Calculate Emissions Associated with Sustainability Activities
To perform emission calculations, emission factors are required for the greenhouse gases that need to be reported as per the various sustainability frameworks and authorities. Emission factors are values that represent the rate at which an activity releases a greenhouse gas, air pollutant, or other substance into the atmosphere.
Oracle Sustainability calculates the greenhouse gas and air pollution emissions associated with a given activity. For each emission-generating activity, you can specify one of the following three calculation modes to be used:
- Using matched factors (the default): The application calculates emissions by using the highest-ranked matching emission factor mapping.
- Manual entry of factors: The application calculates emissions by using emission factors that you specify on the activity.
- Manual entry of emissions: Emissions are calculated or determined externally and are provided on the activity. The emissions are accepted as is.
When using matched factors, Oracle Sustainability automatically calculates emissions by using emission factor mappings that you configure. An emission factor mapping maps an activity type and a set of attribute values to an emission factor. For each emission type, the calculator finds the emission factor mappings that match the activity. Each emission factor mapping includes a ranking. If an activity matches multiple mappings, then the ranking determines the priority. The calculator chooses the highest-priority mapping (the one with the lowest ranking number) and uses its emission factor. Emission factor ranking allows you to set up mappings such that the calculator uses a carbon footprint or a supplier emission intensity instead of a more generic emission factor. This is illustrated by the following example:
Suppose your setup includes:
- A Stationary Combustion activity type with emission types CO2, CH4, and N2O.
- Emission factor mappings for activity type = Stationary Combustion, Country = US, and Fuel Type = Natural Gas as follows:
- Mappings to emission factors for CO2, CH4, and N2O with a rankings of 100.
- Mappings to emission factors for CO2, CH4, and N2O provided by a specific supplier, rankings of 50.
To calculate the CO2 emissions of a Stationary Combustion activity where natural gas is used, the calculator matches the activity to the CO2 mapping with the lower ranking number (in this example, it is the mapping with the ranking of 50) and multiplies the quantity of fuel consumed with the emission factor. The calculator goes through a similar matching process to calculate the CH4 and N2O emissions.
NOTE: When there are emissions for both component gases and CO2e (either entered directly or calculated using a CO2e emission factor), the application uses the CO2e emission for the total instead of adding the CO2e from the component gases.
The following figure shows a conceptual illustration of an activity record and two matching emission factor mappings with different rankings as described in the preceding example. An entry with a lower number in the Rank column (in this example, 50) is preferred over an entry with a higher number (in this example, 100). The calculated emissions are displayed in the columns with the green background.
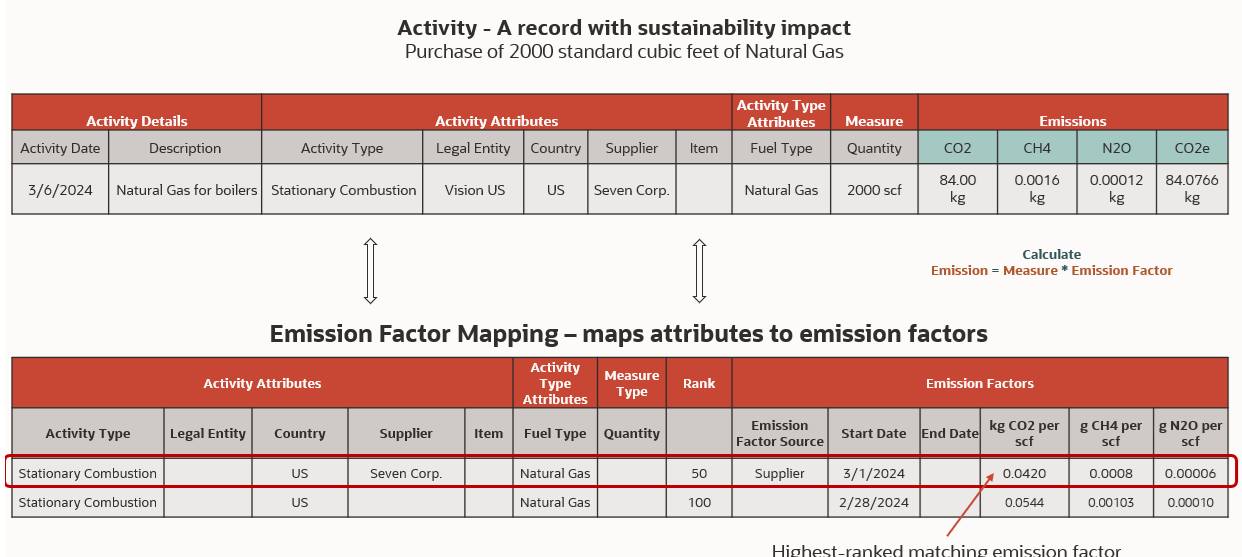
Conceptual Illustration of Mappings for Calculation
The ability to configure the Oracle Sustainability calculator lets you decide which emission factors are most appropriate for your activities. It also allows you to rank more specific and accurate emission factors above less specific, generic ones, so that the calculator uses the most preferred emission factors when they are available.
Here's the demo of these capabilities:
Steps to Enable
Refer to What's new for Update 24D: Set Up Data for Oracle Fusion Cloud Sustainability.
Tips And Considerations
-
You can populate Legal Entity, Supplier, and Country details in the emission factor mappings if required, and map activities with different attribute values to different emission factors.
-
Ensure that you configure emission factors whose denominator UOMs are in the same class (for example, energy, volume, or mass) as the UOMs of the measures in your activities. For example, if you have stationary combustion activities with fuel quantities measured in gallons (a volume UOM), you will need emission factors whose denominators also have volume UOMs. The calculator will perform intraclass UOM conversions (that is, conversions within a UOM class), assuming the required conversion factors are set up in your Fusion instance. If you have an emission factor that is based on a quantity of that item (for example, a product carbon footprint), and you have interclass UOM conversions configured on the item, then the calculator will perform a configured interclass UOM conversion to align the UOM of the measure on the activity with the denominator UOM of the emission factor.
-
If you want to account for inflation when using spend-based emission factors, then you’ll need to incorporate the inflation factor into your emission factors manually.
-
If the calculator finds two or more emission factors for an activity and emission type that have the same ranking, then it will use all of them and calculate multiple emission records. To avoid this scenario, if you need to upload more than one revision of an emission factor mapping (for example, to keep copies of emission factors used in the past), then be sure to end-date any earlier revisions.
-
To avoid rounding issues in emission calculation, set up the UOM conversion factors in Inventory with a high degree of decimal precision as emission factors may have many significant decimal digits. The calculator uses the formula: CO2e emission = emission * GWP * UOM conversion factor rounded to precision as set up in the Inventory profile.
Global Warming Potentials (GWPs) is a measure of how much energy the emissions of 1 ton of a gas will absorb over a given period of time, relative to the emissions of 1 ton of carbon dioxide (CO2).
-
Oracle recommends that you read the EPA or UK guidance on reporting Biogenic CO2 emissions. To align with the guidance by omitting Biogenic CO2 from emission scopes, add Biogenic CO2 as an emission type for any activity type involving biomass fuels. Then, change the emission type in the Emission Factor Mappings template for those fuels from CO2 to Biogenic CO2. The calculator follows the guidance that it omits Biogenic CO2 from total CO2. This behavior requires that you don’t configure a GWP for Biogenic CO2. Oracle doesn’t include one in the GWP accelerator spreadsheet.
-
If you want to track fugitive emissions, then you can create activities and use the Manual entry of emissions calculation mode. When you save an activity, the calculator will apply the GWP to calculate the CO2e. If the fugitive emissions are from a vehicle, you’ll need to create separate activities to track mobile combustion and fugitive emissions.
Key Resources
- What's new for Update 24D: Set Up Data for Oracle Fusion Cloud Sustainability
- What's new for Update 24D: Manage Sustainability Activities
Access Requirements
Users who are assigned a configured job role that contains the below privilege can enter emission factor mappings that are needed to perform the calculation:
- Manage Emission Factor Mapping (SUS_MANAGE_EMISSION_FACTORS_PRIV)
Users who are assigned a configured job role that contains the below privilege can create sustainability activities where calculation of emissions happen upon saving of activities:
- Manage Sustainability Activity (SUS_MANAGE_ACTIVITIES_PRIV)