13.33 FOR LOOP Statement
With each iteration of the FOR LOOP statement, its statements run, its index is either incremented or decremented, and control returns to the top of the loop. The FOR LOOP statement ends when its index reaches a specified value, or when a statement inside the loop transfers control outside the loop or raises an exception.
Topics
Syntax
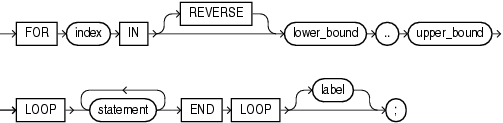
for_loop_statement ::=
Semantics
for_loop_statement
index
Name for the implicitly declared integer variable that is local to the FOR LOOP statement. Statements outside the loop cannot reference index. Statements inside the loop can reference index, but cannot change its value. After the FOR LOOP statement runs, index is undefined.
See Also:
[ REVERSE ] lower_bound .. upper_bound
lower_bound and upper_bound must evaluate to numbers (see "Lower Bound and Upper Bound"). PL/SQL evaluates lower_bound and upper_bound once, when the FOR LOOP statement is entered, and stores them as temporary PLS_INTEGER values, rounding them to the nearest integer if necessary.
If lower_bound equals upper_bound, the statements run only once.
If lower_bound does not equal upper_bound when the FOR LOOP statement begins to run, then:
-
If
REVERSEis omitted:If
lower_boundis greater thanupper_bound, thestatementsdo not run, and control transfers to the statement after theFORLOOPstatement.Otherwise,
lower_boundis assigned toindex, thestatementsrun, and control returns to the top of the loop, whereindexis compared toupper_bound. Ifindexis less thanupper_bound,indexis incremented by one, thestatementsrun again, and control returns to the top of the loop. Whenindexis greater thanupper_bound, control transfers to the statement after theFORLOOPstatement. -
If
REVERSEis specified:If
upper_boundis less thanlower_bound, thestatementsdo not run, and control transfers to the statement after theFORLOOPstatement.Otherwise,
upper_boundis assigned toindex, thestatementsrun, and control returns to the top of the loop, whereindexis compared tolower_bound. Ifindexis greater thanlower_bound,indexis decremented by one, thestatementsrun again, and control returns to the top of the loop. Whenindexis less thanlower_bound, control transfers to the statement after theFORLOOPstatement.
label
A label that identifies for_loop_statement (see "statement ::=" and "label"). CONTINUE, EXIT, and GOTO statements can reference this label.
Labels improve readability, especially when LOOP statements are nested, but only if you ensure that the label in the END LOOP statement matches a label at the beginning of the same LOOP statement (the compiler does not check).
Examples
-
Example 4-15, "FOR LOOP Statements"
-
Example 4-16, "Reverse FOR LOOP Statements"
-
Example 4-17, "Simulating STEP Clause in FOR LOOP Statement"
-
Example 4-19, "Outside Statement References FOR LOOP Statement Index"
-
Example 4-20, "FOR LOOP Statement Index with Same Name as Variable"
-
Example 4-21, "FOR LOOP Statement References Variable with Same Name as Index"
-
Example 4-22, "Nested FOR LOOP Statements with Same Index Name"
-
Example 4-23, "FOR LOOP Statement Bounds"
-
Example 4-24, "Specifying FOR LOOP Statement Bounds at Run Time"
Related Topics
In this chapter:
In other chapters: