1Oracle WMS Cloud Alternate Authentication Mechanisms
Oracle WMS Cloud Alternate Authentication Mechanisms
Oracle® Fusion Cloud Warehouse Management includes a built-in authentication mechanism using with users can be setup with their own user-id and passwords to access the Oracle Warehouse Management (WMS) Web UI, WMS Cloud Mobile App and Mobile RF applications. In addition, it also supports authenticating users against external identity providers (IDP). It supports multiple authentication mechanisms:
- SAML2 Single Sign On, or SSO in short
- A web-based authentication standard that can be used only to login to the WMS Web UI
- OAuth2
- Another authentication standard that can be used for the WMS Web UI, the WMS Cloud Mobile App and Mobile RF.
Identity Providers
Oracle Identity Cloud Service (IDCS) and Azure AD/ADFS are Identity Providers that have been tested with Oracle WMS Cloud. Other providers that support these standards may also work. Customers can request their environments to be configured to use SSO and/or Oauth2 by raising a Service Request (SR). Oracle will provide a template via the SR for customers to fill out certain technical pieces of information which will be used by our Cloud operations team to configure the customers environment.
WMS Configuration for Alternate Authentication
Once the WMS Cloud environment has been setup for SSO or OAuth2 authentication, usernames in WMS Cloud have to be associated with a corresponding username in the external Identity Provider. This is the “Alternate username” field in WMS Cloud and must be of the format:
<username>@<domain>
WMS Cloud users can be created/configured from the Users screen or by uploading a User Excel file from the Input Interface screen.
It is possible to have some WMS users be locally authenticated (add note about temp users) and others externally authenticated. It’s possible to have both SSO and OAuth2 backends configured for one customer.
Built-in Authentication
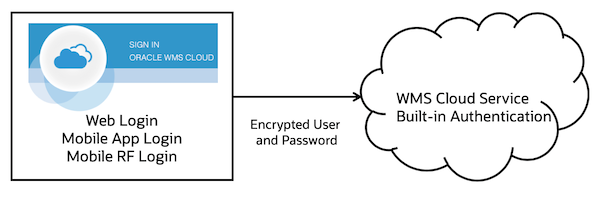
The user types in the username and password on the WMS Cloud login page, whether the Web, Mobile App, or Mobile RF device. The encrypted credentials are validated against the WMS Cloud Service.
OAuth2 Authentication

The user types in the username and password on the WMS Cloud login page, whether the Web, Mobile App or Mobile RF device. The encrypted credentials are sent to the WMS Cloud Service. If the username has an associated “alternate username”, WMS Cloud will delegate the authentication to the external identity provider and validate against that service. If the authentication succeeds, the user is logged into the WMS.
OAuth2 backends that have been validated with WMS Cloud are Oracle IDCS and Azure AD.
Technical Configuration for OAuth2
https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6749#section-4.3
When submitting an SR to My Oracle Support to setup OAuth2 authentication, you need to provide the data per the table below. The technical details are explained in the reference links below.
Oracle IDCS Reference
Azure AD Reference
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/active-directory/develop/v2-oauth-ropc
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Identity Provider Name | Name of IDP such as Azure AD or Oracle IDCS. |
| Endpoint URL | Used by the WMS to authenticate |
| Client ID | Needed for Oracle IDCS and Azure AD |
| Client Secret | Needed for Oracle IDCS and Azure AD |
| Resource/Scope | Needed for Oracle IDCS and Azure AD |
| X-USER-IDENTITY-DOMAIN-NAME | Needed for Oracle IDCS |
| Domain name | Used to link WMS username with the OAuth2 username, using "Alternate username" For example if the username is "jdoe"@somedomain.com, then the domain name is somedomain.com.
NOTE: Customers need to provide ALL domains that they need for WMS. We don’t support generic consumer domains (for example: @yahoo.com @gmail.com) |