ALTER VIEW
Purpose
Use the ALTER VIEW statement to explicitly recompile a view that is invalid or to modify view constraints. Explicit recompilation lets you locate recompilation errors before run time. You may want to recompile a view explicitly after altering one of its base tables to ensure that the alteration does not affect the view or other objects that depend on it.
You can also use ALTER VIEW to define, modify, or drop view constraints.
You cannot use this statement to change the definition of an existing view. Further, if DDL changes to the view's base tables invalidate the view, then you cannot use this statement to compile the invalid view. In these cases, you must redefine the view using CREATE VIEW with the OR REPLACE keywords.
When you issue an ALTER VIEW statement, Oracle Database recompiles the view regardless of whether it is valid or invalid. The database also invalidates any local objects that depend on the view.
If you alter a view that is referenced by one or more materialized views, then those materialized views are invalidated. Invalid materialized views cannot be used by query rewrite and cannot be refreshed.
See Also:
-
CREATE VIEW for information on redefining a view and ALTER MATERIALIZED VIEW for information on revalidating an invalid materialized view
-
Oracle Database Data Warehousing Guide for general information on data warehouses
-
Oracle Database Concepts for more about dependencies among schema objects
Prerequisites
The view must be in your own schema or you must have ALTER ANY TABLE system privilege.
Syntax
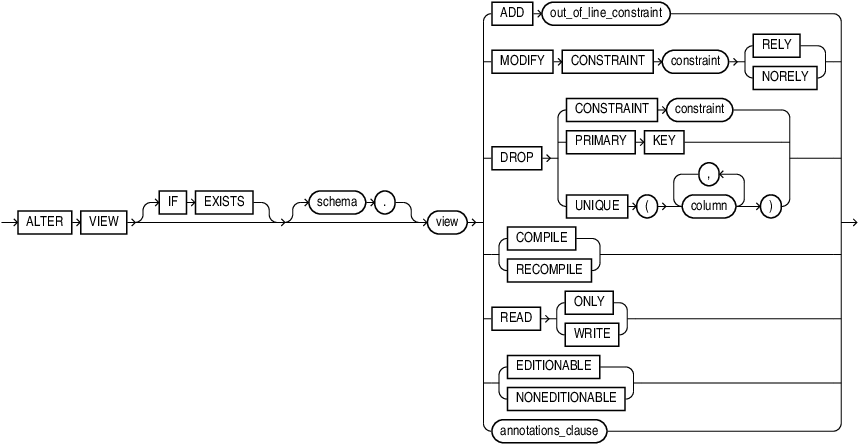
alter_view::=
(out_of_line_constraint::=—part of constraint::= syntax), annotations_clause
Semantics
IF EXISTS
Specify IF EXISTS to alter an existing table.
Specifying IF NOT EXISTS with ALTER VIEW results in ORA-11544: Incorrect IF EXISTS clause for ALTER/DROP statement.
schema
Specify the schema containing the view. If you omit schema, then Oracle Database assumes the view is in your own schema.
view
Specify the name of the view to be recompiled.
MODIFY CONSTRAINT Clause
Use the MODIFY CONSTRAINT clause to change the RELY or NORELY setting of an existing view constraint. Refer to "Notes on View Constraints" for general information on view constraints.
Restriction on Modifying Constraints
You cannot change the setting of a unique or primary key constraint if it is part of a referential integrity constraint without dropping the foreign key or changing its setting to match that of view.
ADD Clause
Use the ADD clause to add a constraint to view. Refer to constraint for information on view constraints and their restrictions.
DROP Clause
Use the DROP clause to drop an existing view constraint.
Restriction on Dropping Constraints
You cannot drop a unique or primary key constraint if it is part of a referential integrity constraint on a view.
COMPILE | RECOMPILE
RECOMPILE and COMPILE keywords direct Oracle Database to recompile the view.
Use RECOMPILE to explicitly recompile a view that is invalid or to modify view constraints. Explicit recompilation allows users to locate recompilation errors, before run time.
{ READ ONLY | READ WRITE }
These clauses are valid only for editioning views.
-
Specify
READONLYto indicate that the editioning view cannot be updated. -
Specify
READWRITEto return a read-only editioning view to read/write status.
When you specify these clauses, the database does not invalidate dependent objects, but it may invalidate cursors.
EDITIONABLE | NONEDITIONABLE
Use these clauses to specify whether the view becomes an editioned or noneditioned object if editioning is later enabled for the schema object type VIEW in schema. The default is EDITIONABLE. For information about altering editioned and noneditioned objects, see Oracle Database Development Guide.
See Also:
CREATE VIEW for information about editioning views
annotations_clause
For the full semantics of the annotations clause see annotations_clause.
You can only change annotations at the view level with the ALTER statement. To drop column-level annotations, you must drop and recreate the view.
Examples
Altering a View: Example
To recompile the view customer_ro (created in "Creating a Read-Only View: Example"), issue the following statement:
ALTER VIEW customer_ro
COMPILE;
If Oracle Database encounters no compilation errors while recompiling customer_ro, then customer_ro becomes valid. If recompiling results in compilation errors, then the database returns an error and customer_ro remains invalid.
Oracle Database also invalidates all dependent objects. These objects include any procedures, functions, package bodies, and views that reference customer_ro. If you subsequently reference one of these objects without first explicitly recompiling it, then the database recompiles it implicitly at run time.
Add and Drop Annotations: Example
The following example drops annotation Title from view MView1 and adds annotation Identity :
ALTER VIEW HighWageEmp ANNOTATIONS(DROP Title, ADD Identity);