19 Managing Oracle Flex ASM
Oracle Flex ASM enables Oracle ASM instances to run on a separate physical server from the database servers.
This section discusses Oracle Flex ASM in the following topics:
See Also:
-
Oracle Clusterware Administration and Deployment Guide for information about Oracle Flex Cluster support
-
Articles at My Oracle Support (
https://support.oracle.com) for information about configuring Oracle Flex ASM with Oracle ASM and Oracle ACFS -
ASMCMD Client Cluster Management Commands for information about ASMCMD commands to manage client clusters
-
Oracle Grid Infrastructure Installation Guide for information about installing and upgrading Oracle Grid Infrastructure
Overview of Oracle Flex ASM
Oracle Flex ASM enables an Oracle ASM instance to run on a separate physical server from the database servers. With this deployment, larger clusters of Oracle ASM instances can support more database clients while reducing the Oracle ASM footprint for the overall system.
When using Oracle Flex ASM, Oracle ASM clients are configured with direct access to storage.
With Oracle Flex ASM, you can consolidate all the storage requirements into a single set of disk groups. All these disk groups are mounted by and managed by a small set of Oracle ASM instances running in a single cluster. You can specify the number of Oracle ASM instances with a cardinality setting. The default is three instances.
A cluster is a set of nodes that provide group membership services. Each cluster has a name that is globally unique. Every cluster has one or more Hub nodes. The Hub nodes have access to Oracle ASM disks. Every cluster has at least one private network and one public network. If the cluster is going to use Oracle ASM for storage, it has at least one Oracle ASM network. A single network can be used as both a private and an Oracle ASM network. For security reasons, an Oracle ASM network should never be public. There can be only one Oracle Flex ASM configuration running within a cluster.
An Oracle ASM instance can operate in several configurations in Oracle Flex ASM:
-
Local Oracle ASM clients with direct access to Oracle ASM disks (Standard Oracle ASM cluster)
-
Oracle Flex ASM clients with direct access to Oracle ASM disks
-
Oracle ACFS access through the Oracle ASM proxy instance
-
Network-based connectivity to Oracle ASM disk groups with Oracle IOServer (IOS)
These configurations are illustrated in Figure 19-1, Figure 19-2, and Figure 19-3.
Local Oracle ASM clients with direct access to Oracle ASM disks (Standard Oracle ASM cluster)
With this mode, illustrated as Hub Node A in Figure 19-1, Oracle ASM continues to support existing standard architecture in which database clients are running with an Oracle ASM instance on the same host computer. The local client architecture is only supported on a Hub node.
Figure 19-1 Oracle Flex ASM Client Configurations
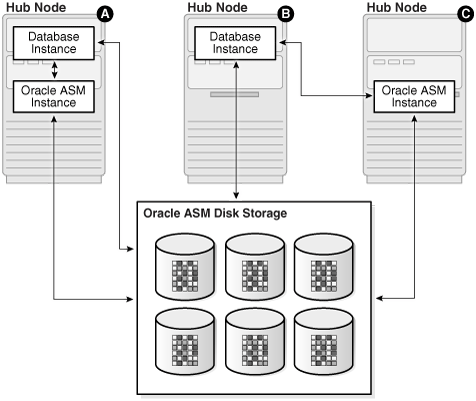
Description of "Figure 19-1 Oracle Flex ASM Client Configurations"
In this configuration, the database instances are on the same Hub node as the Oracle ASM instance and are referred to as local Oracle ASM client instances. Oracle ASM metadata moves between Oracle ASM and the database instances. This client has direct I/O access to Oracle ASM disks.
Local mode does not use Oracle Flex ASM, so clusters configured with local Oracle ASM do not require an Oracle ASM network, nor do they contain other Oracle Flex ASM services.
Oracle Flex ASM clients with direct access to Oracle ASM disks
With this mode, illustrated as Hub Node B in Figure 19-1, database clients that are running on Hub nodes of the Oracle ASM cluster access Oracle ASM remotely for metadata, but perform block I/O operations directly to Oracle ASM disks. The hosts running the Oracle ASM server and the remote database client must both be Hub nodes. A Hub node is a node in an Oracle ASM cluster that is tightly connected with other servers and has direct access to a shared disk.
In this configuration, the database instances are on different host computers than the nearby Oracle ASM instance, as shown on Hub Node C in Figure 19-1, and are referred to as Oracle ASM client instances.
The databases are in the same Oracle ASM cluster as the Oracle ASM instance and the database instances are located on a Hub node. Oracle ASM metadata moves between Oracle ASM and the database instance. This client has direct I/O access to Oracle ASM disks.
Depending on the distribution of database instances and Oracle ASM instances, a database client may access Oracle ASM locally on the same node or remotely over the Oracle ASM network. This mode of operation is used by database clients on Hub nodes in the Oracle ASM cluster. Direct access mode is also the only Oracle Flex ASM configuration supported by Oracle ASM cluster file system.
Oracle ACFS access through the Oracle ASM proxy instance
An Oracle ASM proxy instance is an Oracle instance running on a Hub node with a direct Oracle ASM client. An Oracle ASM proxy instance provides support for Oracle Automatic Storage Management Cluster File System (Oracle ACFS) and Oracle ASM Dynamic Volume Manager (Oracle ADVM).
Figure 19-2 shows the configuration of Oracle ACFS and Oracle ADVM with an Oracle ASM Proxy server in Oracle Flex ASM.
Figure 19-2 Oracle ACFS and Oracle ADVM in Oracle Flex ASM Configuration
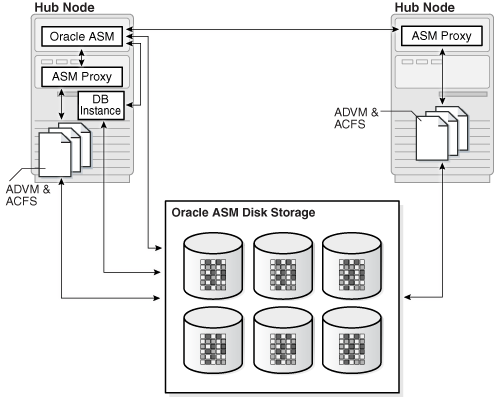
Description of "Figure 19-2 Oracle ACFS and Oracle ADVM in Oracle Flex ASM Configuration"
The INSTANCE_TYPE initialization parameter is set to ASMPROXY for Oracle ASM proxy instances.
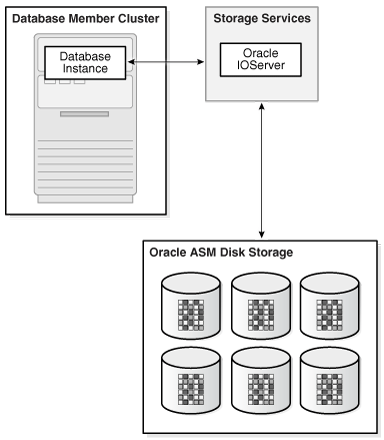
Network-based connectivity to Oracle ASM disk groups with Oracle IOServer (IOS)
An Oracle IOServer instance provides Oracle ASM file access for Oracle Database instances on nodes of Oracle member clusters that do not have connectivity to Oracle ASM managed disks.
Figure 19-3 shows the relationship of Oracle IOServer and an Oracle Database in a member cluster.
In addition, IOS enables you to configure client clusters on such nodes. On the storage cluster, an IOServer instance opens up network ports to which clients send their IO. The IOServer instance receives data packets from the client and performs the appropriate IO to Oracle ASM disks similar to any other database client. On the client side, databases can use dNFS to communicate with an IOServer instance. However, there is no client side configuration so you are not required to provide a server IP address or any additional configuration information. On nodes and clusters that are configured to access Oracle ASM files through IOServer, the discovery of the Oracle IOS instance occurs automatically.
The IOS instance contains the following processes:
-
Network processes: These processes open up network ports and receive dNFS requests from the client side. These requests are then placed in a queue for IO and Identifier processes to pick up and process. Network processes also pick up responses from those other types of processes and send the response back to the client.
-
Identifier processes: These processes pick up dNFS requests to create, delete, identify, un-identify, and resize Oracle ASM files.
-
IO processes: These processes perform the actual IO on files that are identified by the local IOS instance.
The ASM_IO_PROCESSES initialization parameter specifies the number of IO worker processes to be started in an Oracle IO server instance. For information about the ASM_IO_PROCESSES initialization parameter, refer to ASM_IO_PROCESSES.
About Setting Up Oracle Flex ASM
To install an Oracle Flex ASM deployment, categorize the networks and choose the list of networks for use as Oracle ASM networks.
If you choose Oracle Flex ASM during a new installation, OUI requires you to choose the Oracle ASM networks.
The Oracle ASM listener resource is automatically created for each Oracle ASM network and then started on all nodes.
See Also:
Oracle Grid Infrastructure Installation Guide for information about Oracle Clusterware installation
Administering Oracle Flex ASM
Oracle Flex ASM is managed by ASMCA, CRSCTL, SQL*Plus, and SRVCTL. The INSTANCE_TYPE initialization parameter specifies the type of instance.
The INSTANCE_TYPE initialization parameter has an additional value ASMPROXY, in addition to ASM and RDBMS, to identify Oracle ASM proxy instances. An Oracle ASM proxy instance has its parameter set to ASMPROXY.
You can use the ASMCMD showclustermode command to determine whether Oracle Flex ASM is enabled. For example:
$ asmcmd showclustermode ASM cluster : Flex mode enabled
SRVCTL is extended to enable an administrator to create or change attributes of Oracle Clusterware resources. You can use SRVCTL to determine the status of the instances in an Oracle Flex ASM configuration. For example:
$ srvctl status asm -detail ASM is running on mynoden02,mynoden01 ASM is enabled.
You can also use SRVCTL to determine whether Oracle Flex ASM is enabled. If enabled, then srvctl config asm displays the number of Oracle ASM instances that has been specified for use with the Oracle Flex ASM configuration. For example:
$ srvctl config asm ASM instance count: 3
You can modify the Oracle ASM instance count, or cardinality, with the SRVCTL modify asm command. For example:
$ srvctl modify asm -count 4 $ srvctl modify asm -count ALL
You can view Oracle Flex ASM connections with SQL*Plus and ASMCMD commands. Fore example:
SQL> SELECT instance_name, db_name, status FROM V$ASM_CLIENT; INSTANCE_NAME DB_NAME STATUS --------------- -------- ------------ +ASM1 +ASM CONNECTED orcl1 orcl CONNECTED orcl2 orcl CONNECTED $ asmcmd lsct data DB_Name Status Software_Version Compatible_version Instance_Name Disk_Group +ASM CONNECTED 12.1.0.0.2 12.1.0.0.2 +ASM DATA orcl CONNECTED 12.1.0.0.2 12.0.0.0.0 orcl1 DATA orcl CONNECTED 12.1.0.0.2 12.0.0.0.0 orcl2 DATA
Clients are automatically relocated to another instance if an Oracle ASM instance fails. If necessary, clients can be manually relocated.
The SRVCTL UPDATE INSTANCE and SRVCTL UPDATE IOSERVER commands can change the Oracle ASM instance for a database, or the Oracle IOServer instance for a database, or the Oracle ASM instance for an Oracle IOServer. For example:
$ srvctl update instance -db my_orcl_db -instance my_instance_1 -targetinstance my_asm_instance_1 $ srvctl update ioserver -instance my_instance_2 -targetinstance my_asm_instance_2
You can run the SRVCTL STATUS commands with the -detail option to display which Oracle ASM instance or Oracle IOserver instance each client is connected to.
You can also use the ALTER SYSTEM RELOCATE CLIENT command to relocate a client. For example:
SQL> ALTER SYSTEM RELOCATE CLIENT 'client-id';In the previous SQL statement, client-id is of the form instance_name:db_name. The INSTANCE_NAME and DB_NAME columns are contained in the V$ASM_CLIENT view. You must connect as SYSASM to the Oracle ASM instance to run the SQL statement. When you issue this statement, the connection to the client is terminated and the client fails over to the least loaded instance. If the client is currently connected to the least loaded instance, then the connection to the client is terminated and the client fails over to that same instance.
Every database user must have a wallet with credentials to connect to Oracle ASM. CRSCTL commands can be used by the database user to manage this wallet. All Oracle ASM user names and passwords are system generated.
There are no new initialization parameters specifically for instances in an Oracle Flex ASM configuration; however, the settings of existing parameters should be reviewed and possibly adjusted for the Oracle Flex ASM environment. Refer to "Recommended Settings for Oracle ASM Initialization Parameters".
See Also:
-
Oracle Database Reference for more information about the
INSTANCE_TYPEinitialization parameter -
Oracle Database SQL Language Reference for information about the
ALTERSYSTEMstatement -
Oracle Clusterware Administration and Deployment Guide for information about CRSCTL commands
-
Oracle Real Application Clusters Administration and Deployment Guide for information about SRVCTL commands
-
Oracle Grid Infrastructure Installation Guide for information about installing Oracle Clusterware