3.25 VALIDATE
Purpose
Use the VALIDATE command to check for corrupt blocks and missing files, or to determine whether a backup set can be restored.
If VALIDATE detects a problem during validation, then RMAN displays it and triggers execution of a failure assessment. If a failure is detected, then RMAN logs it into the Automated Diagnostic Repository. You can use LIST FAILURE to view the failures.
Note:
Starting in Oracle Database 19c, the Data Recovery Advisor (DRA) feature is deprecated.
The deprecation of
DRA includes deprecation of the following Oracle Recovery Manager (RMAN) commands:
LIST FAILURE, ADVISE FAILURE, REPAIR
FAILURE, and CHANGE FAILURE. Database administrators
will no longer have access to these commands. There is no replacement feature for
DRA.
Prerequisites
The target database must be mounted or open.
Usage Notes
The options in the VALIDATE command are semantically equivalent to options in the BACKUP VALIDATE command. Unlike BACKUP VALIDATE, however, VALIDATE can check individual backup sets and data blocks.
The VALIDATE command does not skip any blocks during validation. If RMAN does not read a block because of unused block compression, and if the block is corrupt, then RMAN does not detect the corruption. A corrupt unused block is not harmful.
In a physical corruption, the database does not recognize the block at all. In a logical corruption, the contents of the block are logically inconsistent. By default, the VALIDATE command checks for physical corruption only. You can specify CHECK LOGICAL to check for logical corruption as well. RMAN populates the V$DATABASE_BLOCK_CORRUPTION view with its findings.
Block corruptions can be divided into interblock corruption and intrablock corruption. In intrablock corruption, the corruption occurs within the block itself and can be either physical or logical corruption. In interblock corruption, the corruption occurs between blocks and can only be logical corruption. The VALIDATE command checks for intrablock corruptions only.
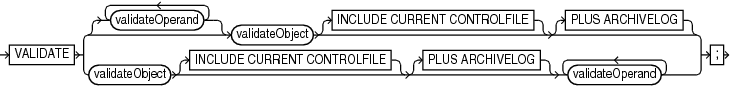
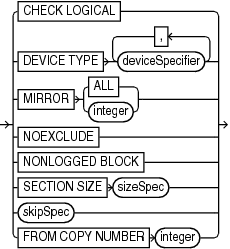
Syntax
(validateObject::=, validateOperand::=)
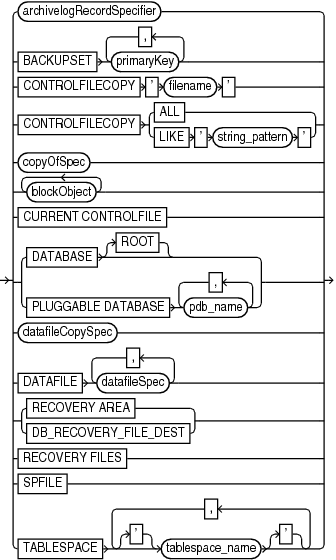
validateObject::=
(archivelogRecordSpecifier::=, copyOfSpec::=, blockObject::=, datafileCopySpec::=, datafileSpec::=)
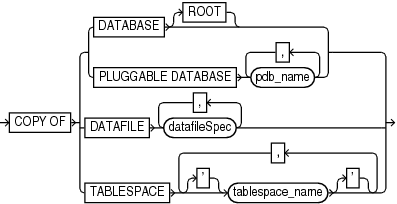
copyOfSpec::=
Semantics
validate
This subclause specifies backup sets for validation. Refer to validate::= for syntax.
| Syntax Element | Description |
|---|---|
|
Specifies options that control the validation. See Also: |
|
|
Specifies the files to be validated. See Also: |
|
INCLUDE CURRENT CONTROLFILE |
Creates a snapshot of the current control file and validates it. |
|
Includes archived redo log files in the validation. Causes RMAN to perform the following steps:
|
validateObject
This subclause specifies database files for validation. Refer to validateObject::= for syntax.
| Syntax Element | Description |
|---|---|
|
Validates a range of archived redo log files. |
|
|
|
Checks that the backup sets specified by You can obtain the primary keys of backup sets by executing a The Use If you do not have automatic channels configured, then manually allocate at least one channel before executing Note: If multiple copies of a backup set exist, then RMAN validates only the most recent copy. The |
CONTROLFILECOPY{'filename' | ALL |LIKE 'string_pattern'} |
Validates control file copies. You can specify a control file copy in one of the following ways:
The control file copy can be created with the |
|
Validates image copies of data files and control files. See Also: |
|
|
|
Validates the current control file. |
|
|
Validates the whole CDB. Connect to the root as a common user with the
When connected to a pluggable database (PDB), validates the PDB. RMAN validates all data files and control files. If the database is currently using a server parameter file, then RMAN validates the server parameter file. Note: The online redo log files and temp files are not validated. |
|
|
Validates only the CDB root. |
|
|
In a CDB, validates the specified PDBs. Use a comma-delimited list to specify
multiple PDBs. Connect to the root as a common user or local user with the
|
|
Validates one or more data file image copies. When validating data file copies, RMAN checks for block corruption but does not terminate the validation if corruption is discovered. Unlike See Also: |
|
|
|
Specifies a list of one or more data files that contain blocks requiring validation. Note: You do not have to take a data file offline if you are validating it. See Also: |
|
|
Validates recovery files created in the current and all previous fast recovery area destinations. Recovery files are full and incremental backup sets, control file autobackups, archived redo log files, and data file copies. Flashback logs, the current control file, and online redo logs are not validated. |
|
|
Semantically equivalent to |
|
|
Validates all recovery files on disk, whether they are stored in the fast recovery area or other locations on disk. Recovery files include full and incremental backup sets, control file autobackups, archived redo log files, and data file copies. Flashback logs are not validated. |
|
|
Validates the server parameter file currently used by the database. RMAN cannot validates other copies of the server parameter file, and cannot validate the server parameter file when the instance was started with an initialization parameter file. |
TABLESPACE tablespace_name |
Validates the specified tablespaces. RMAN translates tablespace names internally into a list of data files, then validates all data files that are currently part of the tablespaces. RMAN validates all data files that are currently members of the specified tablespaces. When connected to the root in a CDB, refers to tablespaces in the root. Refers to tablespaces in a PDB when connected directly to a PDB. |
validateOperand
This subclause specifies modifiers for the validation. Refer to validateOperand::= for syntax.
| Syntax Element | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Tests data and index blocks in the files that pass physical corruption checks for logical corruption, for example, corruption of a row piece or index entry. If RMAN finds logical corruption, then it logs the block in the alert log and server session trace file. The RMAN command completes and Note: |
|
|
Allocates automatic channels for the specified device type only. This option is valid only if you have configured automatic channels and have not manually allocated channels. For example, if you configure automatic disk and tape channels, and run See Also: |
|
|
Validates data files on the specified mirrors. Use the Use |
|
|
When specified on a |
|
|
Checks whether the entries in This clause can be used only for a primary database that is mounted or a physical standby database that is mounted or open read-only. Because validation does not correct the object number associated with the entries in The results of the validation are displayed in the RMAN output and also stored in the |
|
|
Parallelizes the validation by dividing each file into the specified section size. Only specify this parameter when multiple channels are configured or allocated and you want the channels to parallelize the validation, so that multiple channels can validate a single data file. This parameter applies only when validating data files. If you specify a section size that is larger than the size of the file, then RMAN does not parallelize validation for the file. If you specify a small section size that would produce more than 256 sections, then RMAN increases the section size to a value that results in exactly 256 sections. See Also: |
|
Excludes the specified files from the validation. |
|
|
|
Specifies a copy number of the backup piece that will be validated. If the backup was duplexed, then the copy number value ranges from 2 to 4. If no duplexing was performed, then the copy number is 1.
|
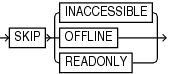
skipSpec
This subclause specifies files to be excluded from the validation.
| Syntax Element | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Excludes data files or archived redo log files if they are inaccessible, offline, or read-only. |
|
|
Excludes data files and archived redo log files that cannot be read due to I/O errors. A data file is only considered inaccessible if it cannot be read. Some offline data files can still be read because they still exist on disk. Others have been deleted or moved and so cannot be read, making them inaccessible. |
|
|
Excludes offline data files. |
|
|
Excludes read-only data files. |
VALIDATE Command Output
Table 3-11 List of Data Files
| Column | Indicates |
|---|---|
|
|
Absolute number of the data file being validated. |
|
|
|
|
|
Number of blocks marked corrupt. These blocks were previously marked corrupt by the database. For example, the database may intentionally mark blocks corrupt during a recovery involving a |
|
|
Number of blocks that either have never been used. |
|
|
Total number of blocks in the file. |
|
|
The highest SCN recorded in the file. |
|
|
The name of the file being validated. |
|
|
The type of block validated: |
|
|
The number of blocks that fail the corruption check. These blocks are newly corrupt. |
|
|
The number of blocks checked for corruption. |
Table 3-12 List of Control File and SPFILE
| Column | Indicates |
|---|---|
|
|
Type of file: |
|
|
|
|
|
The number of blocks that fail the corruption check. These blocks are newly corrupt. |
|
|
Total number of blocks in the file. |
Table 3-13 List of Archived Logs
| Column | Indicates |
|---|---|
|
|
The redo thread number. |
|
|
The log sequence number. |
|
|
|
|
|
The number of blocks that fail the corruption check. These blocks are newly corrupt. |
|
|
Total number of blocks in the file. |
|
|
The name of the archived redo log file. |
Examples
Example 3-85 Validating a Backup Set
This example lists all available backup sets and then validates them. As the sample output indicates, RMAN confirms that it is possible to restore the backups.
RMAN> LIST BACKUP SUMMARY; List of Backups =============== Key TY LV S Device Type Completion Time #Pieces #Copies Compressed Tag ------- -- -- - ----------- --------------- ------- ------- ---------- --- 3871 B F A DISK 08-MAR-13 1 1 NO TAG20130308T092426 3890 B F A DISK 08-MAR-13 1 1 NO TAG20130308T092534
RMAN> VALIDATE BACKUPSET 3871, 3890;
Starting validate at 08-MAR-13 using channel ORA_DISK_1 channel ORA_DISK_1: starting validation of datafile backup set channel ORA_DISK_1: reading from backup piece /disk2/PROD/backupset/2013_03_08/o1_mf_nnndf_TAG20130308T092 426_2z0kpc72_.bkp channel ORA_DISK_1: piece handle=/disk2/PROD/backupset/2013_03_08/o1_mf_nnndf_TAG20130308T092426_2z0kpc72_.bkp ta g=TAG20130308T092426 channel ORA_DISK_1: restored backup piece 1 channel ORA_DISK_1: validation complete, elapsed time: 00:00:18 channel ORA_DISK_1: starting validation of datafile backup set channel ORA_DISK_1: reading from backup piece /disk2/PROD/autobackup/2013_03_08/o1_mf_s_616670734_2z0krhjv_.bkp channel ORA_DISK_1: piece handle=/disk2/PROD/autobackup/2013_03_08/o1_mf_s_616670734_2z0krhjv_.bkp tag=TAG20130308T092534 channel ORA_DISK_1: restored backup piece 1 channel ORA_DISK_1: validation complete, elapsed time: 00:00:00 Finished validate at 08-MAR-13
Example 3-86 Validating the Database
This example validates the database and includes sample output. The validation finds one corrupt block in data file 1. The VALIDATE output indicates that more information about the corruption can be found in the specified trace file.
RMAN> VALIDATE DATABASE; Starting validate at 26-FEB-13 using channel ORA_DISK_1 channel ORA_DISK_1: starting validation of datafile channel ORA_DISK_1: specifying datafile(s) for validation input datafile file number=00001 name=/disk1/oradata/prod/system01.dbf input datafile file number=00002 name=/disk1/oradata/prod/sysaux01.dbf input datafile file number=00003 name=/disk1/oradata/prod/undotbs01.dbf input datafile file number=00004 name=/disk1/oradata/prod/cwmlite01.dbf input datafile file number=00005 name=/disk1/oradata/prod/drsys01.dbf input datafile file number=00006 name=/disk1/oradata/prod/example01.dbf input datafile file number=00007 name=/disk1/oradata/prod/indx01.dbf input datafile file number=00008 name=/disk1/oradata/prod/tools01.dbf input datafile file number=00009 name=/disk1/oradata/prod/users01.dbf channel ORA_DISK_1: validation complete, elapsed time: 00:01:25 List of Datafiles ================= File Status Marked Corrupt Empty Blocks Blocks Examined High SCN ---- ------ -------------- ------------ --------------- ---------- 1 FAILED 0 4140 57600 498288 File Name: /disk1/oradata/prod/system01.dbf Block Type Blocks Failing Blocks Processed ---------- -------------- ---------------- Data 1 41508 Index 0 7653 Other 0 4299 File Status Marked Corrupt Empty Blocks Blocks Examined High SCN ---- ------ -------------- ------------ --------------- ---------- 2 OK 0 8918 20040 498237 File Name: /disk1/oradata/prod/sysaux01.dbf Block Type Blocks Failing Blocks Processed ---------- -------------- ---------------- Data 0 2473 Index 0 2178 Other 0 6471 File Status Marked Corrupt Empty Blocks Blocks Examined High SCN ---- ------ -------------- ------------ --------------- ---------- 3 OK 0 36 2560 498293 File Name: /disk1/oradata/prod/undotbs01.dbf Block Type Blocks Failing Blocks Processed ---------- -------------- ---------------- Data 0 0 Index 0 0 Other 0 2524 File Status Marked Corrupt Empty Blocks Blocks Examined High SCN ---- ------ -------------- ------------ --------------- ---------- 4 OK 0 1 1280 393585 File Name: /disk1/oradata/prod/cwmlite01.dbf Block Type Blocks Failing Blocks Processed ---------- -------------- ---------------- Data 0 0 Index 0 0 Other 0 1279 File Status Marked Corrupt Empty Blocks Blocks Examined High SCN ---- ------ -------------- ------------ --------------- ---------- 5 OK 0 1 1280 393644 File Name: /disk1/oradata/prod/drsys01.dbf Block Type Blocks Failing Blocks Processed ---------- -------------- ---------------- Data 0 0 Index 0 0 Other 0 1279 File Status Marked Corrupt Empty Blocks Blocks Examined High SCN ---- ------ -------------- ------------ --------------- ---------- 6 OK 0 1 1280 393690 File Name: /disk1/oradata/prod/example01.dbf Block Type Blocks Failing Blocks Processed ---------- -------------- ---------------- Data 0 0 Index 0 0 Other 0 1279 File Status Marked Corrupt Empty Blocks Blocks Examined High SCN ---- ------ -------------- ------------ --------------- ---------- 7 OK 0 1 1280 393722 File Name: /disk1/oradata/prod/indx01.dbf Block Type Blocks Failing Blocks Processed ---------- -------------- ---------------- Data 0 0 Index 0 0 Other 0 1279 File Status Marked Corrupt Empty Blocks Blocks Examined High SCN ---- ------ -------------- ------------ --------------- ---------- 8 OK 0 1 1280 393754 File Name: /disk1/oradata/prod/tools01.dbf Block Type Blocks Failing Blocks Processed ---------- -------------- ---------------- Data 0 0 Index 0 0 Other 0 1279 File Status Marked Corrupt Empty Blocks Blocks Examined High SCN ---- ------ -------------- ------------ --------------- ---------- 9 OK 0 1272 1280 393785 File Name: /disk1/oradata/prod/users01.dbf Block Type Blocks Failing Blocks Processed ---------- -------------- ---------------- Data 0 0 Index 0 0 Other 0 8 validate found one or more corrupt blocks See trace file /disk2/oracle/log/diag/rdbms/prod/prod/trace/prod_ora_10609.trc for details channel ORA_DISK_1: starting validation of datafile channel ORA_DISK_1: specifying datafile(s) for validation including current control file for validation including current SPFILE in backup set channel ORA_DISK_1: validation complete, elapsed time: 00:00:01 List of Control File and SPFILE =============================== File Type Status Blocks Failing Blocks Examined ------------ ------ -------------- --------------- SPFILE OK 0 2 Control File OK 0 506 Finished validate at 26-FEB-13