CREATE SPFILE
Purpose
Use the CREATE SPFILE statement to create a server parameter file either from a traditional plain-text initialization parameter file or from the current system-wide settings. Server parameter files are binary files that exist only on the server and are called from client locations to start up the database.
Server parameter files let you make persistent changes to individual parameters. When you use a server parameter file, you can specify in an ALTER SYSTEM SET parameter statement that the new parameter value should be persistent. This means that the new value applies not only in the current instance, but also to any instances that are started up subsequently. Traditional plain-text parameter files do not let you make persistent changes to parameter values.
Server parameter files are located on the server, so they allow for automatic database tuning by Oracle Database and for backup by Recovery Manager (RMAN).
To use a server parameter file when starting up the database, you must create it using the CREATE SPFILE statement.
All instances in an Oracle Real Application Clusters environment must use the same server parameter file. However, when otherwise permitted, individual instances can have different settings of the same parameter within this one file. Instance-specific parameter definitions are specified as SID.parameter = value, where SID is the instance identifier.
The method of starting up the database with a server parameter file depends on whether you create a default or nondefault server parameter file. Refer to "Creating a Server Parameter File: Examples" for examples of how to use server parameter files.
Note on Creating Server Parameter Files in a CDB
When you create a server parameter file in a multitenant container database (CDB), the current container can be the root or a PDB.
-
If the current container is the root, then the values that you set for initialization parameters in the root are used as default values for all other containers.
-
If the current container is a PDB, then the database stores the PDB's initialization parameter values internally, rather than in a file. Therefore, you cannot specify an
spfile_name. The values that you set for initialization parameters in the PDB are persistent and override any values set for those parameters in the root.When PDB is in
MOUNTstate, any query onV$parameter( show parameter) shows the values fromROOTparameter table.When PDB is in
OPENstate, any query onV$parameter( show parameter) shows the values from PDB parameter table.
You can subsequently use the ALTER SYSTEM statement to modify initialization parameter values for the root or a PDB.
See Also:
-
CREATE PFILE for information on creating a regular text parameter file from a binary server parameter file
-
Oracle Database Administrator's Guide for information on traditional plain-text initialization parameter files and server parameter files
-
Oracle Real Application Clusters Administration and Deployment Guide for information on using server parameter files in an Oracle Real Application Clusters environment
Prerequisites
You must have the SYSBACKUP, SYSDBA, SYSDG, or SYSOPER system privilege to execute this statement. You can execute this statement before or after instance startup. However, if you have already started an instance using spfile_name, you cannot specify the same spfile_name in this statement.
To create a server parameter file in a CDB, the current container must be the root and you must have the commonly granted SYSBACKUP, SYSDBA, SYSDG, or SYSOPER system privilege.
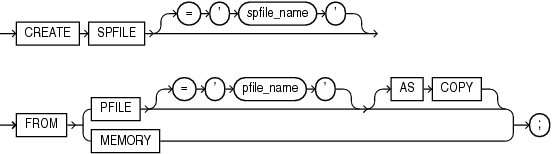
Syntax
create_spfile::=
Semantics
spfile_name
This clause lets you specify a name for the server parameter file you are creating.
If you specify spfile_name, then Oracle Database creates a nondefault server parameter file.
-
For
spfile_name, you can specify a traditional filename, a file in an Oracle ACFS (Oracle Advanced Cluster File System) file system, or an Oracle Storage Management (Oracle ASM) filename. -
If you specify a traditional filename or a file in an Oracle ACFS file system, then
spfile_namecan include a path prefix. If you do not specify such a path prefix, then the database adds the path prefix for the default storage location, which is platform dependent. -
If you specify the Oracle ASM filename syntax, then the database creates the spfile in an Oracle ASM disk group.
-
When using a nondefault server parameter file, you must specify the server parameter filename in the
STARTUPcommand when you start up the database. The exception to this rule is as follows:-
If the database is defined as a resource in Oracle Clusterware, the instance from which the command is issued is running, and you specify the
spfile_name, specify theFROMPFILEclause, and omit theASCOPYclause, then this statement automatically updates the SPFILE in the database resource. In this case, you can start up the database without referring to the server parameter file by name. If the instance from which the command is issued is not running, then the SPFILE in the database resource must be updated manually usingsrvctlmodifydatabase-ddbname-spfilespfile_path.
-
If you omit spfile_name, then Oracle Database uses the platform-specific default server parameter filename. If such a file already exists on the server, then this statement overwrites it. When using a default server parameter file, you can start up the database without referring to the file by name.
Restriction on spfile_name
You cannot specify spfile_name when creating a server parameter file while connected to a PDB.
See Also:
-
"Creating a Server Parameter File: Examples" for information on starting up the database with default and nondefault server parameter files
-
file_specification for the syntax of traditional and Oracle ASM filenames and ALTER DISKGROUP for information on modifying the characteristics of an Oracle ASM file
-
The appropriate operating-system-specific documentation for default parameter file names
pfile_name
Specify the traditional plain-text initialization parameter file from which you want to create a server parameter file. The traditional parameter file must reside on the server.
-
If you specify
pfile_nameand the traditional parameter file does not reside in the default directory for parameter files on your operating system, then you must specify the full path. -
If you do not specify
pfile_name, then Oracle Database looks in the default directory for parameter files on your operating system for the default parameter filename and uses that file. If that file does not exist in the expected directory, then the database returns an error.
Note:
In an Oracle Real Application Clusters environment, you must first combine all instance parameter files into one file before specifying that filename in this statement to create a server parameter file. For information on accomplishing this step, see Oracle Real Application Clusters Administration and Deployment Guide.
AS COPY
This clause applies only if the database is defined as a resource in Oracle Clusterware. By default, if you specify both the spfile_name and the FROM PFILE clause, then the CREATE SPFILE statement automatically updates the SPFILE in the database resource. You can specify AS COPY to prevent the database from updating the SPFILE in the database resource.
MEMORY
Specify MEMORY to create an spfile using the current system-wide parameter settings. In an Oracle RAC environment, the created file will contain the parameter settings from each instance.
Examples
Creating a Server Parameter File: Examples
The following example creates a default server parameter file from a traditional plain-text parameter file named t_init1.ora:
CREATE SPFILE FROM PFILE = '$ORACLE_HOME/work/t_init1.ora';
Note:
Typically you will need to specify the full path and filename for parameter files on your operating system.
When you create a default server parameter file, you subsequently start up the database using that server parameter file by using the SQL*Plus command STARTUP without the PFILE parameter, as follows:
STARTUP
The following example creates a nondefault server parameter file s_params.ora from a traditional plain-text parameter file named t_init1.ora:
CREATE SPFILE = 's_params.ora' FROM PFILE = '$ORACLE_HOME/work/t_init1.ora';
When you create a nondefault server parameter file, you subsequently start up the database by first creating a traditional parameter file containing the following single line:
spfile = 's_params.ora'
The name of this parameter file must comply with the naming conventions of your operating system. You then use the single-line parameter file in the STARTUP command. The following example shows how to start up the database, assuming that the single-line parameter file is named new_param.ora:
STARTUP PFILE=new_param.ora