Debugging Methods
This topic describes the procedure to debug PL/SQL methods in Oracle® Database Navigator.
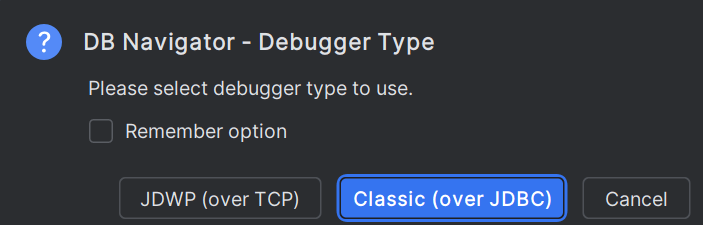
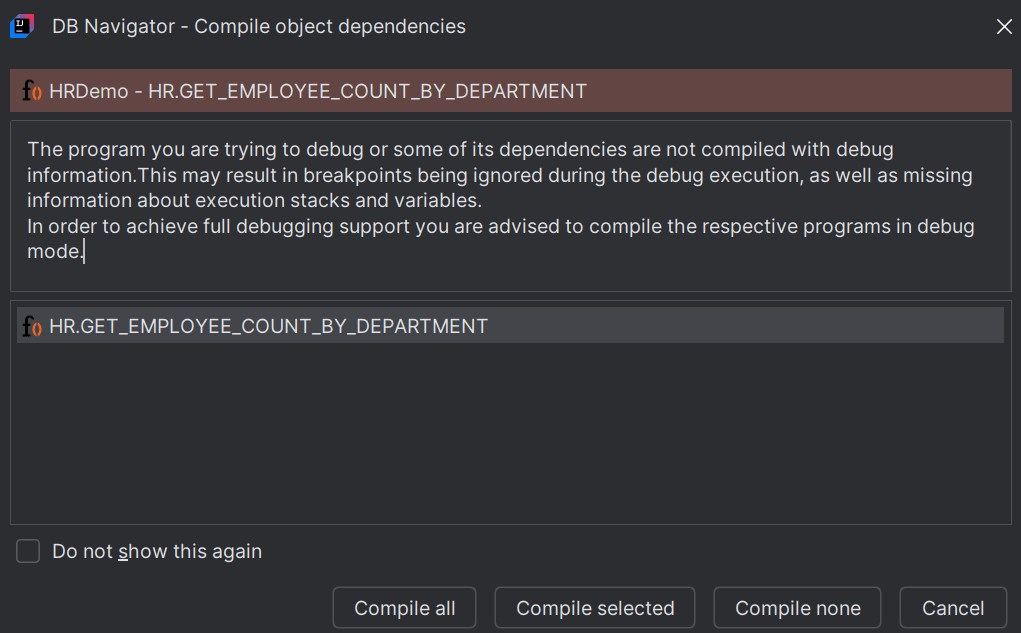
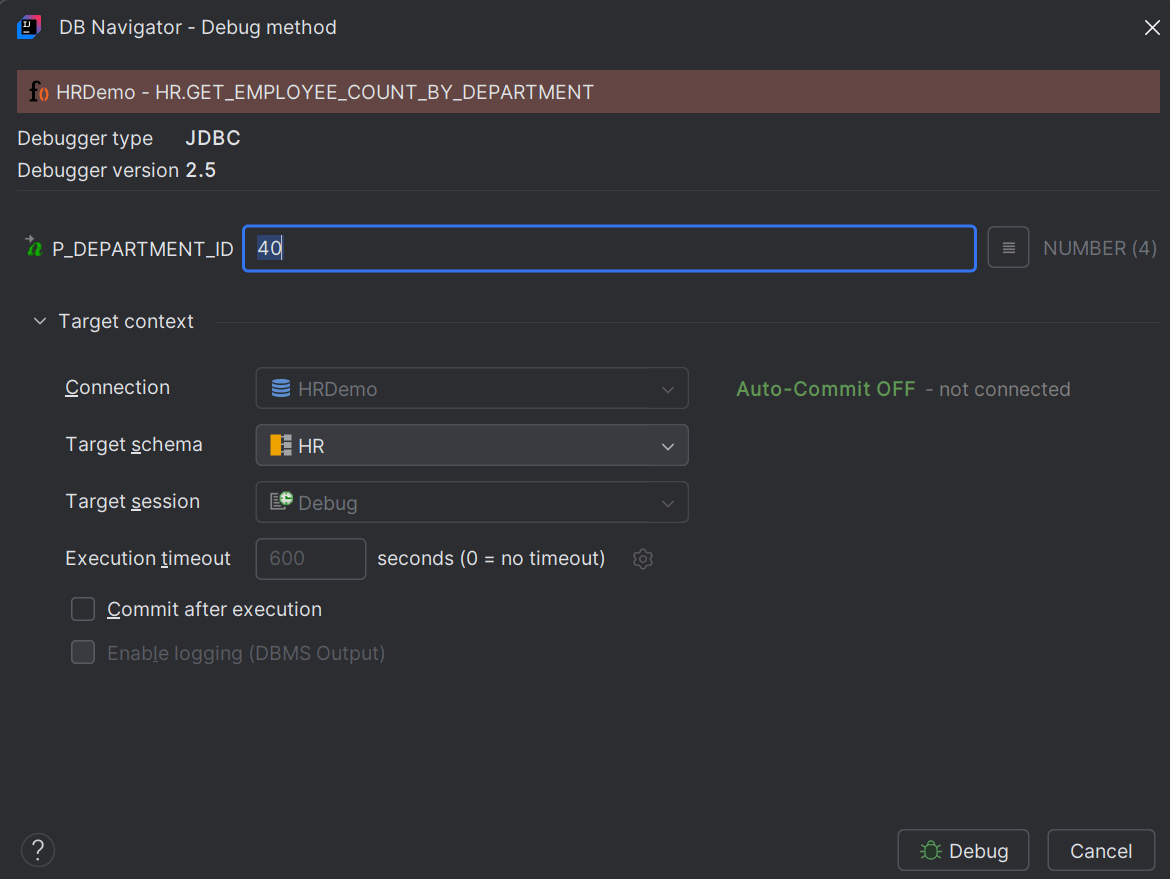
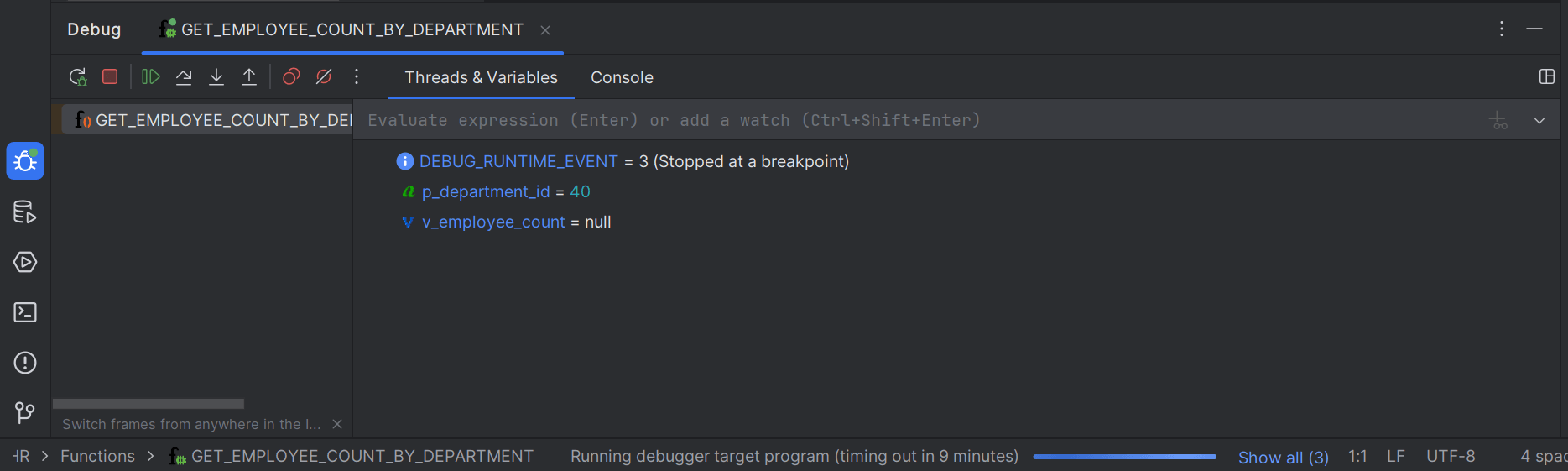
Debugging a PL/SQL program through Oracle® Database Navigator plug-in uses the execution engine and attaches the debugger agent to target process. If the run configuration in your IDE supports debugging and the method is compiled in debug mode, a green bug icon displays next to the object in the DB Browser window, indicating that you can run the program in debug mode.
Follow these steps to debug a PL/SQL method:
Parent topic: Debugging Engine