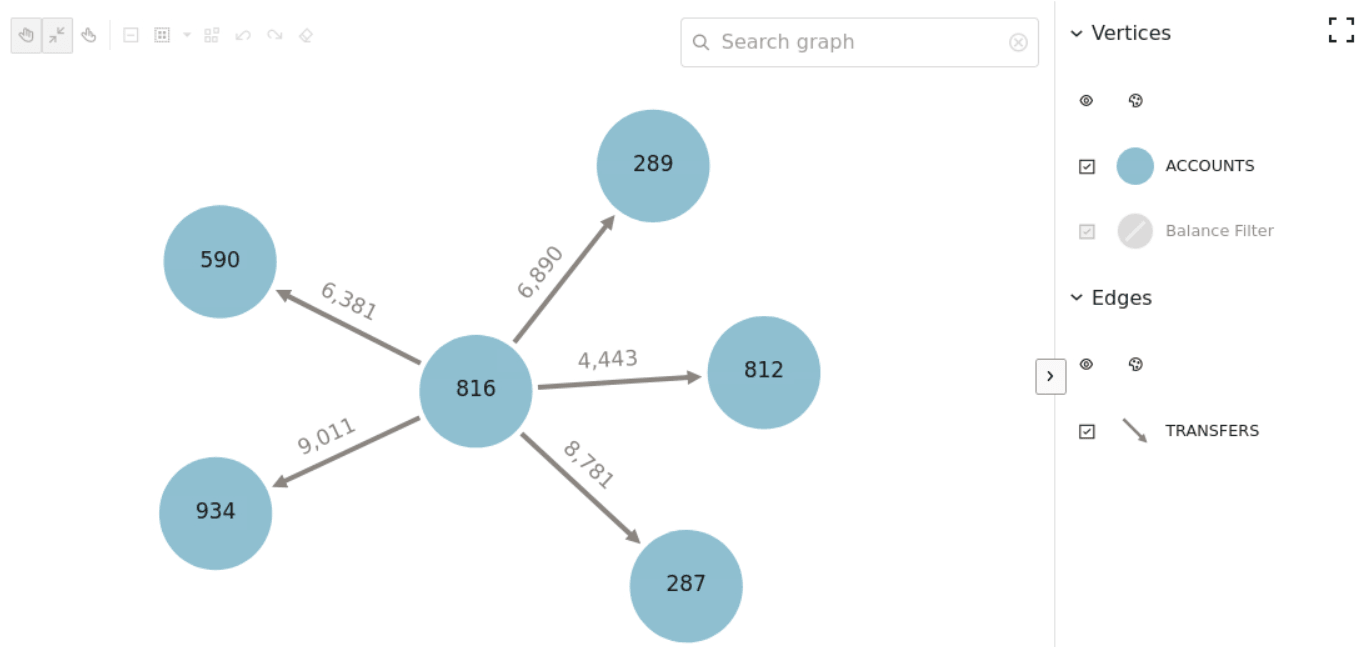
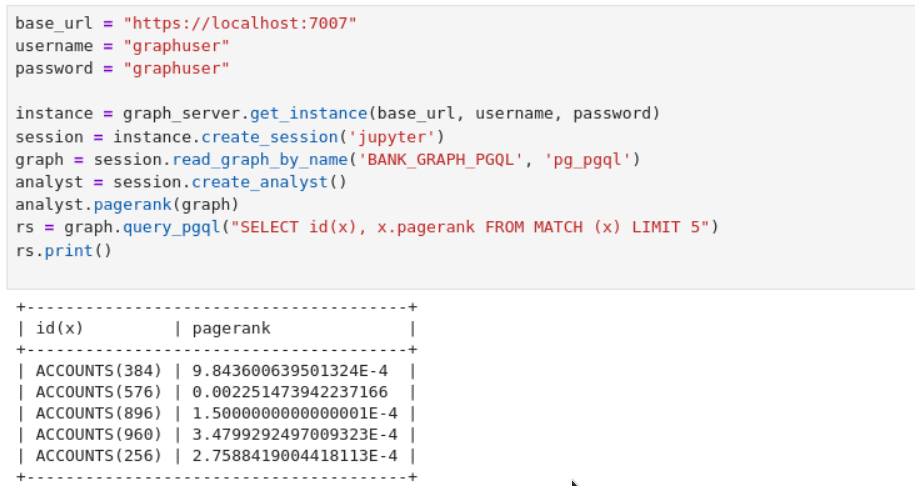
For instance, the following example shows the graph
visualization of a PGQL query on the property graph created at step-4
using
PgqlGraphVisualization in the
oraclegraph Jupyter
extension.
from pypgx import setloglevel
from oraclegraph import GraphVisualization, PgqlGraphVisualization
setloglevel('ROOT', 'WARN')
vq = PgqlGraphVisualization("graphuser", "<password_for_graphuser>", "<host_name:port>/<service>")
query='''
SELECT * FROM GRAPH_TABLE (bank_graph_pgql
MATCH (a) -[e]-> (b)
WHERE a.ID=816
COLUMNS (a.ID AS src_ac, e.AMOUNT AS amount, b.ID AS dest_ac)
)
'''
graph_query = vq.visualize_query(query)
defaults_feature = {
"interactionActive": True,
"1stickyActive": True
}
base_styles = {
"vertex": {
"label": "${properties.ID}",
"size": 20
},
"edge": {
"label": "${properties.AMOUNT}"
}
}
rule_based_styles = [{
"stylingEnabled": True,
"component": "vertex",
"target": "vertex",
"conditions": {
"conditions": [{
"property": "BALANCE",
"operator": "<=",
"value": 5000
}],
},
"style": {
"color": "green"
},
"legendTitle": "Balance Filter",
"legendDisplayed": True
}
]
settings = {
"numberOfHops": 2,
"showLegend": True,
"defaults": defaults_feature,
"baseStyles": base_styles,
"ruleBasedStyles": rule_based_styles
}
bank_graph = GraphVisualization(data = graph_query, settings = settings)
bank_graph.height = 600
display(bank_graph)
The preceding code produces the following visualization
result: