Understand Local Inverted File Flat Vector Indexes
A local IVF index can be used to accelerate search queries. With local IVF indexes, there is a one-to-one relationship between the base table partitions or subpartitions and the index partitions.
Local IVF index creation and DML operations on base tables with IVF indexes can be accelerated if Vector Pool is enabled. Vector Pool is a new memory area stored in the SGA. For more information related to Vector Pool, see Size the Vector Pool.
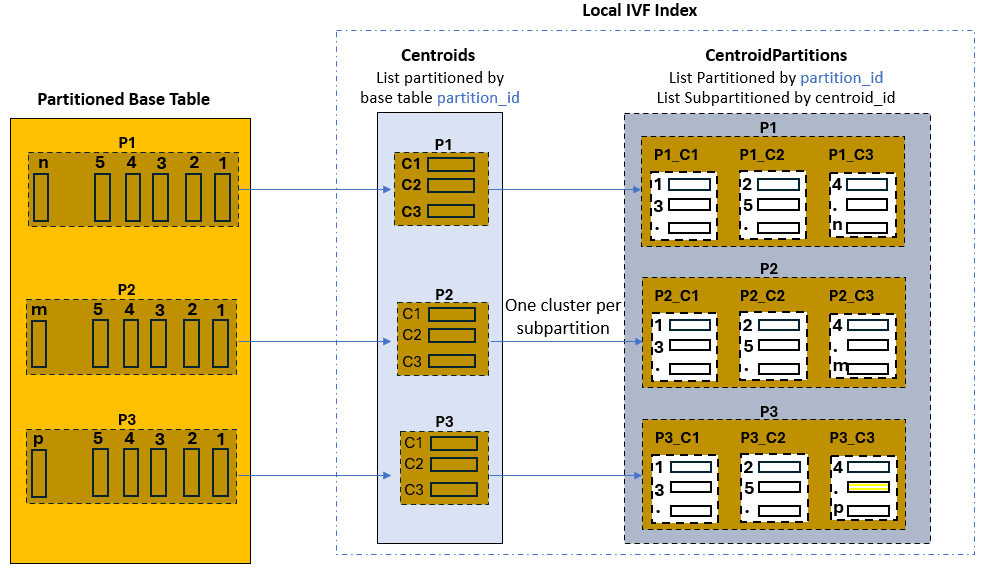
This is illustrated by the following graphic, where the base table has three partitions. The created local IVF index is constituted by two internal tables:
-
One called
VECTOR$<base table name>_IVF_IDX$<object info>$IVF_FLAT_CENTROIDS, which is list-partitioned by base table partition ids, and is thus equi-partitioned with the base table. Each partition contains the list of corresponding identified centroid vectors and associated ids. -
The second called
VECTOR$<base table name>_IVF_IDX$<object info>$IVF_FLAT_CENTROID_PARTITIONS, which is list-partitioned by base table partition id and list-subpartitioned by centroid id. This table is also equi-partitioned with the base table, and each subpartition contains the base table vectors closely related (cluster) to the corresponding centroid id for that subpartition.
If, for example, you search the top-10 houses in California similar to a vectorized picture, your query benefits from partition pruning on the base table and Centroids table (California) as they are both partitioned by state. Once the closest centroid is identified in that partition, the query simply needs to scan the corresponding centroid cluster subpartition in the Centroid Partitions table without having to scan other centroid subpartitions.
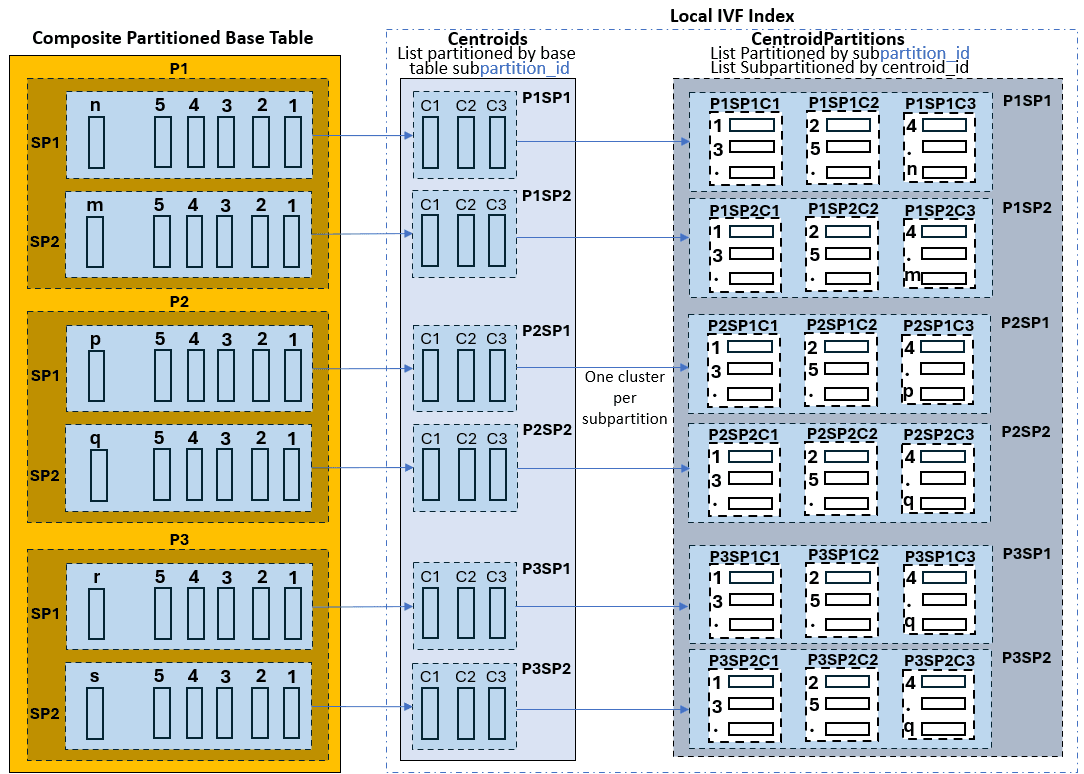
Another possibility is for the base table to be composite partitioned. Here is a graphical representation corresponding to that case. The Centroids table is list-partitioned according to base table subpartitions. Each partition in the Centroids table contains all centroid vectors found in the corresponding base table subpartition. The Centroid Partitions table is list-partitioned by base table subpartition id, and is further subpartitioned by centroid id:
Note:
-
You can create local IVF indexes only on a partitioned base table.
-
Local IVF indexes inherit all system catalog tables and views used by regular local indexes. A flag (
idx_spare2) in thevecsys.vector$indextable indicates if an index is a local or global vector index. -
ALTER INDEXon local IVF indexes is not supported. - If a Partition Maintenance Operation (PMOP), such as
ALTER TABLE SPLIT/MERGE/MOVE/EXCHANGE/COALECSE, is performed on the base table, all corresponding IVF index partitions are marked asUNUSABLEafter the operation. -
Partition Maintenance Operations are not supported with local IVF indexes.
Using local IVF indexes brings additional advantages:
-
Simplified Partition Maintenance Operations:
For example, dropping a table partition just involves dropping the corresponding index partition.
-
Flexible Indexing schemes:
For example, marking certain index partitions
UNUSABLEto avoid indexing certain table partitions through partial indexing.
Note:
If you want your user queries to use the full potential of local IVF indexes by taking advantage of the benefit of partition pruning, user queries must have partition pruning conditions.
Parent topic: Neighbor Partition Vector Index