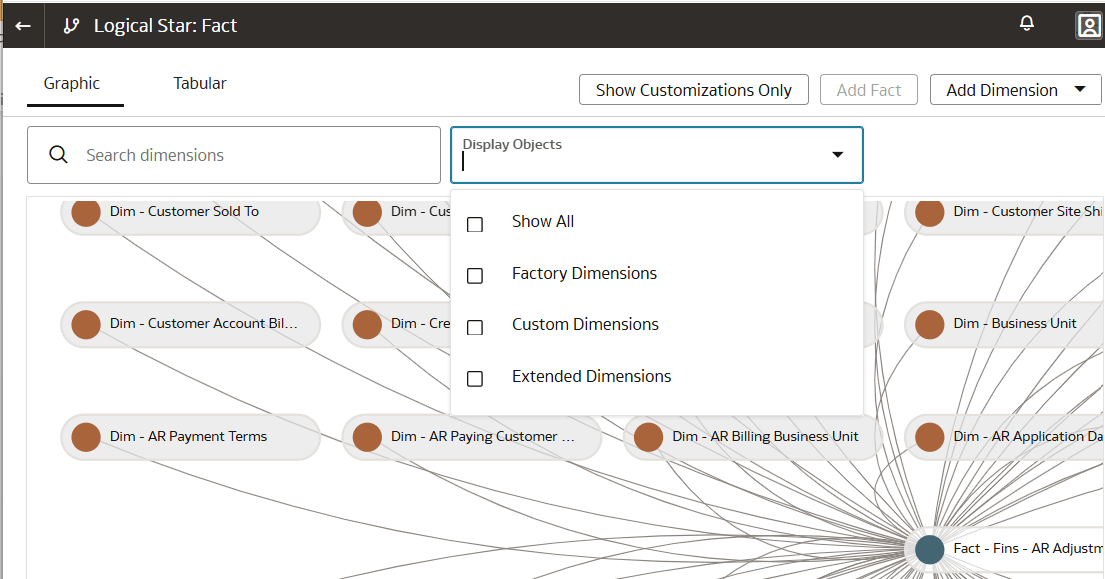
Manage Logical Star
A logical star is the basic complete unit of a dimensional model with a fact at the center and joined to the surrounding dimensions. Manage a logical star by adding and updating objects, attributes, joins, and calculations.
Facts contain elements that you can measure such as count, aggregate, and perform statistical operations on; while dimensions contain elements that provide context to those measurements. Each logical star has one fact and one or more dimensions. You can manage your own custom star or you can manage a prebuilt star by adding dimensions. You do these operations to extend the model to make use of custom data objects or elements that you've added to the warehouse or to create new calculations or joins to address your reporting needs.
You can use the standard prebuilt tables in the semantic model extensions without creating custom SQL views and issuing grant statements. This simplifies the process of working with the prebuilt tables for frequent data refresh and aliasing dimension tables.
Within the Sandbox you can zoom and focus on specific areas of the logical star using the graphic tab on the logical star page. You can rearrange the objects in the logical star using the graphic tab on the logical star page. Additionally, you can view all the joins in a tabular format using the tabular tab on the logical star page.
Create Logical Star
Create a custom logical star to use custom data objects or elements that you have added to the warehouse or to create new calculations or joins to address your reporting needs.
Add Fact
Add elements that you can measure such as count and aggregate, and perform statistical operations to your custom logical star using the Add Fact option.
Manage Dimensions
You can create a custom dimension, join it to the prebuilt or custom facts, and add the custom dimension to any subject area to meet your business requirements.
Create a Dimension
Create and add dimensions to facts to complete a new star or to update existing stars. You can create joins from your custom dimension to a prebuilt fact.
You can define a sort order column to control the sorting order of a logical column, especially when the desired sort order doesn't match the natural sort order of the data. This is useful for situations like sorting months in a specific chronological order or sorting descriptive columns based on a code or hierarchy.
Add Existing Dimension
If you want to provide additional context to facts, you can create your own dimension and join to an existing available column in a fact.
- On the Logical Star – Fact page, click Add Dimension, and select Add Existing Dimension.
- In Add Table, select the dimensions to add.
Manage Extensions
After adding the extension, you can extend the dimensions, add hierarchy, and add columns to ensure that your custom logical star meets your business requirements..
Refer to the Extending section in Recommendations and Tips to Extend the Semantic Model.
- Extend Dim
- Add Hierarchy
- Add Column
Extend Dimension
Extend prebuilt dimensions with additional attributes from another data source. For example, you can create a category column that isn't available in the prebuilt dimensions.
You can define a sort order column to control the sorting order of a logical column, especially when the desired sort order doesn't match the natural sort order of the data. This is useful for situations like sorting months in a specific chronological order or sorting descriptive columns based on a code or hierarchy. Refer to Extend Dimension in the Extending section in Recommendations and Tips to Extend the Semantic Model.
Add Hierarchy
Assemble the product hierarchy using the attributes from a dimension table. Hierarchies enable you to define aggregations and drill downs. This makes it easier to report on summary level and drill into details easily and within the same visualization.
Add Columns
You can create columns to provide additional data elements or calculations. You can add derived and physical columns. While adding physical columns, you can filter available columns and tables to narrow down your selection.
- On the Add Column page, select Add Derived Column, and
complete these steps:
- In Create Column, enter a display name.
- Under Data Elements, search for a data element from the physical table of the selected dimension table.
- From the search results, double-click the data element to place it in the text pane.
- Under Functions, search for a function to construct a column using expressions. For example, search for functions like "substring" or "concatenate" to construct new expression-based columns. From the search results, double-click the applicable result to add it to the central text pane.
- Click Validate, and then click Save.
- On the Add Column page, select Add Physical Column, and
complete these steps:
- In Select Physical Column, select the columns and click OK.
- On the Add Columns page, for the physical columns, select the Display check box to expose the columns, and click the Logical Level icon to set the required level.
- In Set Logical Level, select the dimension, select the level of the dimension hierarchy, and then click OK.
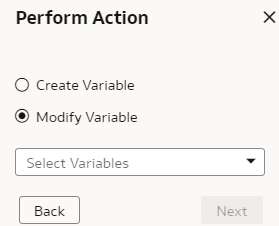
Manage Variables
Use the Manage Variables action to control the behaviour of sessions and queries. You can create and modify the custom variables.
Create Variable
Create custom session variables that you can use in your semantic model. The custom session variables are available for use only after yo've merged the applicable sandbox into the main sandbox.
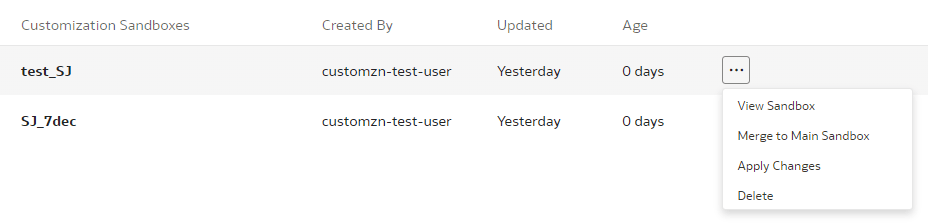
Merge Customization Sandbox to Main Sandbox
After creating the semantic model extensions, you can apply and publish your sandbox or you can apply and merge the customization sandbox into the main sandbox to make the extensions available for processing.
Apply Changes
Apply changes to validate the semantic model's integrity before merging to main or publishing your sandbox.
- Sign in to your service.
- In Oracle NetSuite Analytics Warehouse Console, click Semantic Model Extensions under Application Administration.
- On the Semantic Model Extensions page, click User Extensions.
- On the Semantic Model Extensions page, under Customizations Sandbox, hover over an applicable sandbox to view Actions, and then click Apply Changes.
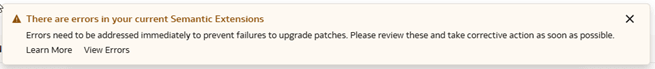
Validate Model
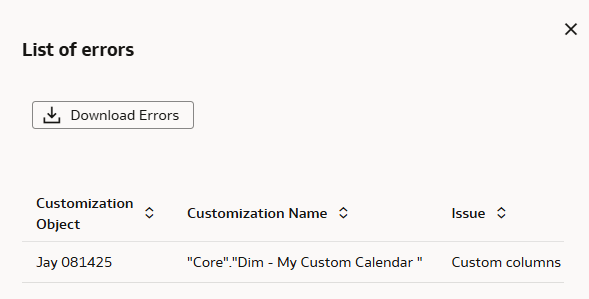
Prior to creating a semantic model bundle to deploy to another instance, you can validate the semantic model to confirm that it's error free.
- You want to confirm that there are no errors in the model.
- You see a banner on the Semantic Model Extensions page alerting you about errors in the model.
The initial banner provides a Learn More option linking to this information e Validate Model chapter, which references the Resolve Common Errors in Semantic Model Extensions appendix that can be used to debug and resolve your semantic model errors.
Publish Model
You can publish the sandbox in the non-production environments such as development or test to ensure that there are no errors.