Plan for Forecast Demand that Doesn't Identify a Fulfillment Organization
In many manufacturing and distribution environments, businesses process forecast demand without specifying the distribution or manufacturing location that will fulfill the demand. This is applicable in supply chain fulfillment networks that are in a state of flux such as opening and closing of distribution centers making the historical data unreliable.
With this update, you can generate a forecast in Oracle Fusion Cloud Demand Management without referencing to the inventory organization that fulfills the forecast. You can specify this forecast as the demand schedule to be used for planning supply. The forecast is consumed globally by sales orders across your supply chain and the remaining forecast is distributed to the fulfillment organization using a sourcing rule that you specify. You can specify the percentages in the sourcing rule of the forecasted demand that each fulfillment organization will be responsible for fulfilling.
Currently in Supply Planning, the forecast is a statement of demand based on the Ship From location. In some cases, forecasts aren’t pre-determined to be shipped from a specific facility. For example, marketing, sales, and manufacturing typically creates forecasts without Ship From locations.
With this update, Supply Planning will also consider the forecast published at a global level, without the context of an organization. Global Forecasts can be published either by Demand Management or uploaded as files through FBDI.
The following image shows a high-level picture of the global forecasting flow:
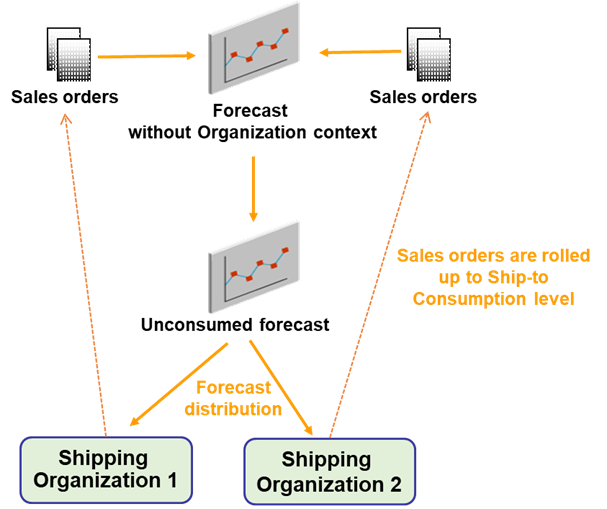
Global Forecasting Flow
With this update, you can consume the forecasts without a reference to the shipment location that is, inventory organization. Forecasts are consumed at the global level with reference to a Ship To level. The unconsumed forecasts are distributed to various shipment facilities or organizations. The distribution needs to follow a specific set of rules that specify the general replenishment policy for the enterprise. The unconsumed forecasts are distributed to shipping organizations based on the souring rules and split percentages defined.
You can publish the forecast at the following Ship To levels and a global Ship From entity without an organization context:
- Item
- Item, Customer
- Item, Customer Site
- Item, Demand Class
- Item, Zone
Forecast can be published at only one level for each hierarchy. For example, for the Customer hierarchy, the forecast can be published at either Item, Customer Site or Item, Customer level and not a combination of these.
You can select the global demand schedule from the Demand Schedules section in a supply plan or demand and supply plan.
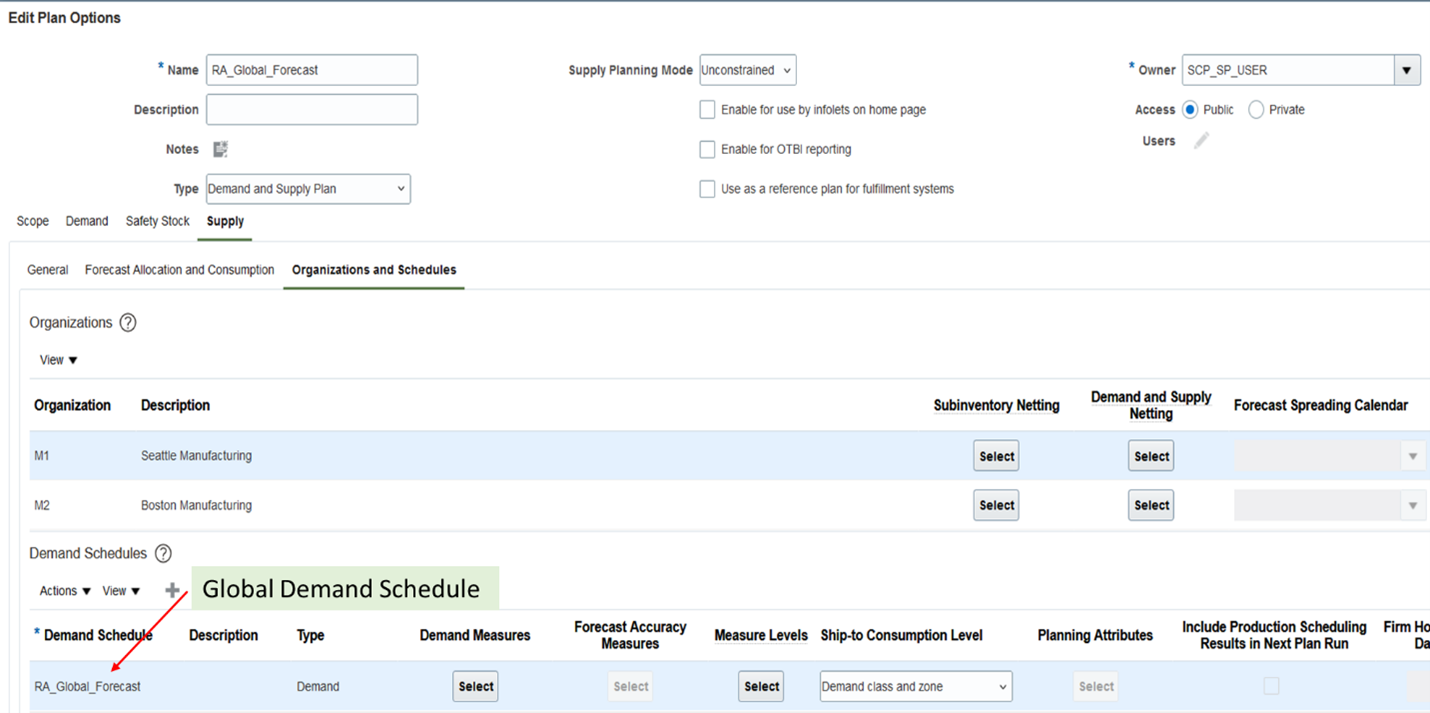
Input Global Demand Schedule
With this update, for a Demand Schedule of type Demand, the Organization dimension is editable in Measure Levels. You must select a null or blank level value for the Organization dimension for Supply Planning to recognize the global forecast. If the Organization level is populated, then the Demand Schedule is considered to be a local forecast.
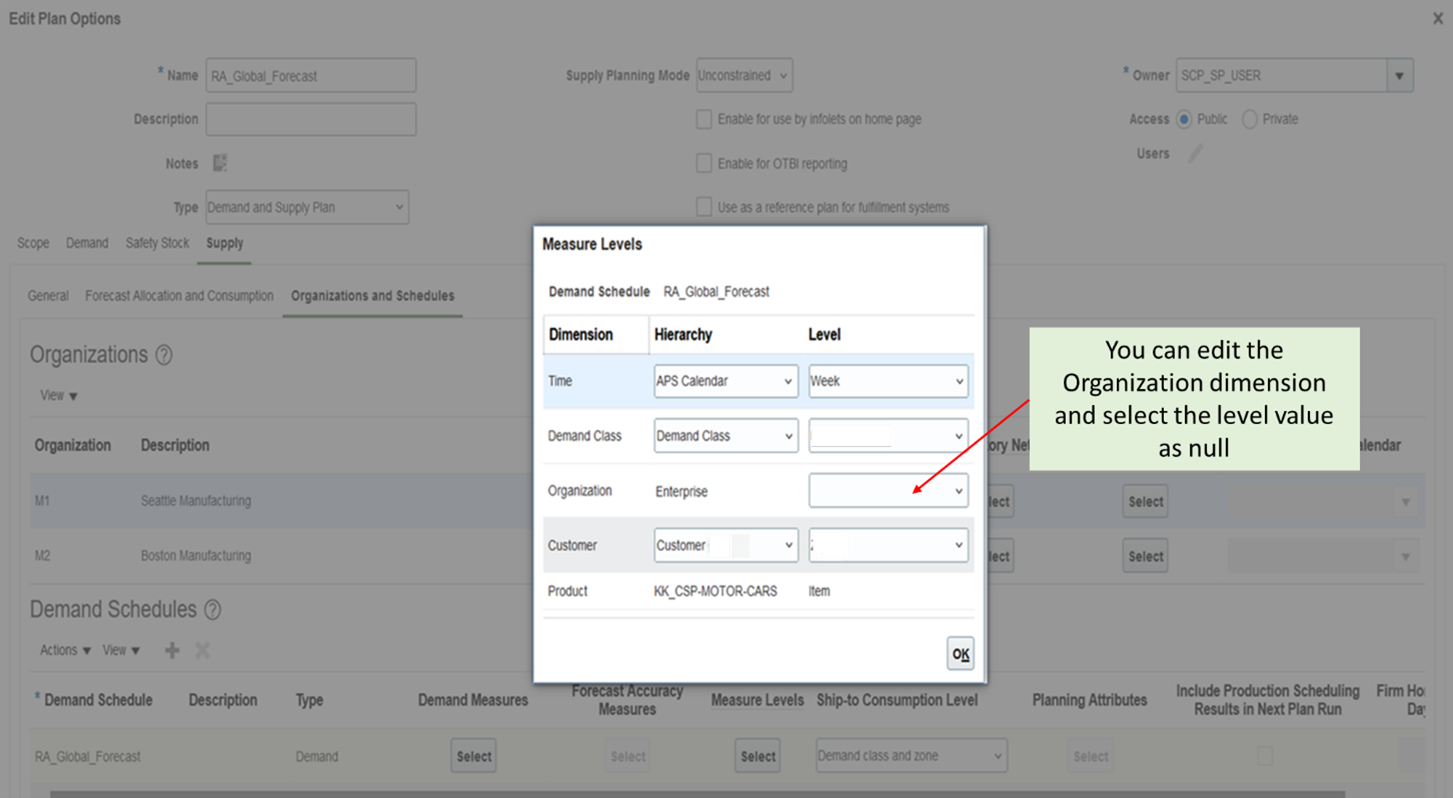
Measure Levels
You can select different measure levels at which the global forecast is published into Supply Planning.
Navigation: Supply Chain Planning -> Supply Planning -> Select plan -> Plan Options -> Supply tab -> Organization and Schedules subtab -> Demand Schedules section -> Measure Levels
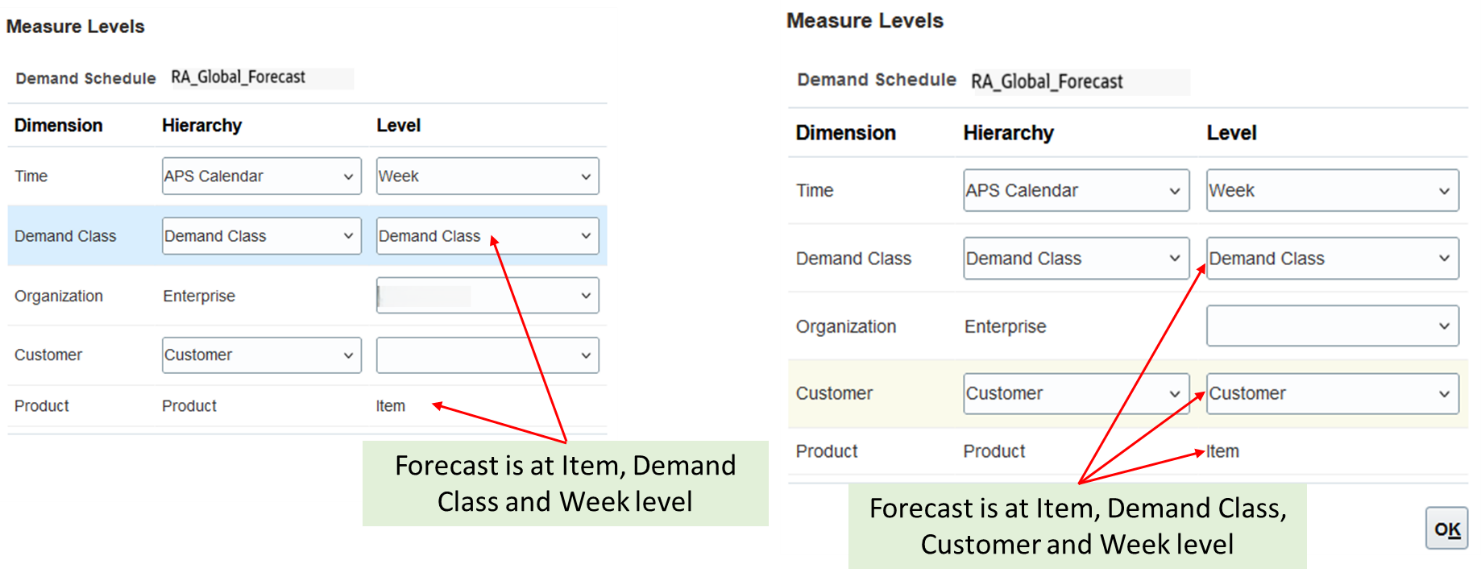
Measure Level Selection for Global Forecast
A seeded hierarchy Customer Zone is added to the Customer dimension. This hierarchy is populated only when the Organization level is null. This hierarchy contains the Zone level.
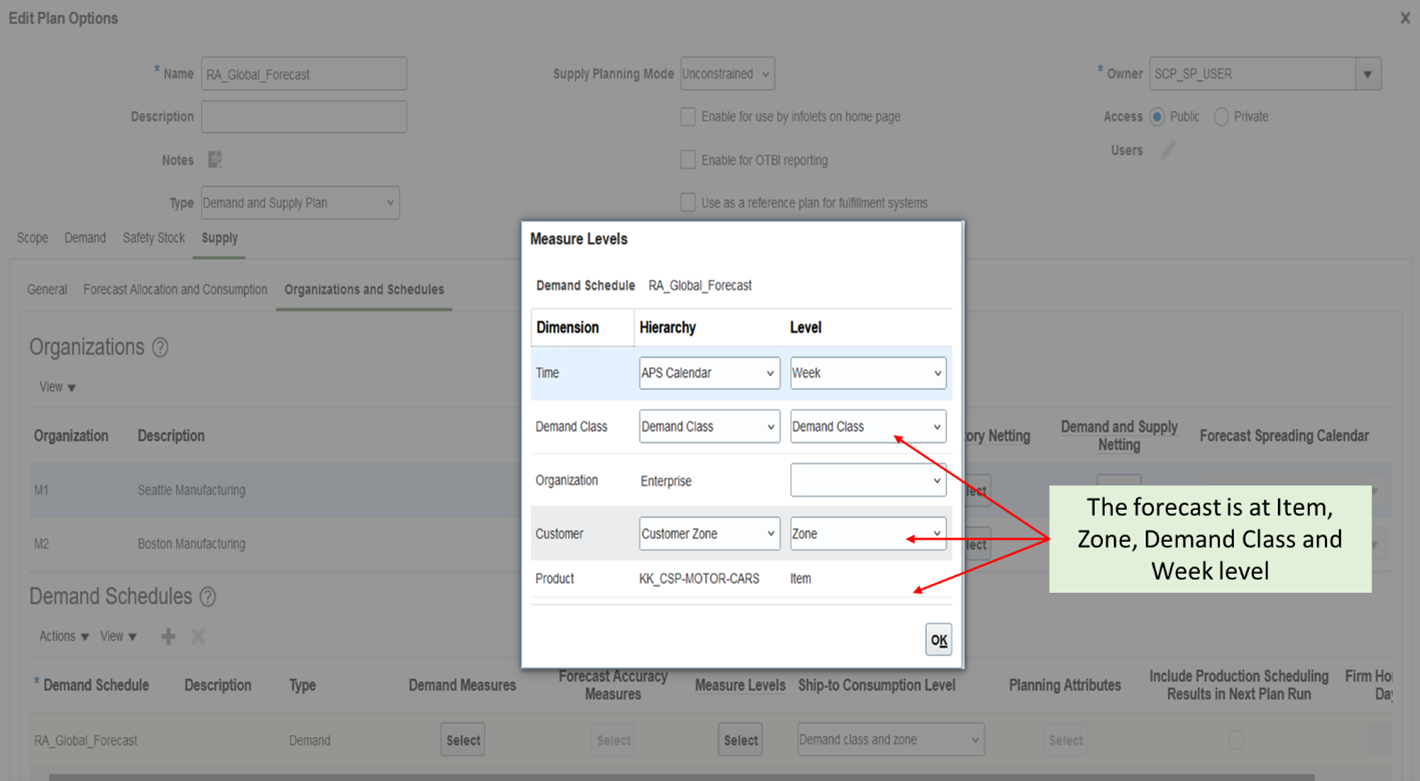
New Customer Zone hierarchy in the Customer Dimension.
Ship-to Consumption Level in supply plan options is populated based on the measure level values selected. Item is always an implicitly selected part of the Ship-to Consumption levels. So, if the Ship-to Consumption Level is set to Demand Class, it means that the global forecast is consumed at the Demand Class-Item level.
- Item is always a valid LOV entry in Ship-to Consumption Level.
- If Demand Class level is selected, then Ship-to Consumption Level list of values shows Demand Class.
- If the forecast is published at Customer level, i.e., measure level value is selected as Customer in Customer dimension, the Ship-to Consumption LOV shows Customer, but if the forecast is at Customer Site level, then LOV for Ship-to Consumption includes both Customer and Customer Site.
- If the measure level is Zone in Customer dimension, then Zone is populated in Ship-to Consumption LOV (Customer and Customer Site aren’t populated).
- If you select both Demand Class and Zone measure levels, then Ship-to Consumption level is also be populated with Demand class and zone, along with Zone and Demand class as separate entries. Global forecast is consumed by both demand class and zone if you select consumption level as Demand class and zone.
-
For external global forecasts, two new level values Zone, and Demand class and zone are added into the Ship-to Consumption Level list of values.
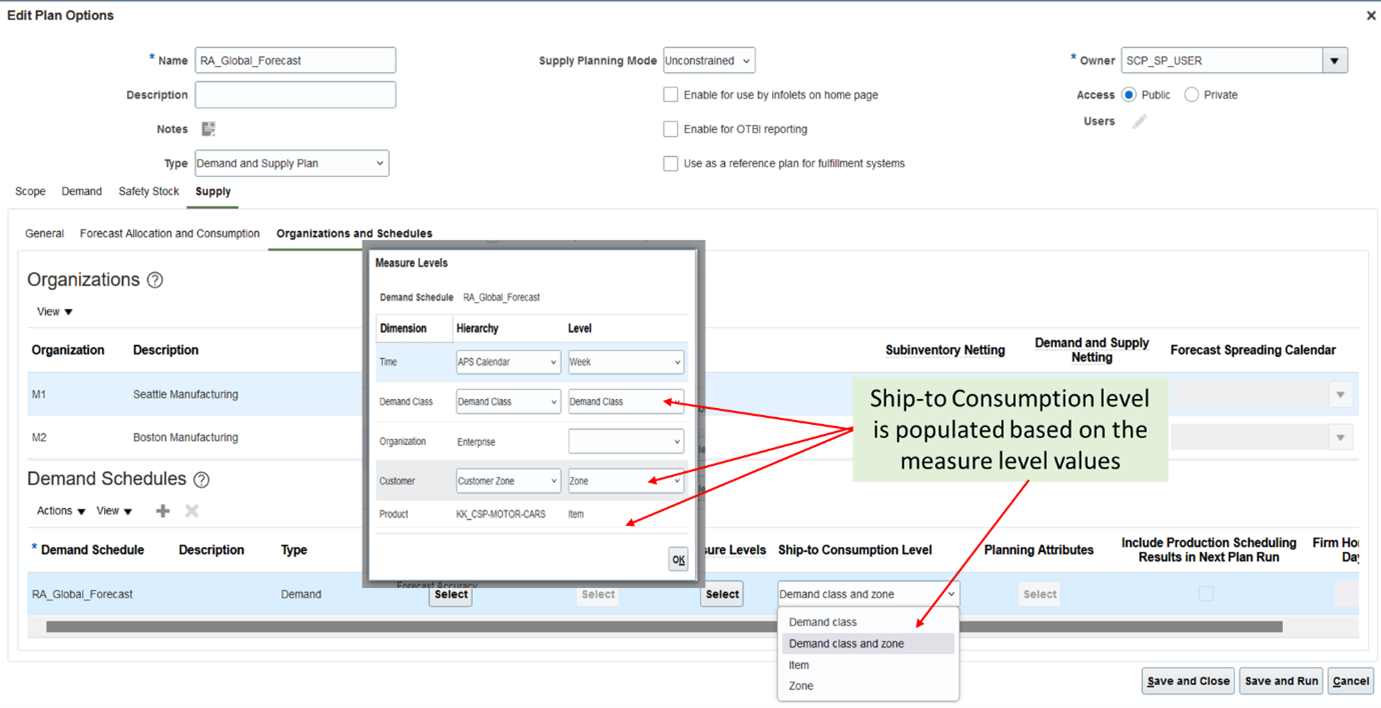
Ship-to Consumption Level
New Measures:
Two new measures are added as part of this feature:
Global Gross Forecast: This measure represents the global forecast published at selected measure levels without the context of an organization.
Global Net Forecast: This measure represents the net forecast after consuming the global gross forecast. The sales orders are aggregated to the selected Ship To consumption level and consume the forecast at that level.
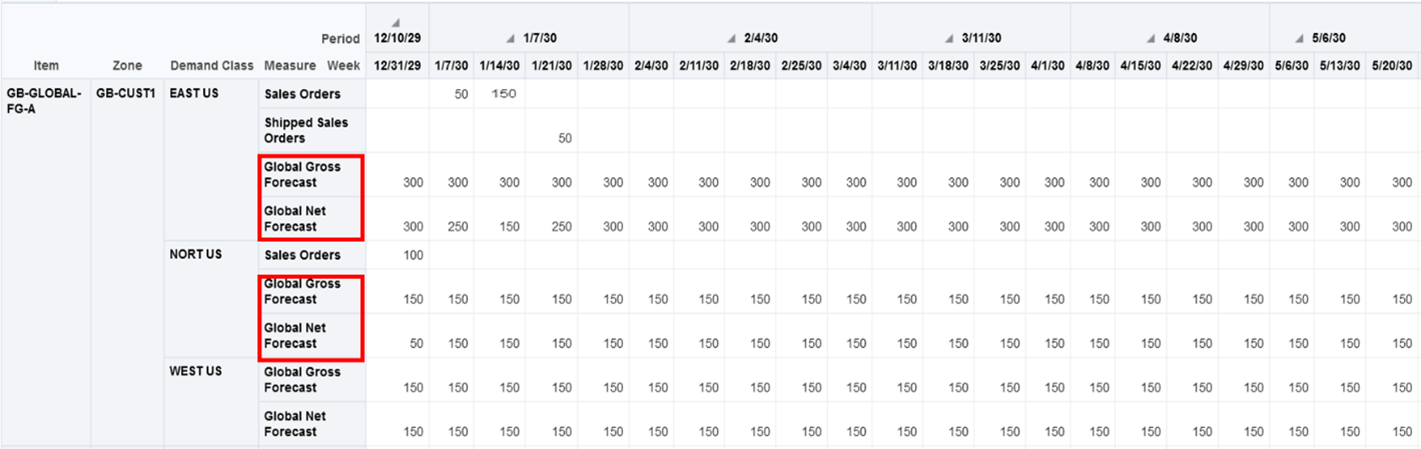
New Global Forecast Measures
During a supply plan run with a global demand schedule as an input, the plan will populate the Global Gross Forecast measure based on the selected measure levels in the supply plan options. The global gross forecast is consumed by the sales orders at the selected Ship-to consumption level.
Global Forecast Consumption:
Forecast consumption needs a statement of forecasts, sales orders, and rules to consume the forecasts. The sales orders have a reference to a ‘Ship To’ entity.
Prior to this update, the forecast consumption would always happen in the context of a shipping facility namely an inventory organization. After this feature, you can consume the forecasts without a reference to shipment location such as an inventory organization. Forecasts are consumed at the selected Ship To entity.
Forecast consumption can happen at the following specific ship to levels:
- Item
- Customer
- Customer site
- Demand class
- Zone
- Demand class and zone
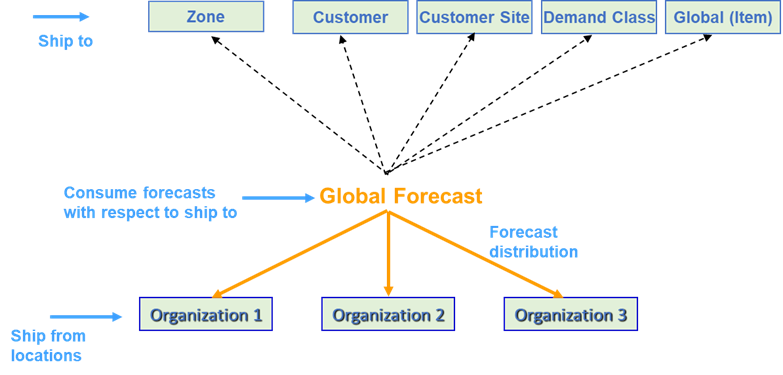
Global Forecast Ship-To Consumption Levels
In the above diagram, the topmost level entities are Ship To entities and lower levels are Ship From entities. The lower-level Ship From entities are true shipment organizations.
For forecast consumption, Supply Planning aggregates all the sales orders to the desired Ship To consumption level and then consumes the forecast at that level. Remember that the Item level is always implicitly selected for forecast consumption. For example, if the Ship-to Consumption level is set to Customer then sales orders will be aggregated to the Customer-Item level and then the forecast is consumed at that level (without a reference to ship from organization).
The existing local forecast consumption parameters (such as backward and forward consumption buckets, consumption bucket type etc.) and logic to consume the forecast applies for global forecast as well. A new plan option is introduced to specify the global forecast spreading calendar. This calendar is defaulted to Supply Planning Calendar and is enabled when the plan option Forecast Spreading is set to Spread forecast evenly.
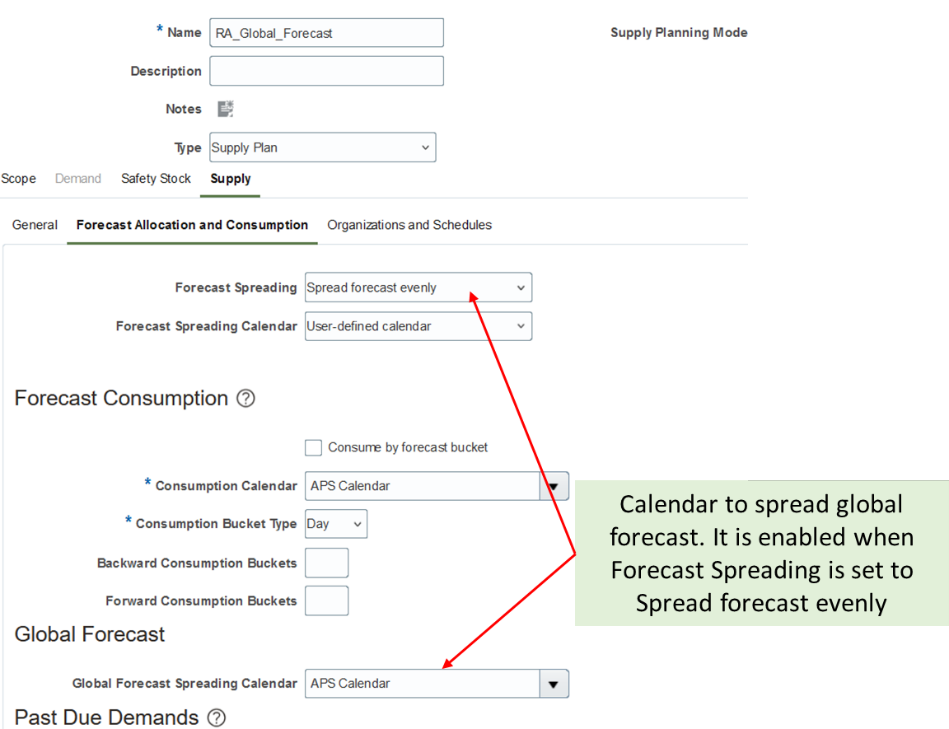
Global Forecast Spreading Calendar
Navigation: Supply Chain Planning -> Supply Planning -> Select plan -> Plan Options -> Supply tab -> Forecast Allocation and Consumption
Sales orders consume the global forecast based on scheduled ship date or requested ship date depending on the plan option setting Date Used to Plan Sales Orders.
Use Case 1:
There are multiple sales orders at different organizations:
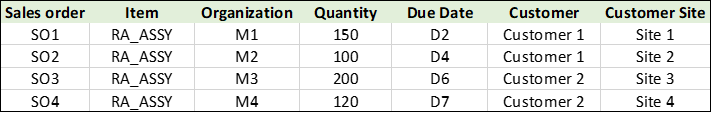
Use Case1: Sales orders
- The measure levels are selected as Item and Day.
- Ship-to consumption level is set to Item.
- The backward and forward consumption buckets are set to 2 days.
.The global forecast picture before and after consumption is as follows:
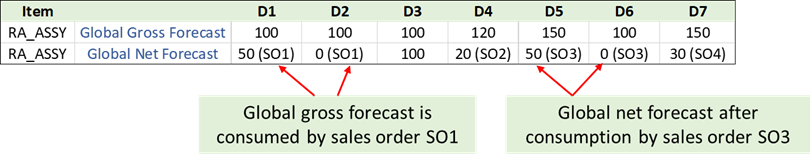
Use Case1: Global Forecast Consumption
Notice that even though there is an organization reference on the sales order, the forecast consumption process doesn’t consider the forecast as specific to the organization. In other words, the forecast consumption process ignores the organization reference on the sales order and consumes the forecast at item level. In this example, the forecasts were provided at an item level, and the sales orders were aggregated to the item level even though they belong to different organizations, customers, and customer sites.
Use Case 2:
There are multiple sales orders on different items at different organizations and on different due dates:
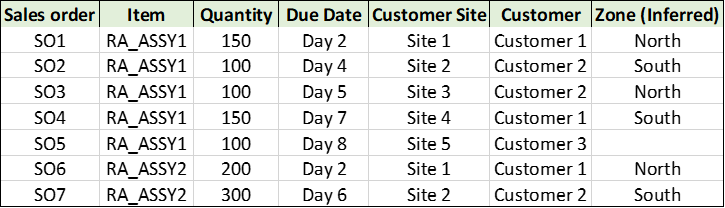
Use Case2: Sales orders
Zones are inferred using the Customer Zone hierarchy (Customer Site -> Zone). No zone is inferred for sales order SO5 as Site 5 isn’t mapped to any zone.
The measure levels are selected as Item, Zone, and Day. The Ship-to consumption level is set to Zone. The backward and forward consumption buckets are set to 2 days.
Since, measure levels are selected as Item, Zone, and Day, the global gross forecast will also be at same level. Following is the global gross forecast and global net forecast picture after consumption:
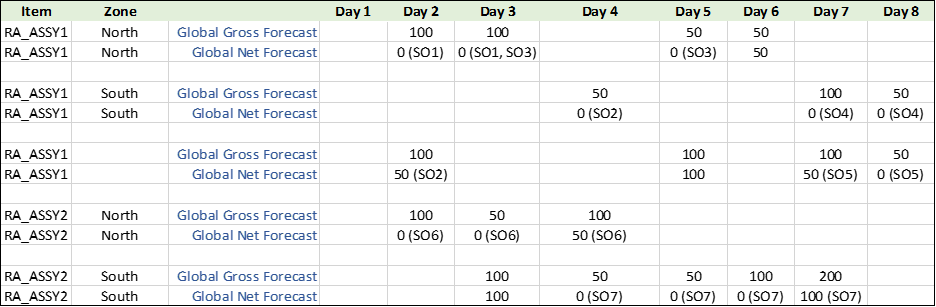
Use Case 2: Global Forecast Consumption
If the Ship-to consumption level is set to Zone, then the sales orders will consume the matching zone first in the entire consumption window and then consume the global forecast with null zone. In the consumption window, the sales order will first look for forecasts in backward consumption buckets and then forward consumption buckets.
In this use case, the sales order SO1 will consume the entire forecast on day 2, and then look for the forecast in backward consumption bucket with matching zone, but since there is none, it will look at the forward consumption bucket. There is a forecast with matching zone on day 3, it will consume the forecast partially.
Use Case 3:
There are multiple sales orders at different organizations and on different due dates:
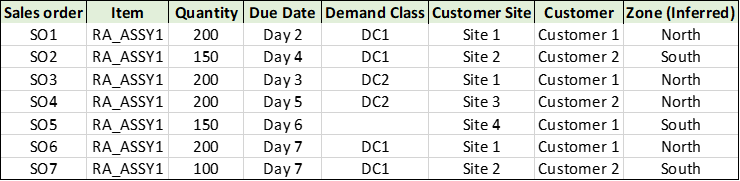
Use Case3: Sales orders
Zones are inferred using the Customer Zone hierarchy (Customer Site -> Zone).
The measure levels are selected as Item, Zone, Demand Class, and Day. The Ship-to consumption level is set to Demand class and zone. The backward and forward consumption buckets are set to 2 days.
If the Ship-to consumption level is set to Demand class and zone, then consumption first happens at the matching zone and demand class in the entire consumption window (first backward and then forward buckets), then either zone or demand class and then null zone and demand class. The global gross forecast and global net forecast picture after consumption is as follows:
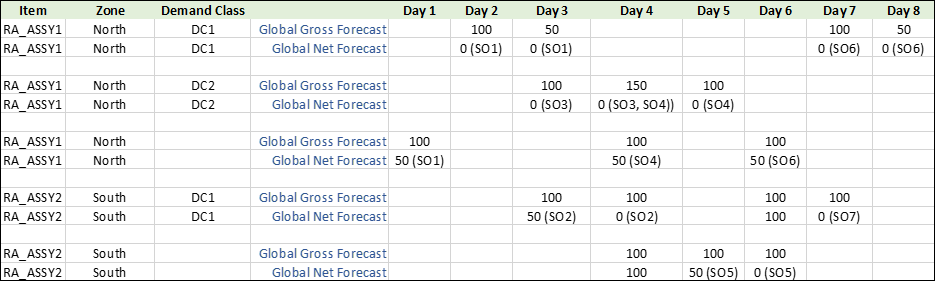
Use Case 3: Global Forecast Consumption
In this use case, the sales order SO1 consumes the global forecast with matching demand class and zone first and then consumes the forecast with matching zone and null demand class. It consumes the entire global forecast on day 2 first with North zone and DC1 demand class, and since there are no matching forecast in backward window, it consumes the forecast on day 3 with matching zone and demand class. Now since there is no matching forecast left in the consumption window, sales order consumes the forecast partially with matching zone but null demand class on day 1.
Global Forecast Consumption by Transfer orders
Demand Management can create forecasts of transfers based on the transfer order history. Forecasts of transfers can also be part of global forecasts.
Supply planning can consume the global forecast with actual transfers. Following are the key set ups and the existing setups remain unchanged:
- Forecast consumption is performed only when the source organization of the transfer order is included in the plan.
- The forecast must include the customer and customer site specified in the supply network model for the destination organization or zone.
- The option Use Customer and Customer Site for Interorganization Transfers must be selected.
- For the input demand plan, either customer/customer site or zone as the measure level for the customer dimension must be selected.
- If measure level is selected as Zone, then the customer site associated with the destination organization is rolled up to zone for consumption purposes.
- The transfer forecast doesn’t include a demand class.
- The demand plan option Include transfer orders must be checked.
Global Forecast Distribution
Companies with multiple fulfillment facilities need the capability to distribute the unconsumed global forecasts to various shipment facilities or organizations for further planning. This forecast distribution is based on the sourcing split percentages as defined in the sourcing rule. For example, create a sourcing rule to distribute 60% of the global forecast to manufacturing organization M1 and 40% to manufacturing organization M2. Sourcing type should be set to “Transfer from”.
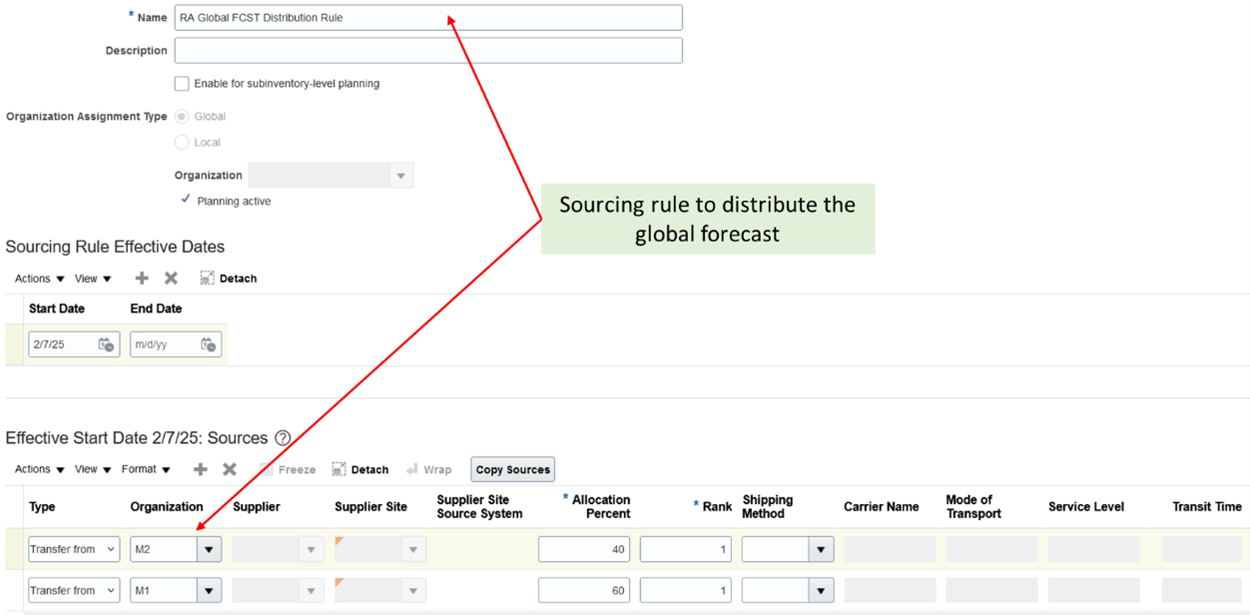
Sourcing Rule for Global Forecast Distribution
Assign this sourcing rule to an assignment set at appropriate assignment levels. A new plan option is created to specify the assignment set for global forecast distribution. This is separate from the regular supply planning assignment set and is used only for global forecast distribution.
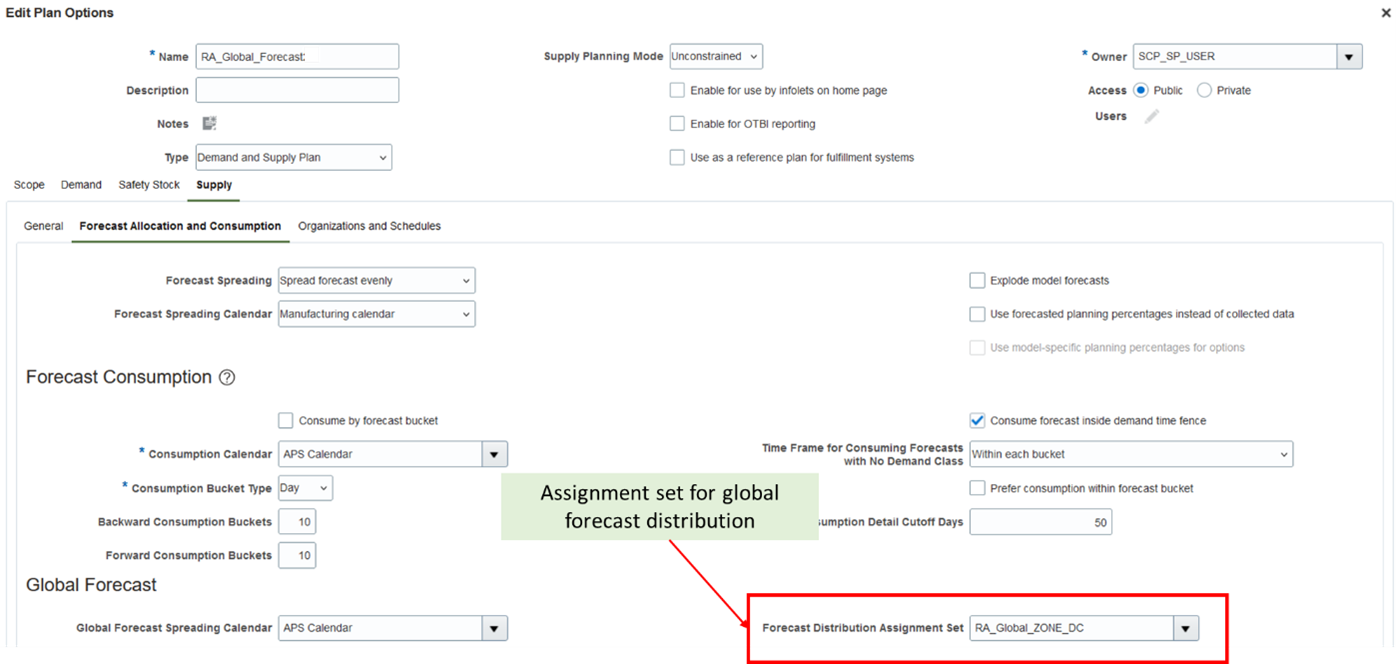
Forecast Distribution Assignment Set
The following two new assignment levels are added in Manage Assignment Sets to distribute the global forecast at more granular levels:
- Item, demand class, and region
- Category, demand class, and region
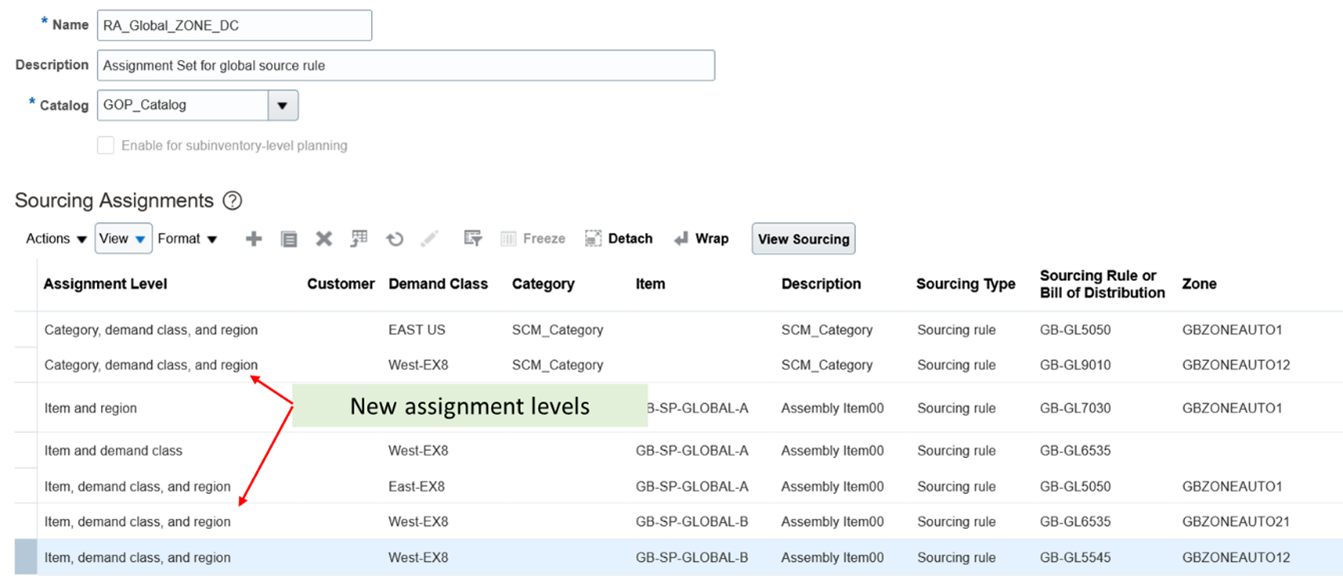
New Assignment Levels
The following table shows the assignment levels that are valid for a selected Ship-to consumption level. Supply Planning looks into the following hierarchy of assignment levels for the selected Ship-to consumption level for global forecast distribution.
For example, if you select Ship-to consumption level as Item, then for global forecast distribution, valid assignment levels are Item, Category, and Global. Supply Planning looks for and uses applicable distribution assignments across distribution assignment levels in detailed-to-aggregate (top-to-bottom) order, as given in the table.
Valid Assignment Levels for Global Forecast Distribution
|
Ship-to Consumption Level |
Valid Distribution Assignment Level |
|
Item |
Item, Category Global |
|
Demand Class |
Item and Demand Class Item Category and Demand Class Category Demand Class Global |
|
Customer |
Item and Customer Item Category and Customer Category Customer Global |
|
Customer site |
Item and Customer and Customer Site Category and Customer and Customer site Category Customer and Customer Site Global |
|
Zone |
Item and Region Item Category and Region Category Zone Global |
|
Demand class and zone |
Item, Demand Class, and Region Item and Demand Class Item and Region Item Category, Demand Class, and Region Category and Demand Class Category and Region Category Global |
For a selected Ship-to consumption level, if you pick an assignment level, that isn’t in the above table, then that assignment isn’t considered for global forecast distribution.
The above assignment levels are only for global forecast distribution. For regular supply planning there is no change in the existing behavior.
Use Case 4:
In this use case, there are multiple sales orders from different customers and customer sites. The Ship-to consumption level is set to Zone and backward and forward consumption buckets are set to 2 days.
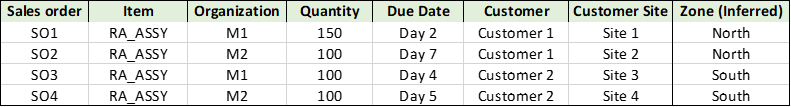
Use Case 4: Sales orders
The zone information is inferred by supply planning using the customer zone hierarchy (Customer Site -> Zone).
The following is the picture of the Global Gross Forecast measure published at Item and Zone level. To consume the forecast, supply planning aggregates all the sales orders to the zone level and consume the forecast at that level. Global Net Forecast shows the remaining (unconsumed) forecast picture at the global level:
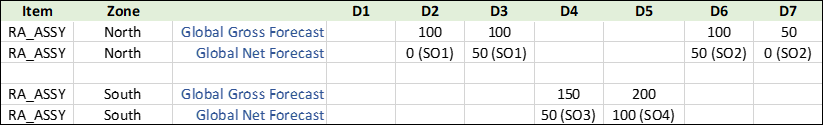
Use Case 4: Global Forecast Consumption
It is recommended to create a separate pivot table with the new global forecast measures. For analysis purposes, you can use a two-panel page structure, the top panel with Global Gross Forecast and Global Net Forecast measures and the bottom panel with Net Forecast and Sales Order measures.
To distribute the unconsumed global forecast to the respective ship from organizations, you need to define the sourcing rules with split percentages. Assign these sourcing rules to an assignment set with assignment level set to Item and region.

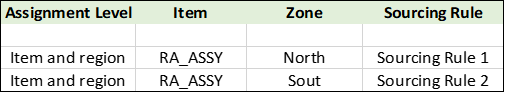
Sourcing Rule for Global Forecast Distribution Assignment Set for Global Forecast Distribution
The forecast for item RA_ASSY and North zone, is distributed to organizations M1 and M2 in the ratio of 60:40 respectively, while the forecast for item RA_ASSY and South zone, are distributed to organizations M1 and M2 in the ratio of 50:50. Following is the picture after forecast distribution.
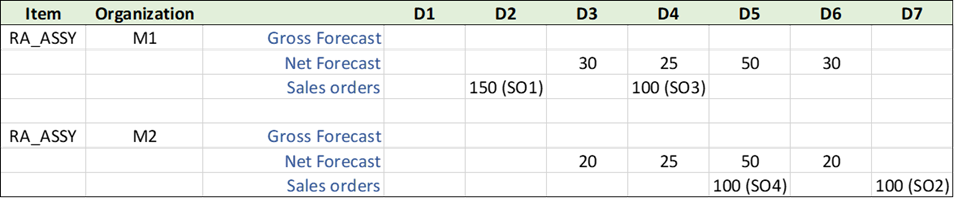
Global Forecast Distributed to Ship-from Organizations
Customer Site with multiple zones
Today a customer site can be associated with multiple zones. For example, site Site11 can be part of North zone as well as North-East zone. Demand Management collects only one of these site-to-zone associations, to maintain an unambiguous Customer Site - Zone analysis hierarchy. The zone that’s collected is the zone with the maximum zone_id. This may cause issues in global forecasts as Demand Management may not pick the zone for which the forecast has been created.
With this update, a new profile option Zone Type for Planning is created. In cases where multiple zones are parents of a common customer site or location, you can create a new zone type and assign it to your desired zone for planning purpose. Set the value of profile Zone Type for Planning to this zone type.
For example, Site11 belongs to both the North-East zone and the North zone. If you want to consider the North zone for planning purposes, create a zone type such as PLN_ZONES and assign that type to zone North. Set the value of profile Zone Type for Planning to PLN_ZONES.
Run the Create Trees for Customer Dimension program when you set or change the profile option value for Demand Management to correctly associate the customer site with the desired zone.
You don’t need to assign the new zone type to a zone if the zone is only parent of a customer site. If you don’t set this profile option, then the existing behavior will continue, that is, the parent zone with the maximum zone_id is selected for cases where multiple zones are parents of a common customer site or location.
Supply Planning looks at the profile Zone Type for Planning to roll up sales orders to the zones associated with the profile value when consuming forecasts at zone level.
External Global Forecast
You can also upload a global forecast from external sources. You can upload the global forecast at the following levels:
- Item
- Customer
- Customer Site
- Demand Class
- Zone
The FBDI file for external forecast (ScpExternalForecastImportTemplate.xlsm) has been enhanced to include the following new columns:
- Forecast Type
- Zone
- Zone Type
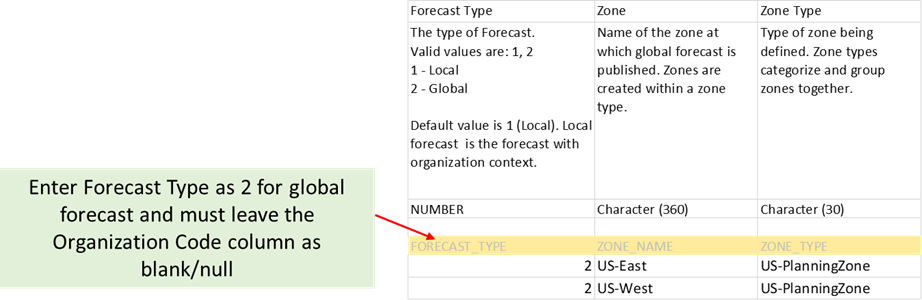
New Columns for Global Forecast in FBDI file
Valid values for Forecast Type are:
- 1 (Local)
- 2 (Global).
By default, the value of Forecast Type is 1 (local forecast). If the value is null, it is a local forecast.
If you are uploading a forecast for the customer dimension, then provide the data either for Customer, Customer Site, or Zone. For example, if you are uploading the forecast at zone level, then you must not provide the values for customer and customer site, else the record is rejected.
The FBDI file for sourcing (ScpSourcingImportTemplate.xlsm) is enhanced to consider two new assignment types in Assignment Sets. The new assignment types are used only for global forecast distribution and aren’t used for item sourcing in Supply Planning, including for drop ship flows.
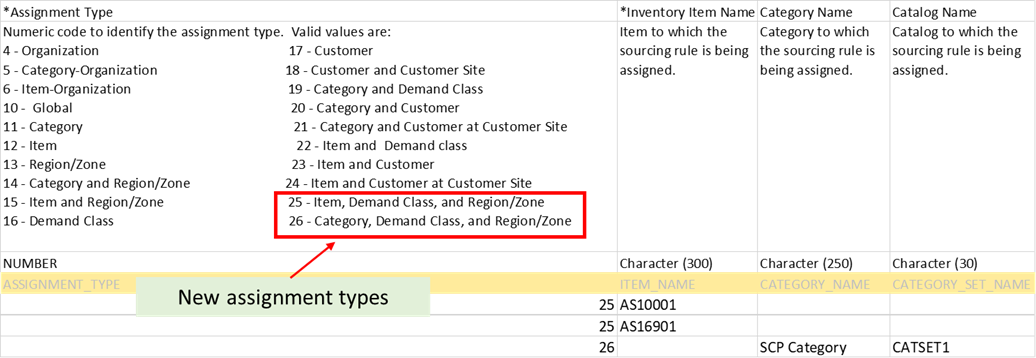
New Assignment Types for Global Forecast Distribution
Two new entries Zone, and Demand class and zone are added to the Ship-to Consumption Level list of values.
Steps to Enable
You don't need to do anything to enable this feature.
Tips And Considerations
- This feature is supported for both unconstrained and constrained supply planning.
- This feature is supported for both Supply Planning and Demand and Supply Planning.
- It isn’t recommended to provide both a local forecast and a global forecast for the same item in same plan. If you do so, then the supply plan will consume both forecasts. If you are modeling a scenario where a portion of the forecast must be met by a specific source, you can remove such a source from the sourcing rule of the forecast distribution.
- The new measures Global Gross Forecast or Global Net Forecast aren’t editable, but you can change the forecast in Demand Management and publish it to Supply Planning.
- In a Demand and Supply plan, you can edit the forecast measures and re-plan. After re-plan, global gross and net forecast measures are updated, and re-distributed to shipping organizations.
- The Supply Planning calendar is used to bucket the global forecast in telescoping buckets.
- In this update, it is assumed that the primary unit of measure (UOM) of an end item (where forecast is generated) is same across all planned organizations. This is also true for other item attributes such as rounding control.
- Demand time fence is applied after the forecast distribution based on the item attribute in the distributed organization.
- Global forecasts with netting attributes aren’t part of this release.
Here's the demo of these capabilities:
Access Requirements
Users who are assigned a configured job role that contains these privileges can access this feature:
- Edit Plans (MSC_EDIT_PLANS_PRIV)
- Run Plan with Snapshot (MSC_RUN_PLAN_WITH_SNAPSHOT_PRIV)
- Monitor Supply Planning Work Area (MSC_MONITOR_SUPPLY_PLANNING_WORK_AREA_PRIV)
These privileges were available prior to this update.