Sales and Service Catalogs
The building blocks of sales and service catalogs are the same. Both use product groups and products and you create them using the same UIs and import processes. You create a root product group and build your catalog underneath. Salespeople use the catalog to enter product interest in opportunities and leads. Service agents use the catalog for entering products into service requests.
There are two differences between sales and service catalogs:
-
How product groups are used.
In sales, you can forecast by product groups and use product groups for assigning opportunities. In service, you can use product groups to channel service requests to the right work queue for resolution.
-
Different product options determine if the product shows up for sales or for service.
Products must have the Eligible to Sell option selected for them to appear in the sales catalog and the Eligible for Service option selected for them to appear in the service catalog.
You can share products and product groups between the two catalogs and you can even create one catalog for both sales and service. If you do opt for a single catalog or even reuse the same product groups for the two catalogs, you must keep in mind that sales may discontinue selling some products that you may still need to service. Or sales may create product groups specific to promotions or seasonal sales.
Products in the Sales and Fusion Service Catalogs
While you can create sales and service catalogs with product groups only, you must create products to take advantage of advanced sales features such as price books. You must also use products to enable integrations with other Oracle cloud services, including Oracle Configure, Price, and Quote (CPQ) Cloud. You can also use Application Composer to add fields and perform other modifications to products, a feature not available on product groups.
Products you create are also stored in the Oracle Fusion Product Model, which serves as the master item repository for all front-office cloud services. So, the product you create can be priced and quoted in Oracle CPQ Cloud and serviced in Sales and Fusion Service.
The Oracle Fusion Product Model, which is included with the different cloud services, provides basic functionality for use in the front-office cloud services. If you're implementing supply chain cloud services or ERP cloud services together with your sales application, then you must license the Oracle Product Hub Cloud Service and set up your items using the UIs and import features of Oracle Product Hub Cloud. You can't create products in your sales application with enough detail that would make them suitable for back-office supply chain applications. Sales applications don't need to track the physical locations of the items you're selling or shipping, for example, so all products you create in the sales application are created at the Item Master Organization level in the Oracle Fusion Product Model. Only the Oracle Product Hub Cloud includes the ability to manage item classes. All products created in the sales application are created at the default item class and use the Production design phase.
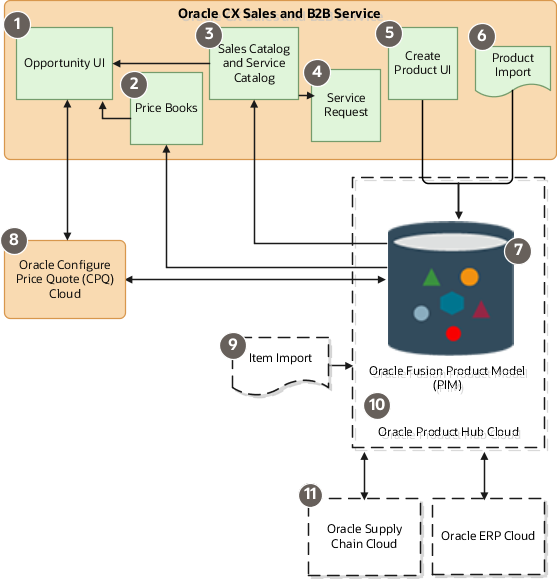
The following diagram outlines the role products play in Sales, Fusion Service and related cloud services:
-
In Oracle CX Sales and Fusion Service, you can create the products for your sales and service catalogs either individually in the UI (indicated by callout 5) or you import products from a file (callout 6).
-
Product records are created both in Sales and Fusion Service and in the Oracle Fusion Product Model (callout 7).
-
You expose the products in the sales or service catalogs (callout 3) by associating them with product groups.
-
Salespeople can browse or search the sales catalog from the Opportunity UI (callout 1) and select the products the customer is interested in buying. Only products with the Eligible to Sell option selected appear in the sales catalog.
-
Service agents enter products from the Service Request UI (callout 4). Only products with the Eligible for Service option selected appear in the service catalog.
-
You can price the products using price books (callout 2), or create quotes for them in Oracle Configure, Price, and Quote Cloud (callout 8). Price books and CPQ Cloud require additional integration, so aren't covered in this guide. (Although price books are a sales feature, you must integrate them with opportunities using Groovy scripting.)
-
The Oracle Fusion Product Model (callout 7) forms the foundation of the Oracle Product Hub Cloud (callout 10), a powerful product management application designed for supply chain, order management, and inventory tasks, which must be licensed separately. Because the sales application uses less than a dozen of the hundreds of the item attributes that can be captured in Oracle Product Hub, you can't use the sales UIs or product import if you're implementing Oracle Product Hub Cloud. To create products in Oracle Product Hub Cloud that can be used with Oracle Supply Chain Cloud or Oracle ERP Cloud (callout 11), you must use the Oracle Product Cloud Hub UI and item import (callout 9).