2 Installing and Configuring Oracle REST Data Services
This chapter describes how to install, configure, and upgrade Oracle REST Data Services (ORDS).
2.1 Installing Oracle REST Data Services
Note:
The procedures in this topic apply to installing Oracle REST Data Services in a non-CDB Database or a PDB. For setting up ORDS in a CDB environment, refer to Using the Multitenant Architecture with Oracle REST Data Services section.
If you are planning to use the Oracle API for MongoDB, then you must install Oracle REST Data Services in a non-CDB or PDB. See Enabling and Configuring the Oracle Database API for MongoDB for more information.
You can then install ORDS using one of the following options:
2.1.1 Downloading ORDS
This section describes the how to download ORDS.
Downloading ORDS Zip file
Download the ords_<latest>.zip file from the Oracle
REST Data Services (ORDS) download page, and then unzip
ords_<latest>.zip file into a folder of your choice. The
folder you choose to unzip the file is referred to as the ORDS product folder. The
ORDS product folder contains a bin folder and other folders and
files required to run ORDS.
bin folder to your Operating System PATH
Oracle recommends to add the ORDS bin folder to your
operating system PATH environment variable.
echo -e 'export PATH="$PATH:/<ords product folder>/bin"' >> ~/.bash_profileStart a new shell to pick up this change.
SetX PATH "%PATH%;<ords product folder>\bin"Start a new command prompt to pick up this change.
echo -e 'export PATH="$PATH:/<ords product folder>/bin"' >> ~/.zprofileStart a new terminal to pick up this change.
Downloading ORDS Using yum
ORDS is published in OL7 and OL8 repositories. The system administrator can then add this repository to the yum configuration in order to install the ORDS and handle its dependencies.
OL7 repo: https://yum.oracle.com/repo/OracleLinux/OL7/oracle/software/x86_64/
OL8 repo: https://yum.oracle.com/repo/OracleLinux/OL8/oracle/software/x86_64/
sudo yum install ordsThe preceding command handles all the ORDS dependencies and place the
ORDS program in /usr/local/bin/ords folder to set up your ORDS
configuration and install or upgrade ORDS in the database.
/etc/ords/conf
configuration directory. The following comand is used to configure
ORDS:ords -–config /etc/ords/config installconfig directory in /etc/ords.conf
folder.
Installing ORDS Using RPM
sudo rpm -i ords-22.1.X-X.elX.noarch.rpm/usr/local/bin/ords folder to set up
your ORDS configuration and install or upgrade ORDS in the database.
/etc/ords/conf folder with the following
command:ords -–config /etc/ords/config install/etc/ords.conf folder.
2.1.2 Setting Up the Configuration Folder Structure
This section describes how to set up the configuration folder structure.
2.1.2.1 Specifying the New ORDS Configuration Folder
New installation has the ORDS configuration files placed in the configuration folder. Configuration files from ORDS release 21.4.x or earlier are migrated to the configuration folder.
- Command option:
Use the
--configoption to specify your configuration folder.Example:
ords --config /path/to/conf install - Environment variable:
Note:
This option is preferred if you forget to include the--configoption when you are using the ORDS command-line Interface.ORDS_CONFIG: Create theORDS_CONFIGenvironment variable.Example for LINUX or UNIX operating system:
Shell script containing ORDS_CONFIG cat example_env export ORDS_CONFIG=/path/to/conf echo $ORDS_CONFIG /path/to/conf
- Current Working Directory:
If the
--config <configuration_folder>option is not specified, and theORDS_CONFIGenvironment variable is not defined, then your current working directory is used as the configuration folder.Example:
If your current working directory is
/path/to/conf, then it uses that location for your configuration folder.
Note:
-
Oracle highly recommends you to ensure that ORDS does not create the configuration directory in the ORDS product folder. For example, you can have a configuration folder in the following location:
/Users/<user_name>/work/dbtools-dev/config/The best practice is to have your configuration files separate from the application files, this makes maintenance and upgrades easier and more reliable.
-
The following command is no longer valid:
Example:
java -jar ords.war installIf you specify the legacy commands using
java -jar ords.war, you get the following warning message:Warning: Support for executing:
java -jar ords.warhas been deprecated. Please add ords to your PATH and use the ords command instead. Run the following command to add ORDS to yourPATH:<Displays an example of adding the bin folder to your PATH>Start a new terminal to pick up this change. Oracle recommends to add the ORDS product
binfolder to your path.
2.1.3 Interactive Command-Line Interface Installation
This section explains various scenarios that use the auto-installation feature found in the interactive Command-Line Interface (CLI) installation prompts.
Table 2-1 ORDS CLI Commands
| ORDS CLI Command | Description |
|---|---|
ords install |
Creates a database pool or upgrades ORDS in existing database pool(s). Generates an upgrade script if more than one database pool exists in the ORDS configuration. |
ords install -i --db-only |
Install or upgrade ORDS that are in the database pools, or specify the database connection. Generates upgrade script if more than one database pool exists in the ORDS configuration. With this command, ORDS configuration is neither created nor updated. |
ords install -i --config-only |
Creates or updates a database pool. This command does not install or upgrade ORDS in the database. |
Configuration Folder
Specify the install command without specifying the --config <CONFIG
FOLDER> option. This assumes that the configuration directory is specified
through the environment variable, or you are defaulting to the current working
directory.
ords installords install -i --config-onlyords install -i --db-only
Specify the install command using the --config <CONFIG
FOLDER> option. Depending on the ORDS CLI commanda used, ORDS uses that
configuration folder to create or update the configuration or read the existing
configuration from that <CONFIG FOLDER> location.
ords --config /path/to/myconfig installords --config /path/to/myconfig install -i --config-onlyords --config /path/to/myconfig install -i --db-only
2.1.3.1 Auto Installation of ORDS
Starting with Oracle REST Data Services (ORDS) release 24.1, auto installation feature is introduced.
Auto-Install operation, discovers the database connections and display them to the user. Creating a database pool is much simpler and default settings are used to minimize the prompting to the user. If a bequeath connection is available, then it is used to retrieve the information from the database, and install or upgrade ORDS in the database without using the credentials of the administrator user.
Following are some of the scenarios demonstrating auto-installation feature:
2.1.3.1.1 Scenario 1: New ORDS Configuration and ORDS Installation
This section explains the interactive command-line interface (CLI) installation prompts for creating a new ORDS configuration.
ords installWhen you run the preceding command, the interactive inataller detects that an ORDS configuration does not exist. A default database pool is created. Refer to Creating an Additional Database Pool, you are prompted to create the default database pool and to install ORDS in the database.
2.1.3.1.2 Scenario 2: Single Database Pool (Default Pool)
ords installWhen you
create a new ORDS configuration, a default pool is created. This scenario indicates
that there is only one database pool, known as the default database
pool. You have the option to select the default database pool and upgrade ORDS in
the database. You also have the option to create an additional database
pool.
Table 2-2 Prompts for Single Database Pool
| Prompt | Description |
|---|---|
|
Refer to |
2.1.3.1.3 Scenario 3: Multiple Database Pools
In this scenario, if more than one database pools exist in your configuration, you have the option to upgrade ORDS in an existing database pool, generate an upgrade script, specify the database pool to upgrade ORDS or create an additional database pool.
Displays a list of the database pools in your configuration. The default database pool is displayed first followed by the other database pools in an alphabetical order.
Run the following ORDS CLI command:ords installTable 2-3 Prompts for Multiple Database Pools
| Prompt | Description |
|---|---|
|
If the total number of database pools is greater
than 9, then the option |
2.1.3.1.4 Scenario 4: Add or Update Configuration Only
ords install -i --config-onlyUsing this scenario, you can update an existing database pool or create
a database pool. The --config-only option does not perform the
install or upgrade ORDS in the database operation.
Table 2-4 Prompts for Add/Update Configuration Only
| Prompt | Description |
|---|---|
|
Refer to: |
2.1.3.1.5 Scenario 5: Install or Upgrade ORDS in Database Only
ords install -i --db-only- upgrade ORDS in an existing database pool
- generate an upgrade script
- specify the database connection or database pool to install or upgrade ORDS in the database
Displays a list of the database pools in your configuration.
The default database pool is displayed first,
followed by the other database pools in alphabetical order. A maximum of 9 database
pools are displayed. If the maximum number of database pools is reached, the option
"Specify the database pool name to upgrade ORDS" is displayed.
Table 2-5 Prompts for Install or Upgrade ORDS in Database Only
| Prompt | Description |
|---|---|
|
If the total number of database pools is greater than 9,
then the option Specify the database pool name to upgrade
ORDS is displayed.
|
2.1.3.1.5.1 Entering a Number to Select the Database Pool
The database pool(s) and its connections are displayed. Enter the number to select the database pool that you want to install or upgrade ORDS in the database. The installer installs ORDS in the database if ORDS does not exist in the database. The installer upgrades ORDS in the database if the ORDS schema version is less than the ORDS product version that you are using.
2.1.3.1.6 Creating an Additional Database Pool
Create an additional database pool option
The Create an additional database pool option, prompts you for the following information:
- Database pool name
- If a database pool already exists in your ORDS
configuration, then you are prompted for the database pool name.
Note:
If you are creating a new ORDS configuration, then you are not prompted for the database pool name since it creates the default database pool.
- If a database pool already exists in your ORDS
configuration, then you are prompted for the database pool name.
- Connection information
- Shows the TNS Net service names from the
tnsnames.orafile. You have the option to select the TNS Net service name.- Automatically locates the
tnsnames.orafile in your folders
- Automatically locates the
- Specify the database connection (
Basic,TNSorCustom URL).
- Shows the TNS Net service names from the
- Administrator username and password
Note:
If you are using Bequeath Connection and the host and servicename or sid exists in the database, then you are not prompted for the administrator username and password. - Multiple options to update the database pool and standalone configuration
- Connection information
- Runtime user
ORDS_PUBLIC_USERpassword - Default and temporary tablespaces for the ORDS runtime user and the ORDS schema
- Additional ORDS Feature
- Standalone Mode Configuration
- HTTP/HTTPS Protocol
- Protocol port
- Certificate Type for HTTPS Protocol
- Self-Signed Certificate
- User provides the Certificate
- APEX Static Resources Location
Note:
If APEX exists in the database, then theAPEX static resources locationoption is displayed.
The multiple options for the database pool and standalone configuration are displayed
and enables you to make any updates. If you are satisfied with the values that are
displayed, then select option A to accept and continue. If the
option contains Accept and Continue - Create configuration and Install ORDS in the
database, then the database pool is created and ORDS is installed in the database.
If you enable the option Configure and start ORDS in Standalone
Mode, then the standalone settings are created or updated, and ORDS
runs after the installation completes.
Example 2-1 Creating an Additional Database Pool
Enter the database pool name: database2
Enter a number to select the TNS Net Service Name to use or specify the database connection
[1] TNS name: DB2 SERVICE_NAME=pdb2
[2] TNS name: DB3 SERVICE_NAME=pdb3
[3] TNS name: DB4 SERVICE_NAME=pdb4
[S] Specify the database connection
Choose [1]: 1
Connecting to administrator user: SYS AS SYSDBA for PDB service name: pdb2 using bequeath connection
ORDS is not installed in the database. ORDS installation is required.
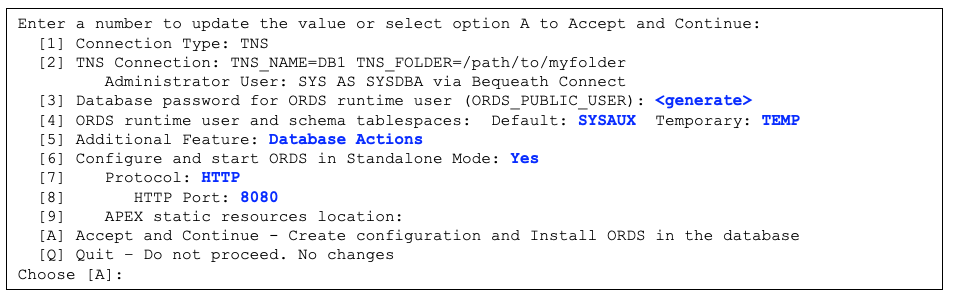
Enter a number to update the value or select option A to Accept and Continue
[1] Connection Type: TNS
[2] TNS Connection: TNS_NAME=DB2 TNS_FOLDER=/path/to/myfolder
Administrator User: SYS AS SYSDBA via Bequeath Connect
[3] Database password for ORDS runtime user (ORDS_PUBLIC_USER): <generate>
[4] ORDS runtime user and schema tablespaces: Default: SYSAUX Temporary TEMP
[5] Additional Feature: Database Actions
[6] Configure and start ORDS in Standalone Mode: Yes
[7] Protocol: HTTPS
[8] HTTPS Port: 8443
[9] Certificate Type: Use Self-Signed Certificate
[10] SSL Hostname: myhost
[11] APEX static resources location: /path/to/apex/images
[A] Accept and Continue - Create configuration and Install ORDS in the database
[Q] Quit - Do not proceed. No changes
Choose [A]:
Table 2-6 Creating an Additional Database Pool Prompts
| Prompt | Description |
|---|---|
|
Prompts for the database pool name if your ORDS configuration already exists and contains a database pool. Note: If you are creating a new configuration, you are not prompted for the database pool name because it creates the database pool nameddefault.
Refer to Entering the Database Pool Name |
|
Refer to |
|
Note: If you are using Bequeath Connection and the host and servicename and sid exists in the database, then you are not prompted for the administrator username or password. |
|
Displays the default values highlighted in blue for the database pool. Displays the Standalone settings that already exists in the ORDS configuration. These settings are displayed after the optionConfigure and start ORDS in
Standalone Mode.
Refer to Multiple Options for Database Pool and Standalone Configuration |
2.1.3.1.6.1 Entering the Database Pool Name
The database pool name displays when you choose the option Create an
Additional Database Pool. Specify the database pool name carefully since it
sets the mapping pattern.
If you select the option c when prompted, then the database pool
name prompt is displayed. Enter the database pool name. For example, if the pool name
you enter is database1, then all the REST requests to that pool starts
with/ords/database1/.
Note:
- The database pool name must only contain lowercase alphabets a-z, digits 0-9, and the characters “-“, “_“ and “.“ .
- When the database pool is created, the database pool folder is also created along with the pool specific settings, and a wallet to store the database user credentials.
- The database pool name also sets the mapping pattern.
If you are creating a new ORDS configuration, then you are not prompted for the database pool name.
2.1.3.1.6.2 Entering a Number to Select the TNS Net Service Name to Use or Specify the Database Connection
A list of the TNS net service name and its service name or SID displays if the
tnsnames.ora file is found in your folder. If the
tnsnames.ora does not exist in your folder, then the database
connection type options are shown.
2.1.3.1.6.3 Entering a Number to Select the Database Connection
Select the database connection type.
Table 2-7 Prompts for Selecting the Database Connection
| Prompt | Description |
|---|---|
|
Refer to: |
2.1.3.1.6.3.1 Entering the Basic Connection
Specify the database host name, database listener port and the service name.
Table 2-8 Entering the Basic Connection Prompts
| Prompt | Description |
|---|---|
|
Refer to Entering the Database Host Name |
|
Refer to Entering the Database Listener Port |
|
Refer to Entering the Database Service Name |
2.1.3.1.6.3.1.1 Entering the Database Host Name
Specify the database host name for the basic connection.
2.1.3.1.6.3.1.2 Entering the Database Listener Port
Specify the database port for a basic connection.
2.1.3.1.6.3.1.3 Entering the Database Service Name
- The service name setting in the ORDS configuration file. If it is not present, then
- It checks for
ORACLE_PDBenvironment variable. If it is undefined, then - It checks for
ORACLE_SIDenvironment variable. If it is undefined, then - It uses
orclas the default value.
2.1.3.1.6.3.2 Entering the TNS Connection
Specify the TNS folder location and select the TNS network alias.
Table 2-9 TNS Connection Prompts
| Prompt | Description |
|---|---|
|
Refer to Entering the TNS Location |
|
Refer to Entering a Number to Select the TNS Network Alias |
2.1.3.1.6.3.3 Entering the Custom URL Connection
Table 2-10 Custom URL Connection Prompt
| Prompt | Description |
|---|---|
|
Refer to Entering the Custom Database URL |
2.1.3.1.6.3.3.1 Entering the Custom Database URL
Specify the custom database URL for custom database URL connection.
jdbc:oracle:<driver>:@//<host>:<port>/<servicename>
jdbc:oracle:thin:@//localhost:1521/orcl
jdbc:oracle:<drivertype>:@(DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=TCP)(HOST=<host>)(PORT=<port>))(CONNECT_DATA=(SERVICE_NAME=<servicename>)))
jdbc:oracle:thin:@(DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=TCP)(HOST=localhost)(PORT=1521))(CONNECT_DATA=(SERVICE_NAME=orcl)))2.1.3.1.7 Multiple Options for Database Pool and Standalone Configuration
If you are creating or updating a database pool, the multiple options display the
database pool and standalone configuration prompts. The standalone configuration options
display after the Configure ORDS and start in Standalone Mode
prompt.
Note:
If a database pool already exists in your ORDS configuration, then the existing standalone settings are displayed.Enter the option number to change the value of the setting. When you are satisfied with the values, press the return key to accept and continue.
2.1.3.1.7.1 Multiple Options with Default Values
- Generate the Runtime user (
ORDS_PUBLIC_USER) password - If you are installing ORDS in the database, the default values for
the default tablespace is
SYSAUXand the temporary tablespace isTEMP.Note:
If any of these tablespaces do not exist, then it uses the database default tablespaces. - The additional feature defaults to
Database Actions. - If you are installing ORDS in standalone mode, then
Configure and Start ORDS in Standalone Modedefaults toYes - Protocol defaults to
HTTP - The default value for Choose is
[A] Accept and Continue
Figure 2-1 Example of Multiple Options with Default Values
Table 2-11 Database Pool and Standalone Configuration Prompts
| Prompt | Description |
|---|---|
|
The type of connection. Displays either Basic, TNS or
Custom URL.
Refer to Entering a Number to Select the Database Connection |
|
Displays Basic Connection if connection type is
Basic.
Refer to Entering the Basic Connection |
|
Displays TNS Connection if connection type is
TNS.
Refer to Entering the TNS Connection |
|
Displays Custom URL Connection if connection type is
Custom URL.
Refer to Entering the Custom URL Connection |
|
Defaults to generate password.
Refer to Entering the Password Option |
|
Displays Tablespace option only if installing ORDS in
the database.
Refer to Entering the Tablespaces |
|
Defaults Additional Feature to Database Actions. |
|
Toggles to Yes or No.
Displays option if installing ORDS in the database and not using the Bequeath Connection. Refer to Standalone Configuration |
|
Toggles to Yes or No
Displays option if
using the Bequeath Connection or the configuration only
( Refer to Standalone Configuration |
|
Defaults Protocol to HTTP. |
|
Defaults HTTP Port to 8080. Displays HTTP Port if protocol is HTTP. |
|
Refer to Entering the APEX Static Resources Location |
|
Refer to Accept and Continue Option |
2.1.3.1.7.1.1 Accept and Continue Option
Once you are done updating and reviewing the values, select option [A]
Accept and Continue. Accept and Continue includes a message on what is
performed. For example, Accept and Continue - Create configuration and Install
ORDS in the database option creates the database pool and ORDS is installed
in the database. If configure ORDS in standalone mode is enabled, then the standalone
configuration is also created or updated.
2.1.3.1.7.1.2 Entering the Password Option
The runtime user password for ORDS_PUBLIC_USER defaults to generate
password. If you want to change the password and specify your own password, select
option S to specify the password. You are prompted twice for the
password.
Table 2-12 Example of the Password Option Prompts
| Prompt |
|---|
|
2.1.3.1.7.1.3 Entering the Tablespaces
SYSAUX and the
default value for the temporary tablespace is TEMP.
Table 2-13 Example of the Tablespaces prompts
| Prompts |
|---|
|
|
2.1.3.1.7.1.4 Entering a Number to Select the Additional Feature
Specify the additional feature that you want to enable.
Table 2-14 Example of Additional Features prompts
| Prompt |
|---|
|
2.1.3.1.7.2 Standalone Configuration
This section explains how to configure Oracle REST Data Services (ORDS) and run in a standalone mode.
Table 2-15 Prompts for standalone configuration
| Prompt | Description |
|---|---|
|
Toggle the option to Note: TheConfigure and start ORDS in Standalone Mode
option is displayed only if you are installing ORDS and you are not
using the bequeath connection.
|
|
You can toggle the option to Yes or
No. A Yes indicates to configure
ORDS in a standalone mode. A No indicates not to make
any standalone configuration changes.
Note:
If ORDS is installed in the database, and you want to
run ORDS in a standalone mode, then use the |
2.1.3.1.7.2.1 Entering a Number to Use HTTP or HTTPS Protocol
Note:
Oracle highly recommends to run ORDS in a standalone mode with HTTPS versus HTTP.2.1.3.1.7.2.2 Entering the HTTPS Port
Specify the HTTPS port. The default HTTPS port is 8443.
Table 2-16 HTTPS Protocol Prompts
| Prompt | Description |
|---|---|
|
Select the protocol (HTTP or HTTPS) that you want to use. |
|
Specify the HTTPS port. The default HTTPS port is 8443. |
|
Refer to: |
2.1.3.1.7.2.3 Entering a Number to Select the Certificate Type
You have the option to select the self-signed certificate that generates automatically when running ORDS in standalone mode, or you provide the SSL certificate which requires both the SSL Certificate and its private key.
2.1.3.1.7.2.4 HTTPS Protocol and Use Self-Signed Certificate
Selecting the prompt Use self-signed certificate prompts
you for the SSL hostname.
Table 2-17 Example of Use Self-Signed Certificate
| Prompt |
|---|
|
ORDS generates the Self-Signed Certificate when running ORDS in a standalone mode.
Table 2-18 HTTPS Protocol and Use Self-Signed Certificate Prompts
| Prompt | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Specify the SSL Hostname. |
2.1.3.1.7.2.5 HTTPS Protocol and Use my SSL Certificate
Selecting Use my SSL Certificate requires you to provide an existing SSL certificate and its private key.
|
Table 2-19 HTTPS Protocol and Use my SSL Certificate Prompts
| Prompt | Description |
|---|---|
|
Refer to Entering a Number to Select the Certificate Type |
|
Refer to Entering the Path for the SSL Certificate |
|
Refer to Entering the Path for the SSL Certificate’s Private Key |
2.1.3.1.7.2.6 Entering the APEX Static Resources Location
ORDS detects if APEX is installed in the database and if the database user
APEX_PUBLIC_USER exists. If found, then it displays
the APEX static resources location option. Provide the folder location of
the APEX images.
2.1.3.1.7.2.7 Generate an Upgrade Script
Selecting the option [G] Generate script to upgrade ORDS in all the database
pools, prompts you for the script location and generates the upgrade
script. The upgrade script contains ORDS non-interactive (silent) command to upgrade
ORDS in the database and includes the database pool to use. You can run this script in
your shell environment.
Table 2-20 Prompts for generating a script to upgrade ORDS
| Prompts |
|---|
|
If you are using the bequeath connection and ORDS exist in the database
based on your database pool connection information such as host, port, servicename/sid,
then the non-interactive (silent) command includes the --bequeath-connect
option.
Example:
ords --config /path/to/myconfig install --db-pool exampledb1 --bequeath-connect --db-onlyOtherwise, you must replace the --admin-user <username> with the
administrator user, and the --password-stdin < <file> with a file
that contains the administrator password.
ords --config /path/to/myconfig install --db-pool <pool> --admin-user <username> --db-only --password-stdin < <file>
ords --config /path/to/myconfig install --db-pool <pool> --admin-user ADMIN --db-only --password-stdin < /path/to/special.txtExample of the Generated Upgrade Script
# ------------------------------------------------------------
# Date : 24 Mar 2024 16:27:05
# Release : Oracle REST Data Services 24.1.0.r0822130
# Type : Generated Upgrade Script
# ------------------------------------------------------------
# ------------------------------------------------------------
# Database : Oracle Database 23c Free
# DB Version : 23.3.0.23.09
# Install/upgrade command using --bequeath-connect option
# ------------------------------------------------------------
ords --config /path/to/myconfig install --bequeath-connect --db-only
ords --config /path/to/myconfig install --db-pool exampledb1 --bequeath-connect --db-only
ords --config /path/to/myconfig install --db-pool exampledb2 --bequeath-connect --db-only
ords --config /path/to/myconfig install --db-pool exampledb3 --bequeath-connect --db-only
ords --config /path/to/myconfig install --db-pool fxdb50 --bequeath-connect --db-only
# ------------------------------------------------------------
# Install/upgrade command using --db-only option
# ------------------------------------------------------------
ords --config /path/to/myconfig install --db-pool hrdb105 --admin-user <username> --db-only --password-stdin < <file>
ords --config /path/to/myconfig install --db-pool sampledb7 --admin-user <username> --db-only --password-stdin < <file>
ords --config /path/to/myconfig install --db-pool sampledb8 --admin-user <username> --db-only --password-stdin < <file>
ords --config /path/to/myconfig install --db-pool sampledb9 --admin-user <username> --db-only --password-stdin < <file>
ords --config /path/to/myconfig install --db-pool testdb111 --admin-user <username> --db-only --password-stdin < <file>
ords --config /path/to/myconfig install --db-pool testdb222 --admin-user <username> --db-only --password-stdin < <file>
ords --config /path/to/myconfig install --db-pool testdb333 --admin-user <username> --db-only --password-stdin < <file>
2.1.3.1.7.2.8 Specify the Database Pool Name to Upgrade ORDS
The option Specify the database pool name to upgrade ORDS prompts
you for the database pool name. If the database pool name exists in your ORDS
configuration, then ORDS is upgraded in the database.
Example:
Enter the database pool name: db12.1.3.1.8 Setup Bequeath Connection for Interactive Install
You can use the bequeath connection to install and upgrade Oracle REST Data Services in the database.
The bequeath connection enables ORDS to connect directly to an Oracle database bypassing the network listener. You can then execute ORDS on the same server as the database.
ORACLE_HOMEORACLE_SIDLD_LIBRARY_PATH (points to the $ORACLE_HOME/lib)
You can then execute one of the following ORDS CLI commands to install ORDS:
ords --java-options "-DuseOracleHome=true" installCreates a database pool or upgrades ORDS that are in the database pool(s).
ords --java-options "-DuseOracleHome=true" install -i --db-onlyInstall or upgrade ORDS that are in the database pools, or specify the database connection. Here, the configuration is not created or updated.
2.1.4 Non-Interactive Command-Line Interface Installation (Silent)
The non-interactive command-line interface (CLI) installation or silent installation, performs the following tasks:
- Creates or updates the ORDS configuration files
- Installs or upgrades the ORDS schema
- Creates the ORDS proxy user and the related objects in the Database
ords serve command.
Note:
If you have setup your OS environment to use the bequeath connection, then ensure that theJDK_JAVA_OPTIONS does not contain the
useOracleHome=true prior to using the
ords serve command. Remove
useOracleHome from the environment variable
JDK_JAVA_OPTIONS or unset
JDK_JAVA_OPTIONS.
If you provide the command-line options for the
non-interactive installation and if you are missing a required option (for
example: Basic connection requires the db-port option),
then an error message is displayed.
The --db-pool <pool_name> option specifies the
database pool to create or update. If the --db-pool option
is omitted, then it defaults to the default database
pool.
2.1.4.1 Non-interactive (Silent) ORDS Operations Using the Bequeath Connection
You can use the bequeath connection to install or upgrade, repair and uninstall Oracle REST Data Services in the database.
The bequeath connection enables ORDS to connect directly to an Oracle database bypassing the network listener. You can then execute ORDS on the same server as the database.
ORACLE_HOMEORACLE_SIDLD_LIBRARY_PATH (points to the $ORACLE_HOME/lib)
Examples using ORDS install command using the --bequeath
option:
Example 2-2 Basic Connection
ords --java-options "-DuseOracleHome=true" --config <PATH TO CONFIG> install --db-pool <POOL NAME> --
bequeath-connect --db-hostname <DB HOST> --db-port <DB PORT> --
db-servicename <DB SERVICENAME> --proxy-user --feature-sdw true
--log-folder <LOG FOLDER> --password-stdin < <PATH TO FILE>Example 2-3 TNS Connection
ords --java-options "-DuseOracleHome=true" --config <PATH TO CONFIG> install --db-pool <POOL NAME> --
bequeath-connect --db-tns-alias <TNS ALIAS> --db-tns-dir <TNS
FOLDER> --proxy-user --feature-sdw true --log-folder <LOG
FOLDER> --password-stdin < <PATH TO FILE>Example 2-4 Custom URL Connection
ords --java-options "-DuseOracleHome=true" --config <PATH TO CONFIG> install --db-pool <POOL NAME> --
bequeath-connect --db-custom-url <Custom URL> --proxy-user --
feature-sdw true --log-folder <LOG FOLDER> --password-stdin <
<PATH TO FILE>Note:
If you omit--db-pool option, then the settings are written to the
default pool settings file.
Example of the ords install --db-only command to upgrade an existing
database pool.
ords --java-options "-DuseOracleHome=true" --config <PATH TO CONFIG> install --db-pool <POOL NAME> --bequeath-connect --db-onlyNote:
If you omit--db-pool option, the upgrade occurs using the
default pool.
ords --java-options "-DuseOracleHome=true" --config <PATH TO CONFIG> install repair --db-pool <POOL NAME> --bequeath-connectNote:
If you omit--db-pool option, the repair occurs using the
default pool.
ords --java-options "-DuseOracleHome=true" --config <PATH TO CONFIG> uninstall --db-pool <POOL NAME> --bequeath-connectNote:
If you omit--db-pool option, the uninstall occurs using the
default pool.
2.1.4.2 Understanding Command Options for Command-Line Interface Installation
Table 2-21 Command Options for Command-Line Interface Installation
| Options | Description |
|---|---|
--admin-user
<USERNAME> |
Specifies the user with privileges to install or upgrade ORDS in the database, or obtains the ORDS status information. |
--bequeath-connect |
Specifies that bequeath connect that enables clients to connect directly to an Oracle database bypassing the network listener. This is when the client is on the same server as the database. Refer to Oracle REST Data Services documentation to setup your environment to use the --bequeath-connect option. |
--config <CONFIG_PATH> |
Specifies the path to the folder containing the configuration files. |
--config-only |
Specifies to create or update the configuration only. |
--db-only |
Specifies to install or upgrade ORDS in the database and not to create or update the configuration files. |
--db-pool
<POOL_NAME> |
Specifies the name of the database pool to
create, update or use. If the db-pool option is
omitted, then the default database pool is
used.
|
--db-custom-url
<URL> |
Specifies the custom database url for the database connection. |
--db-hostname
<HOST> |
Specifies the database host name. |
--db-port
<PORT> |
Specifies the database port. |
--db-servicename
<SERVICENAME> |
Specifies the database service name. |
--db-sid <SID> |
Specifies the database SID. |
--db-tns-alias
<ALIAS_NAME> |
Specifies the TNS alias name that exists in
the tnsnames.ora file.
|
--db-tns-dir
<TNS_DIR> |
Specifies the folder where the
tnsnames.ora file is located.
|
--feature-db-api
<BOOLEAN> |
Specifies if you want to enable DB API feature. Possible values are:true
or false.
Returns an error if the specified options are
|
--feature-rest-enabled-sql
<BOOLEAN> |
Specifies if you want to enable REST-Enabled SQL feature. Possible values are:true or false.
Returns an error if the specified options are
|
--feature-sdw
<BOOLEAN> |
Specifies if you want to enable Database Actions feature. Possible values are:
If the option is set to
Returns an error if
|
--gateway-mode
<MODE> |
Specifies the PL/SQL gateway mode. Possible values are:
Default value is
|
--gateway-user
<USER> |
Specifies the user that exists in the Oracle database and has privileges to access the stored procedures. |
--interactive, -i |
Prompts user for all the required information. |
--help, -h |
Shows how to use the command. |
--legacy-config <FOLDER> |
Specify the legacy configuration folder to migrate to the revised configuration structure. |
--legacy-context <STRING> |
Specifies the context (example: ords,
apex, and so on.) that was used in the legacy
configuration.
|
--log-folder |
Writes the logs from the install, upgrade, repair or uninstall to the log folder. If this option is omitted, then the output is written to standard output. |
--password-stdin |
To run the ORDS install, upgrade, repair, or uninstall command non-interactively, use this option to read the password value from standard input when redirecting input to a file or here document. |
--pdb-exclude
<(PDB...)> |
Specifies the option applicable for CDB. List of PDBs that are excluded from the ORDS install/upgrade, or repair. |
--pdb-open-readwrite-all |
Specifies the option applicable for CDB. Specifies whether to open all PDBs in read write mode if their status is either closed or read only. |
--pdb-open-readwrite
<(PDB...)> |
Specifies the option applicable for CDB. List of PDBs that are read-only or closed to be open for read/write to install, upgrade, repair, or uninstall ORDS. |
--pdb-skip-readonly |
Specifies the option applicable for CDB. Skips PDBs that are read-only. If this option is omitted, an error message is returned
informing the user that the PDB(s) are read-only for install or
upgrade ORDS. Excludes |
--pdb-skip-closed |
Specifies the option applicable for CDB. Skips PDBs that are closed (mounted). If this option is omitted, an error message is returned informing the user that the PDB(s) are closed for installation/upgradation of ORDS. |
--proxy-user |
Specifies the password of the ORDS database
user (ORDS_PUBLIC_USER) that is in a file or in a
here document when redirecting the standard
input.
|
--proxy-user-tablespace
<TABLESPACE> |
Specifies the option applicable for ORDS install. The default tablespace for proxy user (For example:
If this option is omitted, then the defaulted database default tablespace is used. |
--proxy-user-temp-tablespace
<TABLESPACE> |
Specifies the option applicable for an ORDS install. The temporary tablespace for proxy user (For example:
If this option is omitted, then the defaulted database temporary tablespace is used. |
--schema-tablespace
<TABLESPACE> |
Specifies the default tablespace for
If this option is omitted, then the defaulted database default tablespace is used. |
--schema-temp-tablespace
<TABLESPACE> |
Specifies the option applicable for an ORDS install. The temporary tablespace for
If this option is omitted, then the defaulted database temporary tablespace is used. |
2.1.4.3 Using Input Redirection
This section describes how to redirect the standard input using the here command or to a file.
Redirect STDIN to a file
Redirect STDIN to a file that contains the password. In the following example, the file must contain two passwords. Each password must be on a separate line.
$ cat password.txt
firstpassword
secondpasswordThe first password belongs to the first user on the command line (for example:
SYS). The second password belongs to the second user on the command line
(for example: proxy-user).
ords --config <configuration_folder> install --db-pool <pool_name> --admin-user <username> --proxy-user
--db-hostname <host> --db-port <port_number> --db-servicename <service_name>
--log-folder <log_folder> --feature-sdw <boolean> --password-stdin < <filename>
Example:
ords --config /path/to/conf install --db-pool db1 --admin-user SYS --proxy-user --db-hostname localhost
--db-port 1521 --db-servicename orcl --log-folder /path/to/logs --feature-sdw true
--password-stdin < password.txtRedirect Standard Input Using Here Document
Redirect STDIN using the Here document (also known as heredoc) for the
password(s). The heredoc consists of the '<<' redirection operator
followed by a delimiter token.
Each password must be on a separate line and it is ended by the delimiter token.
Example:
The first password belongs to the first user on the command line (for example:
SYS). The second password belongs to the second user on the command line
(for example: proxy-user).
ords --config <configuration_folder> install --db-pool <pool_name> --admin-user <username> --proxy-user --db-hostname
<host> --db-port <port_number> --db-servicename <service_name> --log-folder <log_folder> --feature-sdw <boolean>
--password-stdin << EOF
<password1>
<password2>
EOFords --config /path/to/conf install --db-pool db1 --admin-user SYS --proxy-user --db-hostname
localhost --db-port 1521 --db-servicename orcl --log-folder /path/to/logs --feature-sdw true
--password-stdin << EOF
<password1>
<password2>
EOF2.2 Repairing the Oracle REST Data Services Installation
Note:
To repair ORDS in the database, the ORDS product version must be the same version as the ORDS installed schema version in the database.ords [--config <folder>] install repair --interactive [--log-folder <folder>]If you have an existing configuration, you may choose to select from a list of database pools. You also have the option to specify the database connection for ORDS to be installed. You are prompted to provide the administrator username and password.
Example
Oracle REST Data Services - Interactive Repair
Enter a number to select the database pool to use or specify the database connection
[1] default jdbc:oracle:thin:@//localhost:1521/orcl
[2] sales jdbc:oracle:thin:@//localhost:1521/pdb1
[S] Specify the database connection
Choose [1]:
Provide database user name with administrator privileges.
Enter the administrator username: SYS
Enter the database password for SYS AS SYSDBA:
Note:
When you install Oracle REST Data Services, it attempts to find the Oracle APEX schema and creates a view. This view joins the relevant tables in the APEX schema to the tables in the Oracle REST Data Services schema. If you install Oracle REST Data Services before APEX, then Oracle REST Data Services cannot find the APEX schema and it creates a stub view in place of the missing APEX tables.
Oracle highly recommends that you install Oracle REST Data Services after APEX to ensure that the APEX objects, which Oracle REST Data Services needs to query, are present. If you install Oracle REST Data Services before APEX, then use the repair command to force Oracle REST Data Services to reconstruct the queries against the APEX schema.
proxied:ords --config <config_path> --db-pool <pool_name> get plsql.gateway.mode Run the following command to set
plsql.gateway.mode value to proxied :
ords --config <config_path> config --db-pool <pool_name> set plsql.gateway.mode proxied2.2.1 Command Options for Repair CLI
This section describes the interactive and non-interactive install repair CLI commands used to repair the ORDS schema in the database.
Table 2-22 Command Options for Repair CLI
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
--admin-user <string>
|
Specifies the user with privileges to install, upgrade, or uninstall ORDS in the database. |
--bequeath-connect |
Specifies that the bequeath connect enables clients to connect directly to an Oracle database bypassing the network listener. This occurs if client is on the same server as the database. |
--db-custom-url <url> |
Specifies the custom database url for the database connection. |
--db-hostname <string>
|
Specifies the database host name. |
--db-pool <string> |
Specifies the name of the database connection pool. |
--db-port <int> |
Specifies the database port. |
--db-servicename <string> |
Specifies the database service name. |
--db-sid <string> |
Specifies the system identifier which is a unique name that identifies the database. |
--db-tns-alias <string> |
Specifies the TNS alias name that exist in the
tnsnames.ora file.
|
--db-tns-dir <folder> |
Specifies the folder where the tnsnames.ora file is
located.
|
-h, --help |
Shows how to use and provides information of the command. |
-i, --interactive |
Prompts for the required information. |
--log-folder <folder> |
Writes the logs from the install, upgrade or uninstall to the log folder. If this option is omitted, then the output is written to standard output. |
--password-stdin |
Specifies to use this option to read the password value from standard
input when redirecting input to a file or here document
when you run the ords install or uninstall command non-interactively,
If the --password-stdin option and the redirection
symbol ("<" or "<<") are omitted, then you are prompted for the
password(s) for the command option(s) that require the password.
|
--pdb-exclude <string...> |
Specifies the list of PDBs that are excluded from the ORDS install, upgrade, or repair. This option only applies to the CDB. |
--pdb-open-readwrite <string...> |
Specifies the list of PDBs that are read only or closed to be open for read write for ORDS install, upgrade, repair or uninstall. This option only applies to the CDB. |
--pdb-open-readwrite-all |
Specifies to open all PDBs in read write mode if their status is either closed or read only. This option only applies to the CDB. |
--pdb-skip-closed |
Skips PDBs that are closed (mounted). This option only applies to the CDB. |
--pdb-skip-readonly |
Skips PDBs that are read-only. This option only applies to the CDB. |
2.3 Upgrading Oracle REST Data Services
This section describes how to upgrade to Oracle REST Data Services latest release.
Upgrading from ORDS 22.1.x or Later
Upgrading from ORDS 21.4.x or earlier releases
If you are upgrading from ORDS 21.4.x or earlier releases, then refer to Migrate Configuration and Upgrade from ORDS 21.4.x or Earlier Releases
2.3.1 Migrate Configuration and Upgrade from ORDS 21.4.x or Earlier Releases
This section describes how to upgrade from ORDS 21.4.x or earlier releases.
To upgrade to ORDS 22.x from ORDS 21.4.x or earlier releases:
Provide the location of your configuration files that were used from your previous ORDS release (21.4.x or earlier). If you do not know the location, then specify the command using your previous ORDS release (21.4.x or earlier).
java -jar /path/to/earlierRelease/ords.war configdir
java -jar /path/to/earlierRelease/ords.war configdir
INFO The config.dir value is /path/to/legacy/confIn the preceding example /path/to/legacy/conf is
configuration location
2.3.1.1 Interactive Upgrade
Interactive Upgrade
ords --config <folder> install -i --legacy-config <folder> --log-folder
<folder>Table 2-23 Interactive Upgrade Commands
| Command Options | Description |
|---|---|
--config <folder> |
Specifie the configuration folder to store your migrated configuration files. Your configuration folder must not be in the same location as your legacy configuration folder. Otherwise, an error occurs. |
-i or
--interactive |
Specifies to run the command in interactive mode. You are then prompted for the information. |
--legacy-config
<folder> |
Specifies to provide the location of your configuration files that you used for ORDS 21.4.x or earlier releases. |
--log-folder
<folder> |
Specifies to provide the location to store your log file. |
ords --config /path/to/new/conf install -i --legacy-config /path/to/legacy/conf --log-folder /path/to/logs
Oracle REST Data Services 24.x.x.rNNNNNN - Migrate Configuration
Migrating ORDS Configuration files located at /path/to/legacy/conf
...
Legacy configuration files located at /path/to/legacy/conf/ords are no longer being used
to configure ORDS or its connection pools.
Your migrated configuration files are now located at /path/to/new/conf
Oracle REST Data Services - Interactive Install
Enter a number to select the database pool to upgrade ORDS.
Additional options to Generate script, or Create an additional database pool.
[1] default jdbc:oracle:thin:@//localhost:1521/orcl
[2] db1 jdbc:oracle:thin:@//localhost:1521/pdb1
[3] db2 jdbc:oracle:thin:@//localhost:1521/pdb2
[G] Generate script to upgrade ORDS in all the database pools
[C] Create an additional database pool
Choose [1]:
A list of the migrated database pools are displayed. The legacy configuration database pool named apex is migrated, and the name is changed to default.
If you have multiple database pools to upgrade, you can either select the option
Generate a script to upgrade ORDS in all the database pools, or repeat the install
command again excluding the --legacy-config option since you have
already migrated the configuration.
ords --config /path/to/new/conf install -i --log-folder /path/to/logsSee Also:
Scenario 3: Multiple Database Pools2.3.1.2 Silent Upgrade
- Legacy configuration location
- The database password for the administrator user
Here
document. If you are using a text file, then ensure to delete the text file when the
upgradation is complete. The legacy configuration database pool named
apex is migrated, and the name is changed to
default.
If you omit the --database-pool <name> option,
then it uses the default database pool to upgrade.
Using a Text File
ords --config <folder> install --admin-user <user> --legacy-config <folder> --log-folder <folder>
--password-stdin < <text-file>Example of using a <text-file> with 1 password
The text file contains 1 password for --admin-user <user>
ords --config /path/to/new/conf install --admin-user SYS --legacy-config /path/to/legacy/conf
--log-folder /path/to/logs --password-stdin < adminpwd.txtUsing a Here Document
You can redirect Standard Input using the Here document
(also known as heredoc) for the password(s). The
heredoc consists of the << redirection
operator followed by a delimiter token once the upgrade operation completes. If you
are using a script that contains the password(s), then delete the script.
ords --config <folder> install --admin-user <user> --legacy-config <folder> --log-folder <folder> --password-stdin << <delimiter-token>
> <password>
> <delimiter-token>ords --config /path/to/new/conf install --admin-user SYS --legacy-config /path/to/legacy/conf --log-folder
/path/to/logs --password-stdin << EOF
> <password for admin-user>
> EOF2.4 Uninstalling Oracle REST Data Services
This section describes the interactive and non-interactive uninstallation CLI commands used to uninstall the ORDS schema.
2.4.1 Interactive Uninstall CLI
The interactive uninstallation CLI prompts you for the necessary information to uninstall the ORDS schema, ORDS proxy user and related database objects from the database.
- Specify the uninstall command only. For example:
$ ords uninstallNote:
Assumes that the configuration folder is specified through the environment variable or you are defaulting to the current working directory. - Specify the option
--config <configuration folder>followed by the uninstall command. For example:$ ords --config /path/to/config uninstall - Specify the
--interactiveFor example:
$ ords --config /path/to/config uninstall --interactive
Table 2-24 Interactive Uninstall Prompts
| Prompt Number | Prompt | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1. |
|
Refer to Entering a Number to Select the Database Pool |
| 2. |
|
Refer to Entering a Number to Select the Database Connection Type |
| 3. |
|
Refer to Entering the Database Host Name |
| 4. |
|
Refer to Entering the Database Listener Port |
| 5. |
|
Refer to Entering the Database Service Name |
| 6. |
|
Refer to Entering the TNS Location |
| 7. |
|
Refer to Entering a Number to Select the TNS Network Alias |
| 8. |
|
Refer to Entering the Custom Database URL |
| 9. |
|
Refer to Entering the Administrator Username |
| 10. | Enter the database password for SYS AS
SYSDBA: |
Refer to Entering the Database Password for SYS AS SYSDBA |
| 11. |
|
Refer to Entering an Option for Uninstalling ORDS |
2.4.1.1 Entering a Number to Select the Database Pool
- If you select a database pool, then it bypasses the database connection type and prompts you for the administrator username and password.
- If you select option 2, then you get the prompt number 2.
Note:
If the configuration pool(s) does not exist in your configuration folder, then it prompts you for the database connection type.2.4.1.2 Entering a Number to Select the Database Connection Type
Select the database connection type.
2.4.1.5 Entering the Database Service Name
- The service name setting in the ORDS configuration file. If not present, then
- It checks for
ORACLE_PDBenvironment variable. If undefined, then - It checks for
ORACLE_SIDenvironment variable. If undefined, then - It uses
orclas the default value.
2.4.1.7 Entering a Number to Select the TNS Network Alias
Select the TNS alias name from the list of TNS network alias names displayed.
2.4.1.8 Entering the Custom Database URL
Specify the custom database URL for custom database URL connection.
jdbc:oracle:<driver>:@//<host>:<port>/<servicename>
jdbc:oracle:thin:@//localhost:1521/orcl
jdbc:oracle:<drivertype>:@(DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=TCP)(HOST=<host>)(PORT=<port>))(CONNECT_DATA=(SERVICE_NAME=<servicename>)))
jdbc:oracle:thin:@(DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=TCP)(HOST=localhost)(PORT=1521))(CONNECT_DATA=(SERVICE_NAME=orcl)))2.4.1.9 Entering the Administrator Username
Specify a user who has installer privileges to install or upgrade ORDS in the database.
2.4.1.11 Entering an Option for Uninstalling ORDS
If the ORDS enabled or disabled schemas exist, and the
--force command option is not specified, then it displays the
enabled or disabled schemas and prompts for a confirmation to uninstall ORDS in the
database.
If the --force command option is specified, then the
uninstall confirmation is not shown,
2.4.2 Non-Interactive Uninstall CLI
The non-interactive uninstall CLI uninstalls the ORDS schema, ORDS proxy user, and related database objects from the database.
Provide the command options for the non-interactive uninstall CLI. If you are missing a
required option (for example, db-port for a connection), then you are not
prompted. Instead, an error is returned.
2.4.2.1 Using Input Redirection
This section describes how to redirect standard input using Here document or to a file.
Redirect Standard Input to a File
Redirect STDIN to a file that contains the password. In the following example, the file contains one password.
$ cat adminpwd.txt
passwordThe password belongs to the administrator user on the command line (for
example: SYS). This example assumes that the config folder and the db1 pool
already exists.
ords --config /path/to/conf uninstall --db-pool db1 --admin-user SYS --log-folder
/path/to/logs --password-stdin < adminpwd.txt
Redirect Standard Input using Here Document
Redirect STDIN using the Here document (also known as heredoc)
for the password. The heredoc consists of the << redirection operator
followed by a delimiter token.
The password must be on a separate line and it is ended by the delimiter token.
Example:
ords --config <configuration_folder> uninstall --db-pool <pool_name> --admin-user <username>
--db-hostname <host> --db-port <port_number> --db-servicename <service_name> --log-folder <log_folder>
--password-stdin << EOF
<password>
EOFThe password belongs to the the administrator user on the command line. (for
example: SYS).
ords --config /path/to/config uninstall --db-pool db1 --admin-user SYS --db-hostname
localhost --db-port 1521 --db-servicename orcl --log-folder /path/to/logs << EOF
<password>
EOF2.4.2.2 Command options for Uninstall CLI
Table 2-25 Command Options for Uninstall CLI
| Options | Description |
|---|---|
--admin-user
<USERNAME> |
Specifies the user with privileges to install, upgrade, repair, or uninstall ORDS in the database. |
--bequeath-connect |
Specifies that the bequeath connect enables clients to connect directly to an Oracle database bypassing the network listener. This occurs if client is on the same server as the database. |
--config <CONFIG_PATH> |
Specifies the path to the folder containing the configuration files. |
--db-pool
<POOL_NAME> |
Specifies the name of the database pool. |
--db-custom-url
<URL> |
Specifies the user specified custom url. |
-db-hostname
<HOST>-
|
Specifies the database host name. |
--db-port
<PORT> |
Specifies the database port. |
|
Specifies the database service name. |
--db-sid <SID> |
Specifies the database SID. |
--db-tns-alias
<ALIAS_NAME> |
Specifies the tns alias name that exists in
the tnsnames.ora file.
|
-db-tns-dir
<TNS_DIR>-
|
Specifies the folder where the
tnsnames.ora file is located.
|
--force |
Specifies that you can uninstall ORDS from the database regardless of the number of ORDS enabled/disabled schemas. |
--help, -h |
Shows how to use the command. |
--interactive, -i |
Prompts the user for all the required information. |
--log-folder |
Writes the logs from the install, upgrade, repair, or uninstall to the log folder. If this option is omitted, then the output is written to the standard output. |
-password-stdin |
Specifies when you want to run the ORDS install or uninstall command
non-interactively, you can use this option to read the password value
from standard input when redirecting input to a file or
here document. If the
--password-stdin option and the redirection symbol
("<" or "<<") are omitted, you are prompted for the password(s)
for the command option(s) that requires the password.
|
--pdb-open-readwrite-all |
Specifies the option applicable for CDB. Specifies whether to open all PDBs in read write mode if their status is either closed or read only. |
--pdb-open-readwrite
<(PDB...)> |
Specifies the option applicable for CDB. Specifies the list of PDBs that are readonly or closed to be open for readwrite to uninstall ORDS. |
2.5 Updating the Configuration Settings
The ORDS config command is used to update and edit the
contents of the global and database pool specific settings in the configuration
files.
The config command comprises a list of sub-commands. The
config command has the --db-pool
<POOL_NAME> option that identifies the database pool to which you
want to apply the setting. If this option is omitted, then the default database pool
settings get updated.
ords config [OPTIONS] [SUB-COMMAND]
- OPTIONS:
--db-pool <string>: The name of the database connection pool to configure-h, --help: Show usage information for the command
- SUB-COMMAND:
delete,get,info,list,secret,set, anduser
info
Shows the description of the specified key, explaining its purpose. Indicates if it is a sensitive value and what is the default value.
Example: ords config info
<KEY>
set
Sets the config key to a value. If you wish the setting
to be set at a global level, then use the --global option.
Example: ords config set [--global] <KEY>
<VALUE>
secret
Sets the sensitive values (for example: connection pools password). Use
ords config secret to set the sensitive values. Some values are
sensitive (example: db.password). Per Oracle Secure Coding
Standards such values must not be passed as command line arguments as this leads to
leakage of the value (appears in ps output).
Example: ords config secret --password-stdin <KEY> <
<file>
Note:
If an attempt is made to doords config set on a sensitive value, an error is
returned.
Non-Interactive example:
If the --password-stdin option is specified, then the
value is read from stdin.
Example:
ords config secret --password-stdin db.password < secret.txt
Interactive Example
If --password-stdin is not specified, then the user is
prompted to enter and confirm the secret value.
Example:
ords config secret db.password
get
Echo the config value to stdout. If the value is a secret then it's value
will be replaced by the text ******. If you wish to see the plain
text of the secret, then use the --secret argument.
Example: ords config get [--global] [--secret]
<KEY>
list
Show all explicitly configured values for the pool settings and global
settings. Secret values are replaced with the text ******. Use
-–include-defaults to list all the settings including those
with the default values.
Example: ords config list [--include-defaults]
Setting: Name of the settingValue: The value of the settingSource: Location of the global/pool specific setting
For example the output is similar to the following:
Configuration: /path/to/conf/
Database pool: default
Setting Value Source
------------------- --------------- ------
db.connectionType basic Pool
db.hostname localhost Pool
db.password ****** Pool Wallet
db.port 1521 Pool
db.servicename orcl Pool
db.username ORDS_PUBLIC_USER Pool
feature.sdw true Pool
restEnabledSql.active true Pool Default: Uses the default value for the settingGlobal: The value is specified in the global/settings.xml configuration filePool:The value is explicitly configured in the poolPool Wallet:The (sensitive) value is explicitly configured in the pool wallet
user
delete
Deletes the key from the configuration.
Example: delete [--global]
user add
Add a user and its password and role(s) in the credentials file. If the user already exists, then it is updated.
Non-interactive
Include option --password-stdin to read from STDIN.
Requires the password file of the user.
ords config user add --password-stdin <USERNAME> roles <ROLES> < userpwd.txtInteractive
Prompts for the password if --password-stdin option is
omitted.
ords config user add <USERNAME> roles <ROLES>
Enter the password:
Confirm password:user
delete
ords config user delete <USERNAME>Delete the specified user.
user get
ords config user get <USERNAME>Retrieve the specified user.
user list
ords config user listLists the users in the credential file.