JSON Object Access Expressions
A JSON object access expression is used only when querying a column of JSON data. It yields a character string that contains one or more JSON values found in that data. The syntax for this type of expression is called dot-notation syntax.
Just as for SQL/JSON query functions, the JSON column that you query must be known to contain only well-formed JSON data. That is, it must be of data type JSON, VARCHAR2, CLOB, or BLOB. If the type is not JSON then the column must have an IS JSON check constraint.
If you do not use an item method in your dot-notation query, then a SQL value representing JSON data is returned as follows:
-
If the queried data is of type
JSON, then the returned value is also of typeJSON. -
If the queried data is textual of type
VARCHAR2,CLOB, orBLOB, then the returned data is of typeVARCHAR2(4000).
If a dot-notation query does not use an item method then the returned JSON data depends on the targeted JSON data, as follows:
-
If a single JSON value is targeted, then that value is returned, whether it is a JSON scalar, object, or array.
-
If multiple JSON values are targeted, then a JSON array, whose elements are those values, is returned. (The order of the array elements is undefined.)
For details on querying JSON data using simple dot notation see Simple Dot-Notation Access to JSON Data of the JSON Developer's Guide .
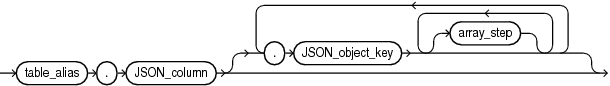
json_object_access_expr::=
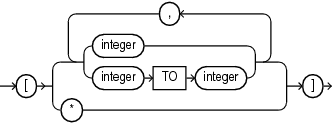
array_step::=
The dot-notation syntax is a table alias (mandatory) followed by a dot, that is, a period (.), the name of a JSON column, and one or more pairs of the form . json_field or . json_field followed by array_step, where json_field is a JSON field name and array_step is an array step expression as described in Basic SQL/JSON Path Expression Syntax of the JSON Developer's Guide.
-
For
table_alias, specify the alias for the table that contains the column of JSON data. This table alias is required and must be assigned to the table elsewhere in the SQL statement. -
For
JSON_column, specify the name of the column of JSON data. The column must be of data typeVARCHAR2,CLOB,BLOB, orJSON.Columns can have data of
JSONdata type if they are the result of JSON generation functions, ofJSON_QUERY, orTREAT.To identify non
JSONtype data types you can define theIS JSONcheck constraint on the column . -
You can optionally specify one or more JSON object keys. The object keys allow you to target specific JSON values in the JSON data. The first
JSON_object_keymust be a case-sensitive match to the key (property) name of an object member in the top level of the JSON data. If the value of that object member is another JSON object, then you can specify a secondJSON_object_keythat matches the key name of a member of that object, and so on. If a JSON array is encountered during any of these iterations, and you do not specify anarray_step, then the array is implicitly unwrapped and the elements of the array are evaluated using theJSON_object_key. -
If the JSON value is an array, then you can optionally specify one or more
array_stepclauses. This allows you to access specific elements of the JSON array.-
Use
integerto specify the element at indexintegerin a JSON array. UseintegerTOintegerto specify the range of elements between the two indexintegervalues, inclusive. If the specified elements exist in the JSON array being evaluated, then the array step results in a match to those elements. Otherwise, the array step does not result in a match. The first element in a JSON array has index 0. -
Use the asterisk wildcard symbol (
*) to specify all elements in a JSON array. If the JSON array being evaluated contains at least one element, then the array step results in a match to all elements in the JSON array. Otherwise, the array step does not result in a match.
-
If you omit JSON_object_key, then the expression yields a character string that contains the JSON data in its entirety. In this case, the character string is of the same data type as the column of JSON data being queried.
A JSON object access expression cannot return a value larger than 4K bytes. If the value surpasses this limit, then the expression returns null. To obtain the actual value, instead use the JSON_QUERY function or the JSON_VALUE function and specify an appropriate return type with the RETURNING clause.
The collation derivation rules for the JSON object access expression are the same as for the JSON_QUERY function.
See Also:
Appendix C in Oracle AI Database
Globalization Support Guide for the collation derivation rules for the JSON_QUERY function
Examples
The following examples use the j_purchaseorder table, which is created in Creating a Table That Contains a JSON Document: Example. This table contains a column of JSON data called po_document. These examples return JSON values from column po_document.
The following statement returns the value of the property with key name PONumber. The value returned, 1600, is a SQL number.
SELECT po.po_document.PONumber.number() FROM j_purchaseorder po; PONumber -------- 1600
The following statement first targets the property with key name ShippingInstructions, whose value is a JSON object. The statement then targets the property with key name Phone within that object. The statement returns the value of Phone, which is a JSON array.
SELECT po.po_document.ShippingInstructions.Phone
FROM j_purchaseorder po;
SHIPPINGINSTRUCTIONS
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
[{"type":"Office","number":"909-555-7307"},{"type":"Mobile","number":"415-555-1234"}]
The following statement first targets the property with key name LineItems, whose value is a JSON array. The expression implicitly unwraps the array and evaluates its elements, which are JSON objects. Next, the statement targets the properties with key name Part, within the unwrapped objects, and finds two objects. The statement then targets the properties with key name Description within those two objects and finds string values. Because more than one value is returned, the values are returned as elements of a JSON array.
SELECT po.po_document.LineItems.Part.Description FROM j_purchaseorder po; LINEITEMS ----------------------------------- [One Magic Christmas,Lethal Weapon]
See Also:
Oracle AI Database JSON Developer’s Guide for more information on querying JSON data using dot-notation syntax