15.2 Migration Methods
This section describes various methods you can use to migrate LONG or BasicFile LOB data to SecureFile storage.
Topics
- Migrating LOBs with SecureFiles Migration Utility
This is the recommended method to migrate BasicFile LOB data to SecureFile storage. - Migrating LOBs with Online Redefinition
Use Online redefinition to migrate LONG or BasicFile LOB data to SecureFile storage by running several API calls. - Migrating LOBs with Data Pump
Oracle Data Pump can either recreate tables as they are in your source database, or recreate LOB columns as SecureFile LOBs.
Parent topic: Migrating Columns to SecureFile LOBs
15.2.1 Migrating LOBs with SecureFiles Migration Utility
This is the recommended method to migrate BasicFile LOB data to SecureFile storage.
This utility encapsulates all the functionality offered by Online Redefinition and saves you the time and effort involved in manually running a series of API calls.
Parent topic: Migration Methods
15.2.1.1 About SecureFiles Migration Utility
You can use the SecureFiles Migration Utility to perform the following tasks:
- Migrate BasicFile LOB data to SecureFile storage, without compressing the data.
- Migrate BasicFile LOB to compressed SecureFile LOBs.
- Migrate uncompressed SecureFile LOBs to compressed SecureFile LOBs.
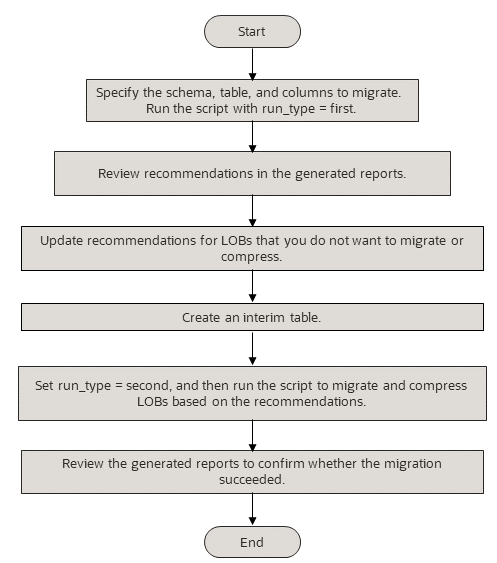
Flowchart to run the SecureFiles Migration Utility twice
To compress and migrate the LOBs, run the SecureFiles Migration Utility twice as shown in the following flowchart. In the first run, the utility analyzes the specified LOBs and generates reports with migration and compression recommendations. After you review the reports, confirm or update the reports to specify which LOBs you want to migrate or compress. Create an interim table, and then run the utility again to migrate and compress the LOBs.
Advantages
- No need to take the table or partition offline.
- Perform the migration at the database, schema, table or LOB segment level.
- After migrating the data, you can also use the SecureFiles Migration Utility to compress the SecureFile LOBs.
Disadvantages
- Additional storage equal to the entire table or partition required and all LOB segments must be available.
- Global indexes must be rebuilt.
Parent topic: Migrating LOBs with SecureFiles Migration Utility
15.2.1.2 Migrate LOBs with SecureFiles Migration Utility
Parent topic: Migrating LOBs with SecureFiles Migration Utility
15.2.2 Migrating LOBs with Online Redefinition
Use Online redefinition to migrate LONG or BasicFile LOB data to SecureFile storage by running several API calls.
Online Redefintion Advantages
- No need not take the table or partition offline
- Can be done in parallel.
To set up parallel execution of online redefinition, run:
ALTER SESSION FORCE PARALLEL DML;
Online Redefinition Disadvantages
- Additional storage equal to the entire table or partition required and all LOB segments must be available
- Global indexes must be rebuilt
Example 15-1 Online Redefinition for Migrating Tables from BasicFiles LOB storage to SecureFile LOB storage
REM Grant privileges required for online redefinition.
GRANT EXECUTE ON DBMS_REDEFINITION TO pm;
GRANT ALTER ANY TABLE TO pm;
GRANT DROP ANY TABLE TO pm;
GRANT LOCK ANY TABLE TO pm;
GRANT CREATE ANY TABLE TO pm;
GRANT SELECT ANY TABLE TO pm;
REM Privileges required to perform cloning of dependent objects.
GRANT CREATE ANY TRIGGER TO pm;
GRANT CREATE ANY INDEX TO pm;
CONNECT pm/pm
-- This forces the online redefinition to execute in parallel
ALTER SESSION FORCE parallel dml;
DROP TABLE cust;
CREATE TABLE cust(c_id NUMBER PRIMARY KEY,
c_zip NUMBER,
c_name VARCHAR(30) DEFAULT NULL,
c_lob CLOB
);
INSERT INTO cust VALUES(1, 94065, 'hhh', 'ttt');
-- Creating Interim Table
-- There is no requirement to specify constraints because they are
-- copied over from the original table.
CREATE TABLE cust_int(c_id NUMBER NOT NULL,
c_zip NUMBER,
c_name VARCHAR(30) DEFAULT NULL,
c_lob CLOB
) LOB(c_lob) STORE AS SECUREFILE (NOCACHE FILESYSTEM_LIKE_LOGGING);
DECLARE
col_mapping VARCHAR2(1000);
BEGIN
-- map all the columns in the interim table to the original table
col_mapping :=
'c_id c_id , '||
'c_zip c_zip , '||
'c_name c_name, '||
'c_lob c_lob';
DBMS_REDEFINITION.START_REDEF_TABLE('pm', 'cust', 'cust_int', col_mapping);
END;
/
DECLARE
error_count pls_integer := 0;
BEGIN
DBMS_REDEFINITION.COPY_TABLE_DEPENDENTS('pm', 'cust', 'cust_int',
1, TRUE,TRUE,TRUE,FALSE, error_count);
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('errors := ' || TO_CHAR(error_count));
END;
/
EXEC DBMS_REDEFINITION.FINISH_REDEF_TABLE('pm', 'cust', 'cust_int');
-- Drop the interim table
DROP TABLE cust_int;
DESC cust;
-- The following insert statement fails. This illustrates
-- that the primary key constraint on the c_id column is
-- preserved after migration.
INSERT INTO cust VALUES(1, 94065, 'hhh', 'ttt');
SELECT * FROM cust;Example 15-2 Online Redefinition for Migrating Tables from the LONG datatype to a SecureFile LOB
LONG to LOB migration are:
- Create an empty interim table. This table holds the migrated
data when the redefinition process is done. In the interim table:
- Define a
CLOBorNCLOBcolumn for eachLONGcolumn in the original table that you are migrating. - Define a
BLOBcolumn for eachLONG RAWcolumn in the original table that you are migrating.
- Define a
- Start the redefinition process. To do so, call
DBMS_REDEFINITION.START_REDEF_TABLEand pass the column mapping using theTO_LOBoperator as follows:
whereDBMS_REDEFINITION.START_REDEF_TABLE( 'schema_name', 'original_table', 'interim_table', 'TO_LOB(long_col_name) lob_col_name', 'options_flag', 'orderby_cols');long_col_nameis the name of theLONGorLONGRAWcolumn that you are converting in the original table andlob_col_nameis the name of the LOB column in the interim table. This LOB column holds the converted data. - Call the
DBMS_REDEFINITION.COPY_TABLE_DEPENDENTSprocedure as described in the related documentation. - Call the
DBMS_REDEFINITION.FINISH_REDEF_TABLEprocedure as described in the related documentation.
The following example demonstrates online redefinition for LONG to LOB migration.
REM Grant privileges required for online redefinition.
GRANT execute ON DBMS_REDEFINITION TO pm;
GRANT ALTER ANY TABLE TO pm;
GRANT DROP ANY TABLE TO pm;
GRANT LOCK ANY TABLE TO pm;
GRANT CREATE ANY TABLE TO pm;
GRANT SELECT ANY TABLE TO pm;
REM Privileges required to perform cloning of dependent objects.
GRANT CREATE ANY TRIGGER TO pm;
GRANT CREATE ANY INDEX TO pm;
CONNECT pm/pm
-- This forces the online redefinition to execute in parallel
ALTER SESSION FORCE parallel dml;
DROP TABLE cust;
CREATE TABLE cust(c_id NUMBER PRIMARY KEY,
c_zip NUMBER,
c_name VARCHAR(30) DEFAULT NULL,
c_long LONG
);
INSERT INTO cust VALUES(1, 94065, 'hhh', 'ttt');
-- Creating Interim Table
-- There is no requirement to specify constraints because they are
-- copied over from the original table.
CREATE TABLE cust_int(c_id NUMBER NOT NULL,
c_zip NUMBER,
c_name VARCHAR(30) DEFAULT NULL,
c_long CLOB
);
DECLARE
col_mapping VARCHAR2(1000);
BEGIN
-- map all the columns in the interim table to the original table
col_mapping :=
'c_id c_id , '||
'c_zip c_zip , '||
'c_name c_name, '||
'to_lob(c_long) c_long';
DBMS_REDEFINITION.START_REDEF_TABLE('pm', 'cust', 'cust_int', col_mapping);
END;
/
DECLARE
error_count PLS_INTEGER := 0;
BEGIN
DBMS_REDEFINITION.COPY_TABLE_DEPENDENTS('pm', 'cust', 'cust_int',
1, true, true, true, false,
error_count);
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('errors := ' || to_char(error_count));
END;
/
EXEC DBMS_REDEFINITION.FINISH_REDEF_TABLE('pm', 'cust', 'cust_int');
-- Drop the interim table
DROP TABLE cust_int;
DESC cust;
-- The following insert statement fails. This illustrates
-- that the primary key constraint on the c_id column is
-- preserved after migration.
INSERT INTO cust VALUES(1, 94065, 'hhh', 'ttt');
SELECT * FROM cust;Parent topic: Migration Methods
15.2.3 Migrating LOBs with Data Pump
Oracle Data Pump can either recreate tables as they are in your source database, or recreate LOB columns as SecureFile LOBs.
When Oracle Data Pump recreates tables, by default it recreates them as they existed in the source database. Therefore, if a LOB column was a BasicFiles LOB in the source database, Oracle Data Pump attempts to recreate it as a BasicFile LOB in the imported database. However, you can force creation of LOBs as SecureFile LOBs in the recreated tables by using a TRANSFORM parameter for the command line, or by using a LOB_STORAGE parameter for the DBMS_DATAPUMP and DBMS_METADATA packages.
impdp system/manager directory=dpump_dir schemas=lobuser dumpfile=lobuser.dmp
transform=lob_storage:securefileNote:
The transform name is not valid in transportable import.See Also:
TRANSFORM for using TRANSFORM parameter to convert to SecureFile LOBsYou can use the keyword HIDDEN to distinguish a default inline LOB size from a user-specified one.
CREATE TABLE <tab> (…) LOB (L1) STORE AS … [ENABLE STORAGE IN ROW [4000|8000]
HIDDEN];Restrictions on Migrating LOBs with Data Pump
You can't use SecureFile LOBs in non-ASSM tablespace. If the source database contains LOB columns in a tablespace that does not support ASSM, then you'll see an error message when you use Oracle Data Dump to recreate the tables using the securefile clause for LOB columns.
To import non-ASSM tables with LOB columns, run another import for these tables without using TRANSFORM=LOB_STORAGE:SECUREFILE.
Example:
impdp system/manager directory=dpump_dir schemas=lobuser dumpfile=lobuser.dmpParent topic: Migration Methods