14.8 CREATE LIBRARY Statement
The CREATE LIBRARY statement creates a library, which is a schema object associated with an operating-system shared library.
Note:
The CREATE LIBRARY statement is valid only on platforms that support shared libraries and dynamic linking.
For instructions for creating an operating-system shared library, or DLL, see Oracle Database Development Guide.
You can use the name of the library schema object in the call_spec of CREATE FUNCTION or CREATE PROCEDURE statements, or when declaring a function or procedure in a package or type, so that SQL and PL/SQL can invoke third-generation-language (3GL) functions and procedures.
Topics
Prerequisites
To create a library in your schema, you must have the CREATE LIBRARY system privilege. To create a library in another user's schema, you must have the CREATE ANY LIBRARY system privilege.
To create a library that is associated with a DLL in a directory object, you must have the EXECUTE object privilege on the directory object.
To create a library that is associated with a credential name, you must have the EXECUTE object privilege on the credential name.
To use the library in the call_spec of a CREATE FUNCTION statement, or when declaring a function in a package or type, you must have the EXECUTE object privilege on the library and the CREATE FUNCTION system privilege.
To use the library in the call_spec of a CREATE PROCEDURE statement, or when declaring a procedure in a package or type, you must have the EXECUTE object privilege on the library and the CREATE PROCEDURE system privilege.
To execute a procedure or function defined with the call_spec (including a procedure or function defined within a package or type), you must have the EXECUTE object privilege on the procedure or function (but you do not need the EXECUTE object privilege on the library).
Syntax
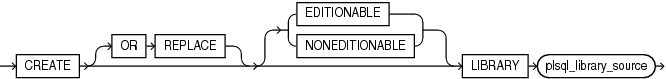
create_library ::=
plsql_library_source ::=
Semantics
create_library
OR REPLACE
Re-creates the library if it exists, and recompiles it.
Users who were granted privileges on the library before it was redefined can still access it without being regranted the privileges.
[ EDITIONABLE | NONEDITIONABLE ]
Specifies whether the library is an editioned or noneditioned object if editioning is enabled for the schema object type LIBRARY in schema. Default: EDITIONABLE. For information about editioned and noneditioned objects, see Oracle Database Development Guide.
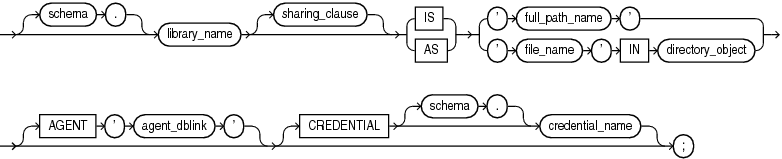
plsql_library_source
schema
Name of the schema containing the library. Default: your schema.
library_name
Name that represents this library when a user declares a function or procedure with a call_spec.
'full_path_name'
String literal enclosed in single quotation marks, whose value your operating system recognizes as the full path name of a shared library.
The full_path_name is not interpreted during execution of the CREATE LIBRARY statement. The existence of the shared library is checked when someone invokes one of its subprograms.
'file_name' IN directory_object
The file_name is a string literal enclosed in single quotation marks, whose value is the name of a dynamic link library (DLL) in directory_object. The string literal cannot exceed 2,000 bytes and cannot contain path delimiters. The compiler ignores file_name, but at run time, file_name is checked for path delimiters.
directory_object
The directory_object is a directory object, created with the CREATE DIRECTORY statement (described in Oracle Database SQL Language Reference). If directory_object does not exist or you do not have the EXECUTE object privilege on directory_object, then the library is created with errors. If directory_object is subsequently created, then the library becomes invalid. Other reasons that the library can become invalid are:
-
directory_objectis dropped. -
directory_objectbecomes invalid. -
Your
EXECUTEobject privilege ondirectory_objectis revoked.
AGENT 'agent_dblink'
Causes external procedures to run from a database link other than the server. Oracle Database uses the database link that agent_dblink specifies to run external procedures. If you omit this clause, then the default agent on the server (extproc) runs external procedures.
CREDENTIAL [schema.]credential_name
Specifies the credentials of the operating system user that the extproc agent impersonates when running an external subprogram that specifies the library. Default: Owner of the Oracle Database installation.
If credential_name does not exist or you do not have the EXECUTE object privilege on credential_name, then the library is created with errors. If credential_name is subsequently created, then the library becomes invalid. Other reasons that the library can become invalid are:
-
credential_nameis dropped. -
credential_namebecomes invalid. -
Your
EXECUTEobject privilege oncredential_nameis revoked.
For information about using credentials, see Oracle Database Security Guide.
Examples
Example 14-17 Creating a Library
The following statement creates library ext_lib, using a directory object:
CREATE LIBRARY ext_lib AS 'ddl_1' IN ddl_dir; /
The following statement re-creates library ext_lib, using a directory object and a credential:
CREATE OR REPLACE LIBRARY ext_lib AS 'ddl_1' IN ddl_dir CREDENTIAL ddl_cred; /
The following statement creates library ext_lib, using an explicit path:
CREATE LIBRARY ext_lib AS '/OR/lib/ext_lib.so'; /
The following statement re-creates library ext_lib, using an explicit path:
CREATE OR REPLACE LIBRARY ext_lib IS '/OR/newlib/ext_lib.so'; /
Example 14-18 Specifying an External Procedure Agent
The following example creates a library app_lib (using an explicit path) and specifies that external procedures run from the public database sales.hq.example.com:
CREATE LIBRARY app_lib as '${ORACLE_HOME}/lib/app_lib.so'
AGENT 'sales.hq.example.com';
/See Also:
Oracle Database SQL Language Reference for information about creating database links
Related Topics