Debugger Engine Configuration for Database Connections
This topic provides an overview of debugger configuration options available for connected databases.
For a database connection, you can configure the general Debugger settings to debug PL/SQL and Java programs. To configure the Debugger settings for a database connection, from the Main menu of Oracle Database Navigator tool, select DB Navigator > Settings > Connections tab > Debugger tab for the specific database connection.
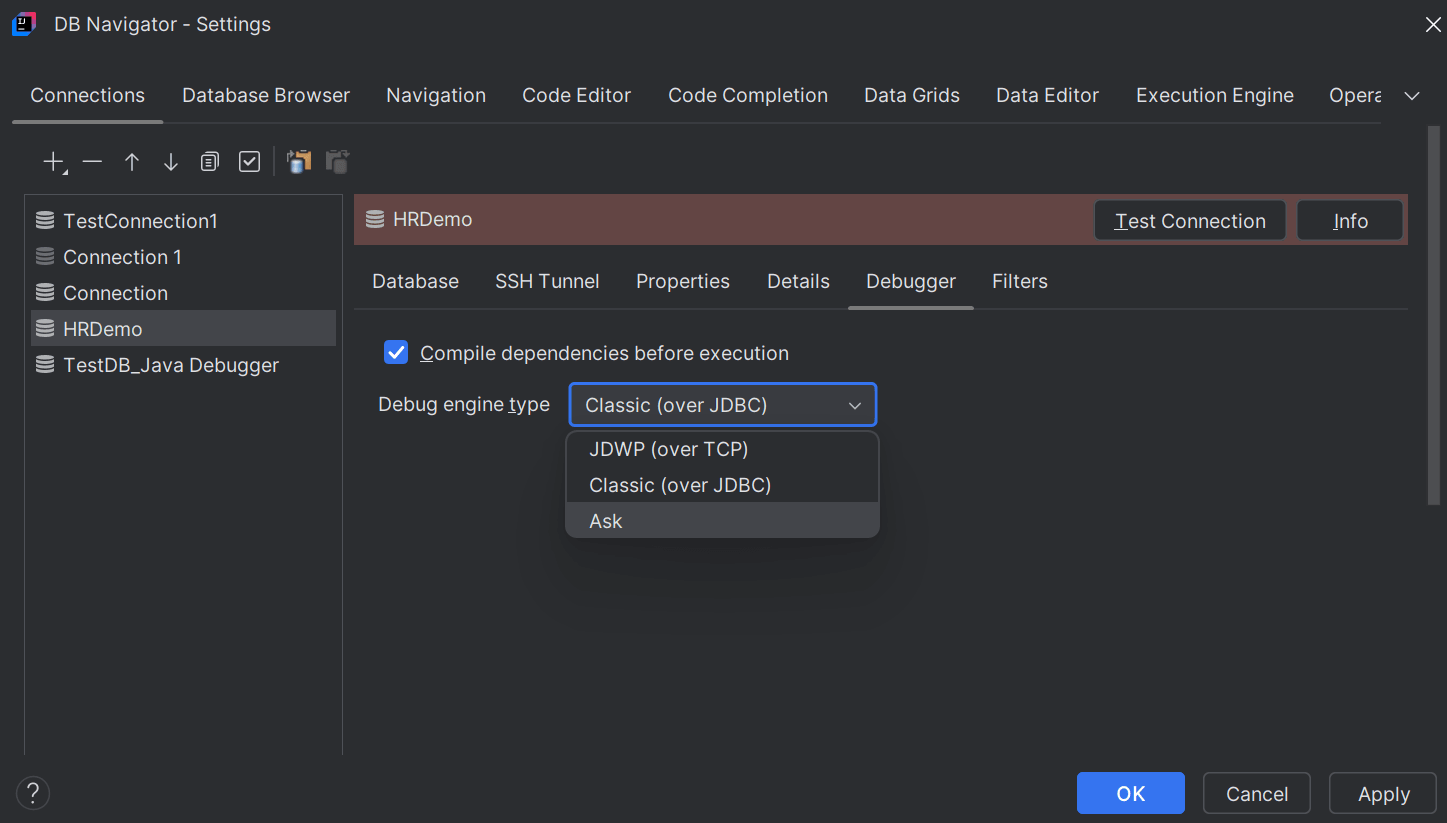
- Select the check box to enable compiling dependencies (such as libraries and object dependencies, backward, module and cyclic dependencies) before executing the Java program.
- Debug engine type:
- Ask - Setting this option presents a confirmation dialog box every time you run the debugger for a program to select the debug engine that will be used for debugging. Options include Classic (over JDBC) and JDWP (over TCP).
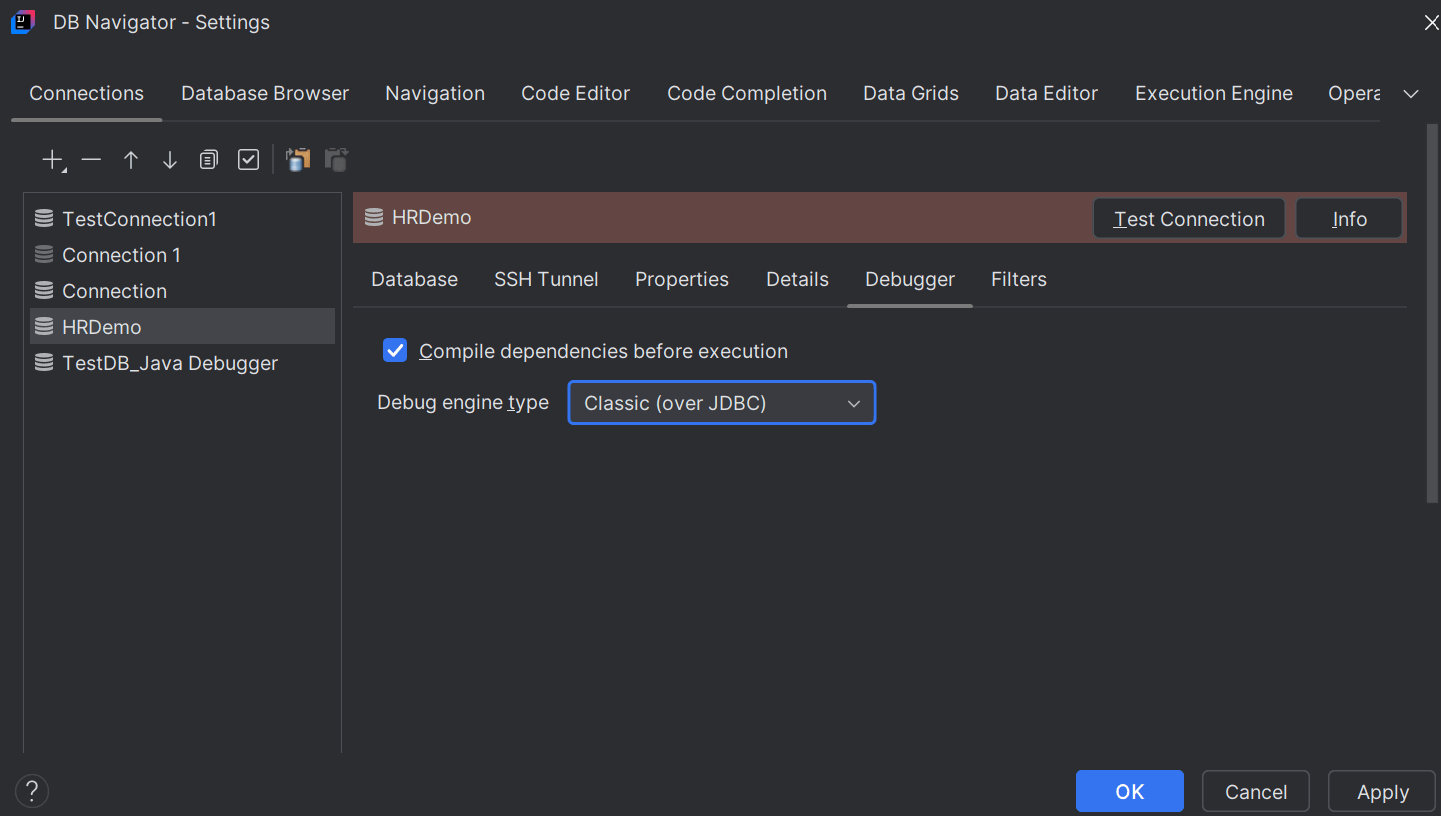
- Classic (over JDBC) - configuring this option debugs the Java program utilizing Oracle's JDBC package in the background. This debug method can be used for cloud-based databases including Oracle Autonomous AI Database.
- JDWP (over TCP) - configuring this option debugs the Java program/Java stored procedure using the JDWP agent that connects to a Java Debugger (JDB) listener (setup in the IDE platform as JVM remote debugging). This debug method can be used for remote databases or OCI DB System.
Note:
The JDWP and JDBC engines use the OracleSYS.DBMS_DEBUG_JDWPandSYS.DBMS_DEBUGpackages to debug PL/SQL and Java code, respectively. - Ask - Setting this option presents a confirmation dialog box every time you run the debugger for a program to select the debug engine that will be used for debugging. Options include Classic (over JDBC) and JDWP (over TCP).
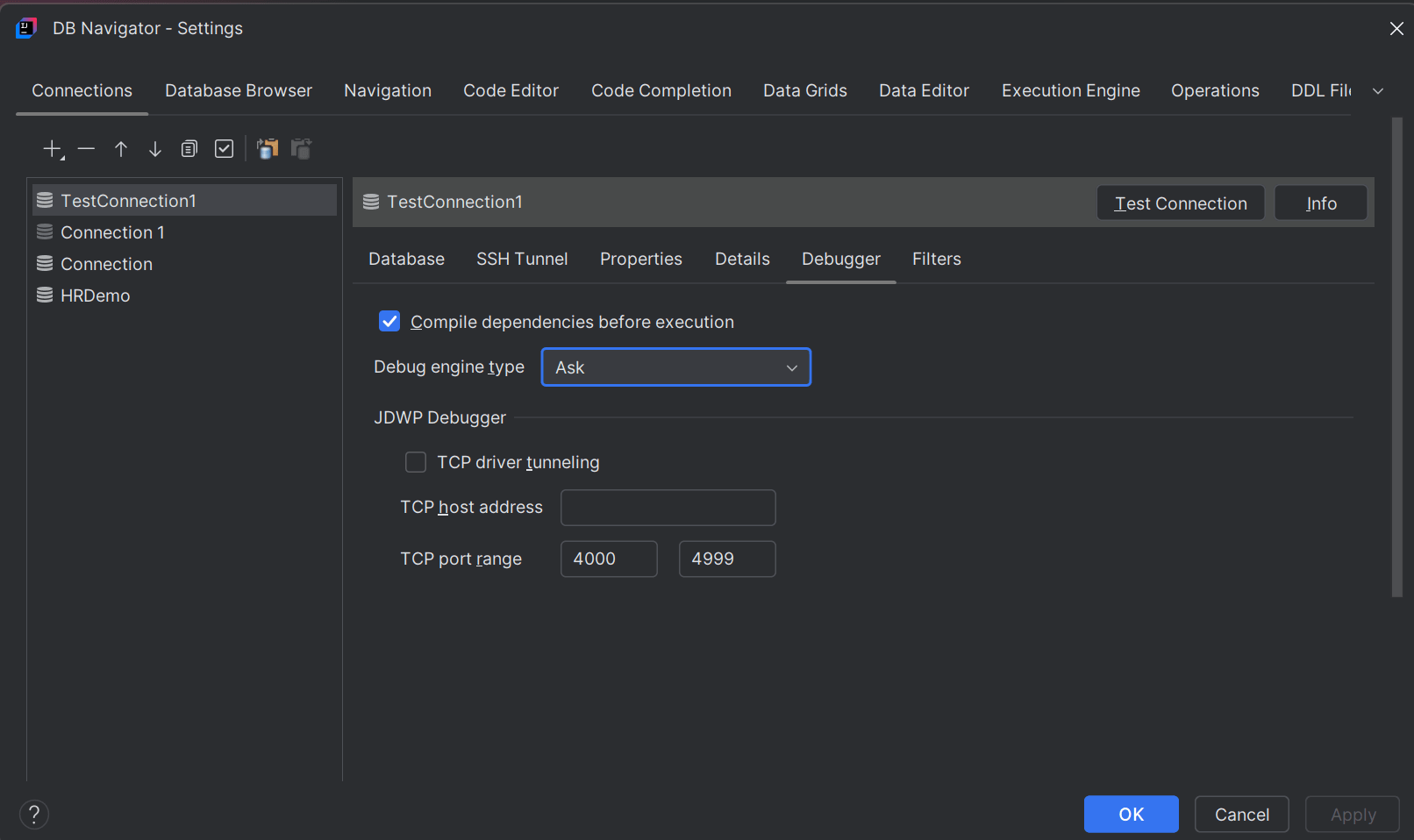
- If you configure JDWP Debugger as the default debug method, you further have to set up the following options:
- JDWP Tunnel Type - Options include 'None', 'TCP Driver Tunnel' and 'SSH Reverse Tunnel'.
- Selecting None requires you to provide the standard TCP host/port requirement to establish a connection between the database and the Java Debugger (JDB) listener.

- Selecting TCP Driver Tunnel enables TCP tunneling to access remote debugging session services offered by the IDE platform.

- Selecting SSH Reverse Tunnel requires you to provide additional Host and Port details of the JDWP Reverse Tunnel along with the authentication information (username/password or config file with Open SSH key value pair).
An SSH Reverse Tunnel is used to project the JDB listener to a port on the database. By doing this, the database is able to connect to the JDB listener as if it were running locally, thus enabling debugging. This method is specifically useful to overcome the restrictive security policies of DB System (OCI Based DB Service) where the IDE is unable to open a JDB listener on any port of the DB System.

By default, OCI DB System allows reverse ssh-tunnel to open only on port 22. These restrictions can be removed by adding appropriate ingress/egress rules and additionally changing the security policy of the DB System.
- Selecting None requires you to provide the standard TCP host/port requirement to establish a connection between the database and the Java Debugger (JDB) listener.
- JDWP Tunnel Type - Options include 'None', 'TCP Driver Tunnel' and 'SSH Reverse Tunnel'.
Parent topic: Debugger Engine Types