3.1.1 Map Request Examples
This section provides examples of map requests.
It refers to concepts, elements, and attributes that are explained in detail in Section 3.1.2. It contains sections with the following examples:
- Simple Map Request
- Map Request with Dynamically Defined Theme
- Map Request with Base Map, Center, and Additional Predefined Theme
- Map Request with Center, Base Map, Dynamically Defined Theme, and Other Features
- Map Request for Point Features with Attribute Value and Dynamically Defined Variable Marker Style
- Map Request with an Image Theme
- Map Request for Image of Map Legend Only
- Map Request with SRID Different from Data SRID
- Map Request Using a Pie Chart Theme
- Map Request Using Ratio Scale and Mixed Theme Scale Modes
- Map Request Using Predefined Theme (Binding Parameter and Custom Type)
- Map Request Using Advanced Styles and Rendering Rules
- Map Request Using Stacked Styles
- WFS Map Requests
- Java Program Using MapViewer
- PL/SQL Program Using MapViewer
Parent topic: MapViewer Map Server
3.1.1.1 Simple Map Request
Example 3-1 is a very simple map request. It requests a map consisting of a blank blue image
(from the mvdemo data source) with the string Hello World
drawn on top. (The datasource attribute is required for a map request, even though
this specific map request does not retrieve any map data from the data source.)
Example 3-1 Simple Map Request ("Hello World")
<?xml version="1.0" standalone="yes"?>
<map_request title="Hello World"
datasource="mvdemo" />Parent topic: Map Request Examples
3.1.1.2 Map Request with Dynamically Defined Theme
Example 3-2 is a simple map request with one dynamically defined theme. It requests a map of all Oracle Spatial and Graph geometries from the COUNTIES table.
Example 3-2 Simple Map Request with a Dynamically Defined Theme
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<map_request datasource="lbs_data">
<themes>
<theme name="t1">
<jdbc_query spatial_column="GEOM"
datasource="lbs_data">
SELECT geom FROM counties
</jdbc_query>
</theme>
</themes>
</map_request>Parent topic: Map Request Examples
3.1.1.3 Map Request with Base Map, Center, and Additional Predefined Theme
Example 3-3 requests a map with a specified center for the result map, and specifies a
predefined theme (poi_theme_us_restaurants) to be rendered in
addition to the predefined themes that are part of the base map
(basemap="us_base").
Example 3-3 Map Request with Base Map, Center, and Additional Predefined Theme
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<map_request datasource="lbs_data"
title="LBS CUSTOMER MAP"
basemap="us_base"
width="500"
height="375"
bgcolor="#a6cae0"
format="GIF_URL">
<center size="1">
<geoFeature typeName="mapcenter"
label="Motel 1"
text_style="T.MOTEL"
render_style="M.MOTEL"
radius="300">
<geometricProperty>
<Point>
<coordinates>-122.2615, 37.5266</coordinates>
</Point>
</geometricProperty>
</geoFeature>
</center>
<srs>SDO:8265</srs>
<themes>
<theme name="poi_theme_us_restaurants" />
</themes>
</map_request>- Because basemap is specified, MapViewer first draws all predefined
themes for that base map before drawing the specified theme
(
poi_theme_us_restaurants). - The center will be drawn with a marker of the
M.MOTELstyle and the labelMotel 1in theT.MOTELstyle. - A circle with a radius of 300 meters will be drawn around the center.
Parent topic: Map Request Examples
3.1.1.4 Map Request with Center, Base Map, Dynamically Defined Theme, and Other Features
Example 3-4 requests a map with a specified center, a predefined theme named
theme_lbs_customers, a dynamically defined theme named
sales_by_region, and all base themes in the base map
us_base_road, plus two features: a polygon representing the top
sales region, and a point. The requested map will be stored at the MapViewer host
and a URL to that GIF image (format="GIF_URL") will be returned to
the requester.
Example 3-4 Map Request with Center, Base Map, Dynamically Defined Theme, and Other Features
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<map_request datasource="lbs_data2"
title="LBS CUSTOMER MAP 2"
width="400"
height="300"
format="GIF_URL"
basemap="us_base_road">
<center size="1.5">
<geoFeature typeName="nil">
<geometricProperty>
<Point>
<coordinates>-122.2615, 37.5266</coordinates>
</Point>
</geometricProperty>
</geoFeature>
</center>
<themes>
<theme name="theme_lbs_customers" />
<theme name="sales_by_region">
<jdbc_query spatial_column="region"
label_column="manager"
render_style="V.SALES COLOR"
label_style="T.SMALL TEXT"
jdbc_host="data.my_corp.com"
jdbc_sid="orcl"
jdbc_port="1521"
jdbc_user="scott"
jdbc_password="password"
jdbc_mode="thin">
select region, sales, manager from my_corp_sales_2001
</jdbc_query>
</theme>
</themes>
<geoFeature typeName="nil"
label="TopSalesRegion"
text_style="9988"
render_style="2837">
<geometricProperty>
<Polygon srsName="SDO:8265">
<outerBoundaryIs>
<LinearRing>
<coordinates>42.9,71.1 43.2,72.3 39.2,73.0 39.0,73.1 42.9,71.1</coordinates>
</LinearRing>
</outerBoundaryIs>
</Polygon>
</geometricProperty>
</geoFeature>
<geoFeature render_style="1397"
text_style="9987">
<geometricProperty>
<Point>
<coordinates>-122.5615, 37.3266</coordinates>
</Point>
</geometricProperty>
</geoFeature>
</map_request>In Example 3-4, sales_by_region is a dynamically defined theme. For information
about dynamically defining a theme, see theme Element and jdbc_query Element.
Parent topic: Map Request Examples
3.1.1.5 Map Request for Point Features with Attribute Value and Dynamically Defined Variable Marker Style
Example 3-5 shows a map request to render point features with a dynamically defined variable
marker style. The attribute_values attribute defines the value that
will be used to find the appropriate bucket (for the range into which the value
falls), as defined in the variable marker style.
Example 3-5 Map Request for Point Features with Attribute Value and Dynamically Defined Variable Marker Style
<?xml version="1.0" standalone="yes"?>
<map_request title="Point Features with Variable Marker Style"
datasource="mvdemo"
srid="0"
width="500"
height="375"
bgcolor="#a6caf0"
antialiase="true"
format="PNG_URL">
<center size="19.2">
<geoFeature>
<geometricProperty typeName="center">
<Point>
<coordinates>-116.65,38.92</coordinates>
</Point>
</geometricProperty>
</geoFeature>
</center>
<geoFeature render_style="varmarkerpf"
attribute_values="50000.0">
<geometricProperty>
<Point>
<coordinates>-112.0,43.0</coordinates>
</Point>
</geometricProperty>
</geoFeature>
<geoFeature render_style="varmarkerpf"
attribute_values="125000.0">
<geometricProperty>
<Point>
<coordinates>-123.0,40.0</coordinates>
</Point>
</geometricProperty>
</geoFeature>
<geoFeature render_style="varmarkerpf"
attribute_values="200000.0">
<geometricProperty>
<Point>
<coordinates>-116.64,38.92</coordinates>
</Point>
</geometricProperty>
</geoFeature>
<geoFeature render_style="varmarkerpf"
attribute_values="300000.0">
<geometricProperty>
<Point>
<coordinates>-112.0,35.0</coordinates>
</Point>
</geometricProperty>
</geoFeature>
<styles>
<style name="varmarkerpf">
<AdvancedStyle>
<VariableMarkerStyle basemarker="mkcircle"
startsize="10"
increment="5">
<Buckets>
<RangedBucket label="less than 100k"
high="100000.0" />
<RangedBucket label="100k - 150k"
low="100000.0"
high="150000.0" />
<RangedBucket label="150k - 250k"
low="150000.0"
high="250000.0" />
<RangedBucket label="250k - 350k"
low="250000.0"
high="350000.0" />
</Buckets>
</VariableMarkerStyle>
</AdvancedStyle>
</style>
<style name="mkcircle">
<svg>
<g class="marker"
style="stroke:blue;fill:red;">
<circle r="20" />
</g>
</svg>
</style>
</styles>
</map_request>Parent topic: Map Request Examples
3.1.1.6 Map Request with an Image Theme
Example 3-5 requests a map in which an image theme is to be plotted underneath all other
regular vector data. The image theme is specified in the
<jdbc_image_query> element as part of the
<theme> element in a map request. (For an explanation of
image themes, see Image Themes.)
Example 3-6 Map Request with an Image Theme
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<map_request datasource="lbs_data"
title="LBS Image MAP"
basemap="us_roads"
format="GIF_STREAM">
<center size="1">
<geoFeature>
<geometricProperty>
<Point>
<coordinates>-122.2615, 37.5266</coordinates>
</Point>
</geometricProperty>
</geoFeature>
</center>
<themes>
<theme name="anImageTheme">
<jdbc_image_query image_format="ECW"
image_column="image"
image_mbr_column="img_extent"
jdbc_srid="33709"
datasource="lbs_data">
SELECT image, img_extent, image_id FROM my_images
</jdbc_image_query>
</theme>
</themes>
</map_request>MapViewer processes the request in Example 3-6 as follows:
- MapViewer retrieves the image data by executing the user-supplied query
(
SELECT image, img_extent, image_id FROM my_images) in the current map window context. - MapViewer checks its internal list of all registered image renderers
to see if one supports the ECW format (
image_format="ECW"). Because MapViewer as supplied by Oracle does not support the ECW format, you must implement and register a custom image renderer that supports the format, as explained in Creating and Registering a Custom Image Renderer. - MapViewer calls the
renderImagesmethod, and image data retrieved from the user-supplied query is passed to the method as one of its parameters. - MapViewer retrieves and renders any requested vector data on top of the rendered image.
Parent topic: Map Request Examples
3.1.1.7 Map Request for Image of Map Legend Only
Example 3-7 requests a map with just the image of the map legend, but without rendering any spatial data. In this example, the legend explains the symbology used for identifying cities, state boundaries, interstate highways, and county population density. (Map legends are explained in map_request Attributes.)
Example 3-7 Map Request for Image of Map Legend Only
<?xml version="1.0" standalone="yes"?>
<map_request datasource="mvdemo"
format="PNG_URL">
<legend bgstyle="fill:#ffffff;stroke:#ff0000"
profile="MEDIUM"
position="SOUTH_EAST">
<column>
<entry text="Map Legend"
is_title="true" />
<entry style="M.STAR"
text="center point" />
<entry style="M.CITY HALL 3"
text="cities" />
<entry is_separator="true" />
<entry style="C.ROSY BROWN STROKE"
text="state boundary" />
<entry style="L.PH"
text="interstate highway" />
<entry text="County population:" />
<entry style="V.COUNTY_POP_DENSITY"
tab="1" />
</column>
</legend>
</map_request>Generating just the map legend image, as in Example 3-7, can save processing time if you display the stored map legend image on a web page separately from the actual displayed maps. This avoids the need to generate a legend each time there is a map request.
Parent topic: Map Request Examples
3.1.1.8 Map Request with SRID Different from Data SRID
Example 3-8 requests a map displayed in a coordinate system (srid="32775"
for US - Equal Area Projection) that is different from the coordinate system
associated with the county theme data (jdbc_srid="8265" for
Longitude/Latitude - NAD 83). As a result, during the rendering process, MapViewer
converts all geometries from the data SRID to the map request SRID.
If no coordinate system is associated with the theme data, MapViewer assumes that the data is associated with the coordinate system of the map request, and no conversion occurs.
Example 3-8 Map Request with SRID Different from Data SRID
<?xml version="1.0" standalone="yes"?>
<map_request title="US Counties: Equal-Area Projection (SRID=32775)"
datasource="mvdemo"
srid="32775"
width="500"
height="375"
bgcolor="#a6caf0"
antialiase="true"
format="PNG_URL">
<center size="4000000.0">
<geoFeature>
<geometricProperty typeName="center">
<Point>
<coordinates>-218191.9643,1830357.1429</coordinates>
</Point>
</geometricProperty>
</geoFeature>
</center>
<themes>
<theme name="county_th"
user_clickable="false">
<jdbc_query spatial_column="geom"
render_style="C.COUNTIES"
jdbc_srid="8265"
datasource="mvdemo"
asis="false">select geom from counties</jdbc_query>
</theme>
</themes>
</map_request>Parent topic: Map Request Examples
3.1.1.9 Map Request Using a Pie Chart Theme
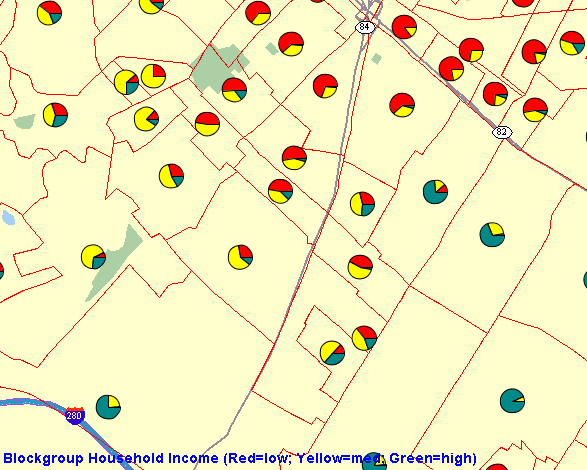
This section shows how to use thematic mapping with a pie chart theme. The result is a map in which each county contains a pie chart in which the size of each slice reflects the proportion of the population in a specified household income level category (low, medium, or high) in the county.
The basic steps are as follows.
- Create an advanced style that defines the characteristics of the pie
charts to be used. The following example creates an advanced style named
V.PIECHART1.INSERT INTO user_sdo_styles VALUES ( 'V.PIECHART1', 'ADVANCED', null, '<?xml version="1.0"?> <AdvancedStyle> <PieChartStyle pieradius="10"> <PieSlice name="low" color="#ff0000" /> <PieSlice name="medium" color="#ffff00" /> <PieSlice name="high" color="#00ff00" /> </PieChartStyle> </AdvancedStyle>', null, null);When the style defined in the preceding example is applied to a geographic feature, a pie chart is created with three slices. The
pieradiusattribute specifies the size of each pie chart in pixels. Each slice (<PieSlice>element) has a color defined for it. Thenameattribute for each slice is ignored by MapViewer. - Create a new theme that uses the style that you created, as in the following
example:
INSERT INTO user_sdo_themes VALUES ( 'THEME_PIE_CHART', null, 'COUNTIES', 'GEOM', '<?xml version="1.0" standalone="yes"?> <styling_rules> <rule column="INC_LOW,INC_MED,INC_HIGH"> <features style="C.US MAP YELLOW" /> <label column="''dummy''" style="V.PIECHART1"> 1 </label> </rule> </styling_rules>');In the theme definition in the preceding example, the
<label>element of the styling rule specifiesstyle="V.PIECHART1", to indicate that this pie chart style (the style created in Step 1) is used to label each geometry displayed on the map.The column attribute (
column="''dummy''"in this example) is required, even though it has no effect on the resulting map. The column attribute value can be dummy or any other string, and the value must be enclosed on both sides by two single quotation marks.Because the
V.PIECHART1style is defined with three slices, the preceding example must specify the names of three columns from theCOUNTIEStable, and these columns must have a numeric data type. The column names areINC_LOW,INC_MED, andINC_HIGH. These columns will supply the value that will be used to determine the size of each pie slice. - Issue a map request that uses the theme that you created. Example 3-9 requests a map that uses the
THEME_PIE_CHARTtheme that was created in Step 2.
Example 3-9 Map Request Using a Pie Chart Theme
<?xml version="1.0" standalone="yes"?>
<map_request datasource="mvdemo"
format="PNG_STREAM">
<themes>
<theme name="THEME_PIE_CHART" />
</themes>
</map_request>The following figure shows part of a display resulting from the map request in Example 3-9.
Figure 3-1 Map Display Using a Pie Chart Theme
You can also use the pie chart style in a dynamic (JDBC) theme when issuing a map request. You must specify the complete SQL query for a JDBC theme in the map request, because you must identify the attribute columns that are needed by the pie chart style. Any columns in the SELECT list that are not SDO_GEOMETRY columns or label columns are considered to be attribute columns that can be used by an advanced style.
Example 3-10 JDBC Theme Using a Pie Chart Style
The following example is a sample request with a JDBC theme using a pie
chart style. The SQL query (SELECT geom, 'dummy', sales, service, training
FROM support_centers) is included in the theme definition.
<?xml version="1.0" standalone="yes"?>
<map_request basemap="CA_MAP"
datasource="mvdemo"
format="PNG_URL">
<themes>
<theme name="support_center">
<jdbc_query spatial_column="geom"
datasource="tilsmenv"
label_column="dummy"
label_style="V.PIECHART1">
SELECT geom, 'dummy', sales, service, training
FROM support_centers
</jdbc_query>
</theme>
</themes>
</map_request>Parent topic: Map Request Examples
3.1.1.10 Map Request Using Ratio Scale and Mixed Theme Scale Modes
Example 3-11 requests a map specifying a center and a ratio scale to define the map area. Two
themes are used: a predefined theme named THEME_US_COUNTIES1, which
uses the default screen inch scale mode, and a JDBC theme names
STATES_TH, which uses the ratio mode.
Example 3-11 Map Request Using Ratio Scale and Mixed Theme Scale Modes
<?xml version="1.0" standalone="yes"?>
<map_request title="States (ratio), counties (screen inch), center and scale"
datasource="tilsmenv"
width="500"
height="400"
bgcolor="#a6caf0"
antialiase="true"
format="PNG_URL">
<center scale="5000000">
<geoFeature>
<geometricProperty typeName="center">
<Point>
<coordinates>-90.0,32.0</coordinates>
</Point>
</geometricProperty>
</geoFeature>
</center>
<themes>
<theme name="STATES_TH"
min_scale="5.0E7"
max_scale="1.0E7"
scale_mode="ratio">
<jdbc_query label_column="STATE"
spatial_column="geom"
label_style="T.STATE NAME"
render_style="C.COUNTIES"
jdbc_srid="8265"
datasource="tilsmenv"
asis="false">
select geom,state from states
</jdbc_query>
</theme>
<theme name="THEME_US_COUNTIES1"
min_scale="2.286" />
</themes>
</map_request>Parent topic: Map Request Examples
3.1.1.11 Map Request Using Predefined Theme (Binding Parameter and Custom Type)
Example 3-12 requests a map using a predefined theme with a styling rule that selects all counties where a state abbreviation is in the selection list. When the predefined theme is created, the selection list is represented as a binding parameter, as follows:
INSERT INTO user_sdo_themes VALUES (
'COUNTIES_BY_STATES', null, 'COUNTIES', 'GEOM',
'<styling_rules>
<rule>
<features style="C.COUNTIES"> (state_abrv in (select column_value from table(:1))) </features>
<label column="COUNTY"
style="T.CITY NAME"> 1 </label>
</rule>
</styling_rules>');This binding parameter can accept one or more values, for which you can create a custom SQL data type that represents this set of values, as follows:
CREATE OR REPLACE TYPE string_array AS TABLE OF VARCHAR2(64);
Then, you can use this custom data type on the binding parameter of the map request, as shown in Example 3-12.
Example 3-12 Map Request Using Predefined Theme (Binding Parameter and Custom Type)
<?xml version="1.0" standalone="yes"?>
<map_request title="Binding Parameters and STRING_ARRAY type"
datasource="mvdemo"
width="640"
height="480"
bgcolor="#a6cae0"
antialiase="false"
format="PNG_STREAM">
<themes>
<theme name="COUNTIES_BY_STATES">
<binding_parameters>
<parameter value="FL,ME,CA,OH" type="STRING_ARRAY" />
</binding_parameters>
</theme>
</themes>
</map_request>Parent topic: Map Request Examples
3.1.1.12 Map Request Using Advanced Styles and Rendering Rules
Example 3-13 requests a map using the <rendering> element, and it
combines two advanced styles that are based on different columns. In this example,
an advanced style named POPVMK is based on column
POP90, and another advanced style named
EQRBRANK is based on column RANK90. Point
features (from the CITIES table) are rendered. The shape of the
feature is defined by the advanced style associated with column
POP90, and the feature color is defined by the advanced style
associated with column RANK90.
Example 3-13 Map Request Using Advanced Styles and Rendering Rules
<?xml version="1.0" standalone="yes"?>
<map_request title="Cross advanced styles"
datasource="mvdemo"
width="640"
height="480"
bgcolor="#a6caf0"
antialiase="false"
format="PNG_STREAM">
<center size="7.7">
<geoFeature>
<geometricProperty typeName="center">
<Point>
<coordinates>-72.96,41.25</coordinates>
</Point>
</geometricProperty>
</geoFeature>
</center>
<themes>
<theme name="cities">
<jdbc_query label_column="city"
spatial_column="location"
label_style="T.CITY NAME"
jdbc_srid="8265"
datasource="mvdemo"
asis="false">
select location,city,pop90,rank90 from cities
</jdbc_query>
<rendering>
<style name="POPVMK"
value_columns="POP90">
<substyle name="EQRBRANK"
value_columns="RANK90"
changes="FILL_COLOR" />
</style>
</rendering>
</theme>
</themes>
<styles>
<style name="STAR_TRANSP">
<svg width="1in"
height="1in">
<desc />
<g class="marker"
style="stroke:#000000;fill:#FF0000;fill-opacity:0;width:15;height:15;font-family:Dialog;font-size:12;font-fill:#FF0000">
<polyline points="138.0,123.0,161.0,198.0,100.0,152.0,38.0,198.0,61.0,123.0,0.0,76.0,76.0,76.0,100.0,0.0,123.0,76.0,199.0,76.0" />
</g>
</svg>
</style>
<style name="POPVMK">
<AdvancedStyle>
<VariableMarkerStyle basemarker="STAR_TRANSP"
startsize="7"
increment="5">
<Buckets>
<RangedBucket seq="0"
label="100217 - 1905803.75"
low="100217"
high="1905803.75" />
<RangedBucket seq="1"
label="1905803.75 - 3711390.5"
low="1905803.75"
high="3711390.5" />
<RangedBucket seq="2"
label="3711390.5 - 5516977.25"
low="3711390.5"
high="5516977.25" />
<RangedBucket seq="3"
label="5516977.25 - 7322564"
low="5516977.25"
high="7322565" />
</Buckets>
</VariableMarkerStyle>
</AdvancedStyle>
</style>
<style name="EQRBRANK">
<AdvancedStyle>
<BucketStyle>
<Buckets low="1"
high="196"
nbuckets="4"
styles="C.RED,C.RB13_1,C.RB13_6,C.SEQ6_01" />
</BucketStyle>
</AdvancedStyle>
</style>
</styles>
<legend bgstyle="fill:#ffffff;fill-opacity:50;stroke:#ff0000"
profile="SMALL"
position="SOUTH_EAST">
<column>
<entry text="Map Legend"
is_title="true" />
<entry text="POP90:" />
<entry style="POPVMK"
tab="1" />
<entry text="RANK90:" />
<entry style="EQRBRANK"
tab="1" />
</column>
</legend>
</map_request>Parent topic: Map Request Examples
3.1.1.13 Map Request Using Stacked Styles
Example 3-14 requests a map using the <rendering> element, and it
defines multiple styles (C.COUNTIES and PIECHART1) to be applied on
each theme feature.
Example 3-14 Map Request Using Stacked Styles
<?xml version="1.0" standalone="yes"?>
<map_request title="Theme with Stacked Styles"
datasource="mvdemo"
width="600"
height="450"
bgcolor="#a6caf0"
antialiase="true"
format="PNG_STREAM">
<center size="18">
<geoFeature>
<geometricProperty typeName="center">
<Point>
<coordinates>-122.729,40.423</coordinates>
</Point>
</geometricProperty>
</geoFeature>
</center>
<themes>
<theme name="STACKEDSTYLES">
<jdbc_query label_column="state"
spatial_column="geom"
label_style="T.STATE NAME"
jdbc_srid="8265"
datasource="mvdemo"
asis="false">
select geom,state,HHI0_10,HHI10_15,HHI100UP,HHI15_25,HHI25_35 from states
</jdbc_query>
<rendering>
<style name="C.COUNTIES" />
<style name="PIECHART1"
value_columns="HHI0_10,HHI10_15,HHI100UP,HHI15_25,HHI25_35" />
</rendering>
</theme>
</themes>
<styles>
<style name="piechart1">
<AdvancedStyle>
<PieChartStyle pieradius="10">
<PieSlice name="A"
color="#FFFF00" />
<PieSlice name="B"
color="#000000" />
<PieSlice name="H"
color="#FF00FF" />
<PieSlice name="I"
color="#0000FF" />
<PieSlice name="W"
color="#FFFFFF" />
</PieChartStyle>
</AdvancedStyle>
</style>
</styles>
</map_request>Parent topic: Map Request Examples
3.1.1.14 WFS Map Requests
This section contains examples of WFS map requests, one using a predefined theme and one using a dynamic theme.
Example 3-15 requests a map using a predefined WFS theme named BC_MUNICIPALITY, which is defined as follows:
INSERT INTO user_sdo_themes VALUES (
'BC_MUNICIPALITY',
'WFS theme',
'BC_MUNICIPALITY',
'THE_GEOM',
'<?xml version="1.0" standalone="yes"?>
<styling_rules theme_type="wfs"
service_url="http://www.refractions.net:8080/geoserver/wfs/GetCapabilities?"
srs="EPSG:3005">
<rule>
<features style="C.BLUE" />
<label column="name"
style="T.CITY NAME"> 1 </label>
</rule>
</styling_rules>');Example 3-15 Map Request Using Predefined WFS Theme
I<?xml version="1.0" standalone="yes"?>
<map_request title="Predefined WFS MAP"
datasource="mvdemo"
width="640"
height="480"
bgcolor="#a6cae0"
antialiase="true"
format="PNG_STREAM">
<center size="76000">
<geoFeature>
<geometricProperty typeName="center">
<Point>
<coordinates>1260500,470000</coordinates>
</Point>
</geometricProperty>
</geoFeature>
</center>
<themes>
<theme name="bc_municipality" />
</themes>
</map_request>Example 3-16 shows a map request that uses a dynamic WFS theme.
Example 3-16 Map Request Using Dynamic WFS Theme
<?xml version="1.0" standalone="yes"?>
<map_request title="WFS MAP"
datasource="mvdemo"
width="640"
height="480"
bgcolor="#a6cae0"
antialiase="true"
format="PNG_STREAM">
<center size="76000">
<geoFeature>
<geometricProperty typeName="center">
<Point>
<coordinates>1260500,470000</coordinates>
</Point>
</geometricProperty>
</geoFeature>
</center>
<themes>
<theme name="wfs">
<wfs_feature_request service_url="http://www.refractions.net:8080/geoserver/wfs/GetCapabilities?"
srs="EPSG:3005"
feature_name="bc_hospitals"
spatial_column="the_geom"
render_style="M.STAR"
label_column="name"
label_style="T.CITY NAME"
datasource="mvdemo" />
</theme>
</themes>
</map_request>Example 3-17 shows a map request for a dynamic WFS theme with an advanced style to render features.
Example 3-17 Map Request Using Dynamic WFS Theme with an Advanced Style
<?xml version="1.0" standalone="yes"?>
<map_request title="WFS Theme with Advanced Style"
datasource="mvdemo"
width="640"
height="480"
bgcolor="#a6cae0"
antialiase="true"
format="PNG_STREAM">
<center size="10.">
<geoFeature>
<geometricProperty typeName="center">
<Point>
<coordinates>-70., 44.</coordinates>
</Point>
</geometricProperty>
</geoFeature>
</center>
<themes>
<theme name="wfs">
<wfs_feature_request service_url="http://199.29.1.81:8181/miwfs/GetFeature.ashx?"
srs="EPSG:4326"
feature_name="usa"
spatial_column="obj"
render_style="CBSTATES"
label_column="STATE_NAME"
label_style="T.CITY NAME"
feature_attributes="state"
datasource="mvdemo" />
</theme>
</themes>
<styles>
<style name="CBSTATES">
<AdvancedStyle>
<BucketStyle>
<Buckets default_style="C.COUNTIES">
<CollectionBucket seq="0"
type="string"
style="C.RB13_13">MA</CollectionBucket>
<CollectionBucket seq="1"
type="string"
style="C.RB13_1">NH</CollectionBucket>
<CollectionBucket seq="2"
type="string"
style="C.RB13_7">ME</CollectionBucket>
</Buckets>
</BucketStyle>
</AdvancedStyle>
</style>
</styles>
</map_request>Parent topic: Map Request Examples
3.1.1.15 Java Program Using MapViewer
Example 3-18 uses the java.net package to send an XML request to MapViewer and to receive the response from MapViewer.
Example 3-18 shows a map request that renders this predefined WFS theme.Example 3-18 Java Program That Interacts with MapViewer
import java.net.*;
import java.io.*;
/**
* A sample program that shows how to interact with MapViewer
*/
public class MapViewerDemo {
private HttpURLConnection mapViewer = null;
/**
* Initializes this demo with the URL to the MapViewer server.
* The URL is typically http://my_corp.com:8888/mapviewer/omserver.
*/
public MapViewerDemo(String mapViewerURLString) {
URL url;
try {
url = new URL(mapViewerURLString);
mapViewer = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
mapViewer.setDoOutput(true);
mapViewer.setDoInput(true);
mapViewer.setUseCaches(false);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace(System.err);
System.exit(1);
}
}
/**
* Submits an XML request to MapViewer.
* @param xmlreq the XML document that is a MapViewer request
*/
public void submitRequest(String xmlreq) {
try {
mapViewer.setRequestMethod("POST"); //Use HTTP POST method.
OutputStream os = mapViewer.getOutputStream();
//MapViewer expects to find the request as a parameter
//named "xml_request".
xmlreq = "xml_request=" + URLEncoder.encode(xmlreq);
os.write(xmlreq.getBytes());
os.flush();
os.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace(System.err);
System.exit(1);
}
}
/**
* Receives an XML response from MapViewer.
*/
public String getResponse() {
ByteArrayOutputStream content = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
InputStream is = null;
try {
is = mapViewer.getInputStream();
int c;
while ((c = is.read()) != -1)
content.write(c);
is.close();
content.flush();
content.close();
return content.toString();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace(System.err);
return null;
}
}
// A simple main program that sends a list_data_sources XML
// request to MapViewer through HTTP POST
public static void main(String[] args) {
if (args.length < 1) {
System.out.println("Usage: java MapViewerDemo <mapviewer url>");
System.out.println("Example: java MapViewerDemo http://my_corp.com/mapviewer/omserver");
System.exit(1);
}
// A sample XML request for MapViewer
String
listDataSources = "<?xml version=\"1.0\" standalone=\"yes\"?>" +
" <non_map_request>" +
" <list_data_sources/>" +
" </non_map_request>";
MapViewerDemo tester = null;
tester = new MapViewerDemo(args[0]);
System.out.println("submitting request:\n" + listDataSources);
tester.submitRequest(listDataSources);
String response = tester.getResponse();
System.out.println("response from MapViewer: \n" + response);
}
}Parent topic: Map Request Examples
3.1.1.16 PL/SQL Program Using MapViewer
Example 3-19 is a sample PL/SQL program that sends an XML request to the MapViewer server.
Example 3-19 PL/SQL Program Using MapViewer
set serverout on size 1000000;
--
-- Author: Clarke Colombo
--
declare
l_http_req utl_http.req;
l_http_resp utl_http.resp;
l_url varchar2(4000):= 'http://my_corp.com:8888/mapviewer/omserver';
l_value varchar2(4000);
img_url varchar2(4000);
response sys.xmltype;
output varchar2(255);
map_req varchar2(4000);
begin
utl_http.set_persistent_conn_support(TRUE);
map_req := '<?xml version="1.0" standalone="yes"?>
<map_request title="MapViewer Demonstration"
datasource="mvdemo"
basemap="course_map"
width="500"
height="375"
bgcolor="#a6cae0"
antialiasing="false"
format="GIF_URL">
<center size="5">
<geoFeature>
<geometricProperty>
<Point>
<coordinates>-122.2615, 37.5266</coordinates>
</Point>
</geometricProperty>
</geoFeature>
</center>
</map_request>';
l_http_req := utl_http.begin_request(l_url, 'POST', 'HTTP/1.0');
--
-- Sets up proper HTTP headers.
--
utl_http.set_header(l_http_req, 'Content-Type', 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded');
utl_http.set_header(l_http_req, 'Content-Length', length('xml_request=' || map_req));
utl_http.set_header(l_http_req, 'Host', 'my_corp.com');
utl_http.set_header(l_http_req, 'Port', '8888');
utl_http.write_text(l_http_req, 'xml_request=' || map_req);
--
l_http_resp := utl_http.get_response(l_http_req);
utl_http.read_text(l_http_resp, l_value);
response := sys.xmltype.createxml (l_value);
utl_http.end_response(l_http_resp);
img_url := response.extract('/map_response/map_image/map_content/@url').getstringval();
dbms_output.put_line(img_url);
end;
/Parent topic: Map Request Examples