1.3 Components of Oracle Net Services
Learn about the connectivity, manageability, scalability, and security features.
- About Oracle Net
- About Oracle Net Listener
- About Oracle Connection Manager
- About Networking Tools
- About Oracle Advanced Security
Oracle Advanced Security is a separately licensable product that provides Oracle Database Transparent Data Encryption (TDE) and Oracle Data Redaction. TDE encrypts data so that only an authorized recipient can read it.
Parent topic: Introducing Oracle Net Services
1.3.1 About Oracle Net
Oracle Net is a software layer that resides on the client and on the Oracle Database server. It is responsible for establishing and maintaining the connection between the client application and server, as well as exchanging messages between them, using industry-standard protocols. Oracle Net has two software components:
- Oracle Net Foundation Layer
- Oracle Protocol Support
The Oracle Net foundation layer uses Oracle protocol support to communicate with these industry-standard network protocols.
Parent topic: Components of Oracle Net Services
1.3.1.1 Oracle Net Foundation Layer
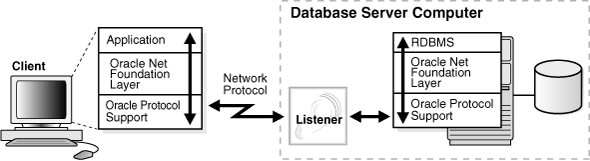
On the client side, applications communicate with Oracle Net foundation layer to establish and maintain connections. The Oracle Net foundation layer uses Oracle protocol support that communicates with an industry-standard network protocol, such as TCP/IP, to communicate with the Oracle Database server.
Figure 1-15 illustrates the communication stack on the client.
The Oracle Database server side is similar to the client side as illustrated in Figure 1-16. A network protocol sends client request information to an Oracle protocol support layer, which then sends information to the Oracle Net foundation layer. The Oracle Net foundation layer then communicates with the Oracle Database server to process the client request.
Parent topic: About Oracle Net
1.3.1.2 Oracle Protocol Support
The Oracle Net foundation layer uses Oracle protocol support to communicate with these industry-standard network protocols.
-
TCP/IP (version 4 and version 6)
-
TCP/IP with Transport Layer Security (TLS)
-
Named Pipes
-
SDP
Oracle protocol support maps Oracle Net foundation layer functionality to industry-standard protocols used in client/server connections.
Related Topics
Parent topic: About Oracle Net
1.3.2 About Oracle Net Listener
Oracle Database server receives the initial connection through Oracle Net Listener. Oracle Net Listener, referred to in this document as the listener, brokers a client request, handing off the request to the server. The listener is configured with a protocol address, and clients configured with the same protocol address can send connection requests to the listener. When a connection is established, the client and Oracle server communicate directly with one another.
Oracle Net listener supports ACLs (Access Control Lists) for service and this is supported for all IP protocols.
See Also:
DBSFWUSER.DBMS_SFW_ACL_ADMIN in Oracle Database PL/SQL Packages and Types Reference for more information about listener ACLsThe following figure shows the listener accepting a connection request from a client and forwarding that request to an Oracle server.
Figure 1-17 Listener in a Connection Request
Description of "Figure 1-17 Listener in a Connection Request"
See Also:
Configuring and Administering Oracle Net Listener for additional information about the listener
Parent topic: Components of Oracle Net Services
1.3.3 About Oracle Connection Manager
Oracle Connection Manager is the software component that resides on its own computer, separate from a client or an Oracle Database server. It proxies and screens requests for the database server. In addition, it multiplexes database sessions.
In its session multiplexing role, Oracle Connection Manager funnels multiple sessions through a single transport protocol connection to a particular destination. In this way, Oracle Connection Manager reduces the demand on resources needed to maintain multiple sessions between two processes by enabling the Oracle Database server to use fewer connection endpoints for incoming requests.
As an access control filter, Oracle Connection Manager controls access to Oracle databases.
Note:
Oracle Connection Manager can act as a Connection Manager in Traffic Director Mode by settingtdm=yes in cman.ora.
Oracle Connection Manager in Traffic Director mode provides improved high availability (HA) (planned and unplanned), connection multiplexing support, and load balancing. This feature also provides an inband client notification mechanism to deliver planned shutdown for Oracle Connection Manager down and service down events to the OCI client.
See Also:
-
"Firewall Access Control" for a description of filtering
Parent topic: Components of Oracle Net Services
1.3.4 About Networking Tools
Oracle Net Services provides user interface tools and command-line utilities to configure, manage, and monitor the network.
-
Oracle Net Configuration Assistant is a standalone tool that enables you to configure listeners and naming methods.
-
Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control combines configuration functionality across multiple file systems, along with listener administrative control to provide an integrated environment for configuring and managing Oracle Net Services.
-
Oracle Net Manager provides configuration functionality for an Oracle home on a local client or server host.
-
Command-line control utilities to configure, administer, and monitor network components, including listeners and Oracle Connection Managers.
With Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control or Oracle Net Manager, you can fine-tune the listener and naming method configuration created with Oracle Net Configuration Assistant. In addition, Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control and Oracle Net Manager offer built-in wizards and utilities to test connectivity, migrate data from one naming method to another, and create additional network components.
See Also:
Parent topic: Components of Oracle Net Services
1.3.5 About Oracle Advanced Security
Oracle Advanced Security is a separately licensable product that provides Oracle Database Transparent Data Encryption (TDE) and Oracle Data Redaction. TDE encrypts data so that only an authorized recipient can read it.
Oracle Data Redaction enables an administrator to redact (mask) column data, using the following types of redaction:
-
Full redaction redacts all the contents of the column data. The redacted value returned to the querying user depends on the data type of the column. For example, columns of the NUMBER data type are redacted with a zero (0) and character data types are redacted with a blank space.
-
Partial redaction redacts a portion of the column data. For example, masking most of a credit card number with asterisks (*), except for the last four digits.
-
Regular expressions enable using patterns of data to redact. For example, use regular expressions to redact email addresses, which can have varying character lengths. It is designed for use with character data only.
-
Random redaction present the redacted data to the querying user as randomly-generated values each time it is displayed.
-
No redaction enables an administrator to test the internal operation of the redaction policies, with no effect on the results of queries against tables with policies defined on them.
Related Topics
Parent topic: Components of Oracle Net Services

