4.1 Base Styles
If base styles or any rule based styles are not defined (or applied), then the following default base styles are applied to the graph:
const border = {
width: 1,
color: '#404040'
};
const badge = {
size: 6,
color: '#FF584A',
label: {
text: '${group.size}',
angle: null,
color: 'white',
font: {
weight: 'bold'
}
}
};
const defaults: Styles = {
'*': {
filter: 'none',
label: {
maxLength: 15,
font: {
size: 10
}
}
},
vertex: {
size: 8,
color: 'lightgray',
image: {
scale: 1
},
border,
icon: {
color: 'white'
},
label: {
angle: 270,
d: 2
}
},
'vertex:group': {
size: '${interpolate("group.size", 8, 16)}',
opacity: 1,
color: '#75BBF0',
border,
label: {
text: '',
angle: 270,
d: 2
},
icon: null,
image: null,
legend: null,
children: {
size: badge
}
},
edge: {
width: 2,
color: '#C0C0C0',
label: {
position: 0,
d: 1
}
},
'edge:group': {
width: 2,
opacity: 1,
label: null,
children: {
size: badge
}
},
'* > *': {
size: 5,
d: 0,
color: 'darkgray',
border: null,
icon: {
color: 'white'
},
image: {
scale: 1
},
label: {
d: 1
}
},
'vertex > *': {
angle: 45
},
'edge > *': {
position: 0
},
':unselected': {
filter: 'grayscale(100%)'
},
'vertex:unselected': {
opacity: 0.3
},
'edge:unselected': {
opacity: 0.3
},
'vertex:hover': {
size: '${previous + 4}'
},
'edge:hover': {
width: '${previous + 2}'
},
'edge:hover > *': {
size: '${previous + 2}'
}
};If you wish to create a custom base style, then you can provide your own
settings.baseStyles, which overrides the defaults shown
in the preceding code.
The following shows an usage example to create a custom base style that applies for all vertices and edges:
Note:
The Graph Visualization library also contains TypeScript definitions if you are using TypeScript).// This import is not necessary if you are using Oracle JET.
import '@ovis/graph/alta.css';
import Visualization from '@gvt/graphviz';
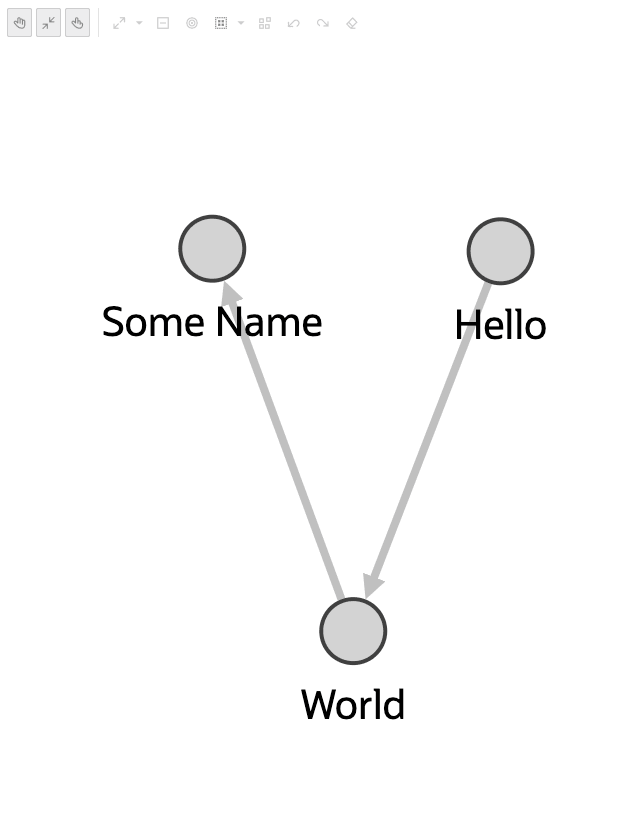
const vertices = [
{
id: 1,
properties: {
label: 'blue',
name: 'Hello'
},
labels: ['color']
},
{
id: 2,
properties: {
label: 'blue',
name: 'World'
},
labels: ['color']
},
{
id: 3,
properties: {
name: 'Some Name'
},
labels: ['text']
}
];
const edges = [
{
id: 1,
source: 1,
target: 2,
labels: ['edge']
},
{
id: 2,
source: 2,
target: 3,
labels: ['edge']
}
];
const settings = {
baseStyles: {
vertex: {
label: { text: '${properties.name}' }
}
}
};
new GraphVisualization({
target: document.body,
props: { data: { vertices, edges }, settings }
});The following shows the graph visualization using the preceding custom base style:
It is important to note that some specified properties of
settings.baseStyles (such as color) may get overridden
if the vertices or edges have labels in it. This is due to ruleBasedStyles getting
automatically generated which applies distinct colors to vertices and edges belonging to
each label.
You can still enforce the styling of your choice by fetching the
ruleBasedStyles using getCurrentRuleBasedStyles method
and overriding the default styles (those with isDefaultRule property
true) as follows:
- Updating the default ruleBasedStyles
stylingEnabledproperty tofalse. This will disable the generated ruleBasedStyles and cause the styles defined insettings.baseStylesto apply. - Updating the properties of the default ruleBasedStyles to reflect the styling you require.
See Default Legend Styles for more information.
Parent topic: Usage Examples