Set Up Maps for Dashboards and Analyses
As the administrator, you define how data columns that you've modeled are displayed on maps. You configure the map data, then users can analyze the data in map views.
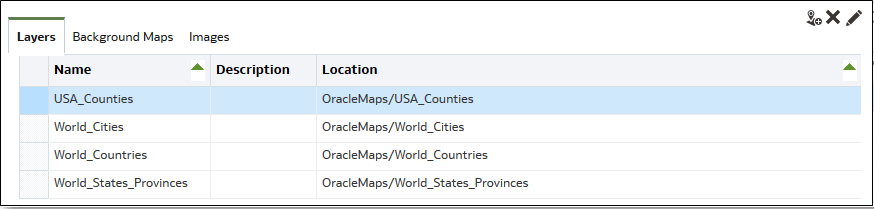
Map views allow users to display data on maps in different formats and to interact with data. As the administrator, you must configure the metadata that defines the mapping between business intelligence data and spatial data.
Spatial features such as shape definitions are managed by database administrators for your instance. If a shape geometry definition doesn’t exist for a particular column value, then the shape can't be shown on the map and might affect user interactions on the map.
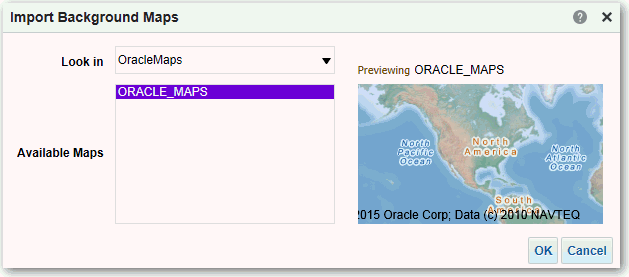
After you've added background maps and map layers, you can use the information
to create a static image for a map. The static image is displayed to content designers
and users who work with map views.