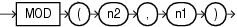MOD
Syntax
Purpose
MOD returns the remainder of n2 divided by n1. Returns n2 if n1 is 0.
This function takes as arguments any numeric data type or any nonnumeric data type that can be implicitly converted to a numeric data type. Oracle determines the argument with the highest numeric precedence, implicitly converts the remaining arguments to that data type, and returns that data type.
See Also:
Table 2-8 for more information on implicit conversion and "Numeric Precedence" for information on numeric precedence
Examples
The following example returns the remainder of 11 divided by 4:
SELECT MOD(11,4) "Modulus"
FROM DUAL;
Modulus
----------
3
This function behaves differently from the classical mathematical modulus function, if the product of n1 and n2 is negative. The classical modulus can be expressed using the MOD function with this formula:
n2 - n1 * FLOOR(n2/n1)
The following table illustrates the difference between the MOD function and the classical modulus:
| n2 | n1 | MOD(n2,n1) | Classical Modulus |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|