1.2 Understanding Database Instances
A database has at least one instance. An instance is comprised of a memory area called the System Global Area (SGA) and Oracle background processes.
The memory and processes of an instance efficiently manage the associated database's data and serve the database users.
Note:
An instance also manages other services, such as Oracle XML DB.
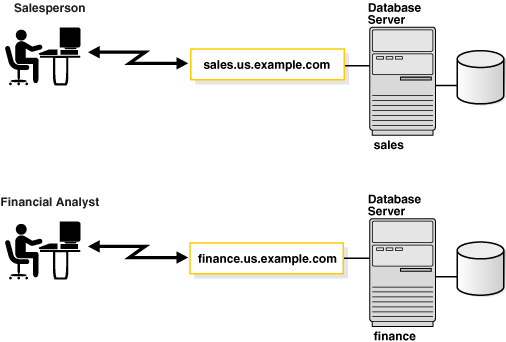
The following figure shows two database instances, sales and
finance, associated with their respective databases and service
names.
Figure 2-13 One Instance for Each Database
Description of "Figure 2-13 One Instance for Each Database"
Instances are identified by an instance name, such as sales and finance in this example. The instance name is specified by the INSTANCE_NAME initialization parameter. The instance name defaults to the Oracle system identifier (SID) of the database instance.
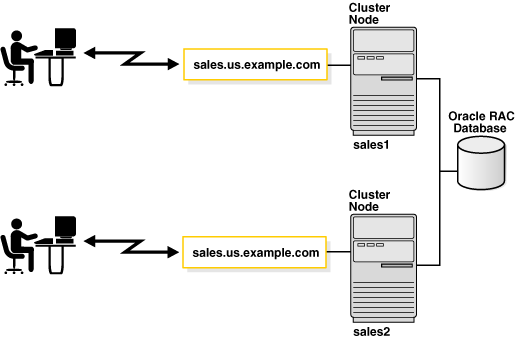
Some hardware architectures allow multiple computers to share access to data, software, or peripheral devices. Oracle Real Application Clusters (Oracle RAC) can take advantage of such architecture by running multiple instances on different computers that share a single physical database.
The following figure shows an Oracle RAC configuration. In this example, two
instances, sales1 and sales2, are associated with one
database service, sales.us.example.com.
Figure 2-14 Multiple Instances Associated with an Oracle RAC Database
Description of "Figure 2-14 Multiple Instances Associated with an Oracle RAC Database"
Parent topic: Introducing Oracle Net Services