5 The Worksheet Page
The Worksheet page provides a code editor that is used to enter and execute SQL and PL/SQL statements.
You can use SQL and PL/SQL statements in the worksheet to create a table, insert data, create and edit a trigger, select data from a table, and save that data to a file. Some other features are syntax highlighting and error detection.
Database administrators can also access the worksheet from the Quick Links pane in Dashboard.
The Worksheet page consists of the left pane for navigating worksheets and objects, the editor for executing SQL statements, and the output pane for viewing the results. These panes are described in the following sections:
5.1 Navigating Objects and Worksheets
The Navigator tab in the left pane displays the saved objects for the selected schema. The drop-down menus enable you to select the schema for which you want to see the objects, and filter the results by object type.
The Worksheets tab displays the worksheets that are saved in the browser. The worksheets displayed are dependent on the browser used (Internet Explorer, Mozilla Firefox, or Google Chrome) for the SQL Developer Web session at the time of saving the worksheet, and they will not be accessible from any other browser. You can open or delete an existing worksheet by using the context (right-click) menu.
You can also search the contents of a saved worksheet or search for objects in the Navigator tab by name. The search functionality is not case-sensitive, retrieves all matching entries and does not require the use of wildcard characters.
Using the context (right-click) menu for objects in the Navigator tab, you can create and edit objects, add indexes and synonyms, and upload data from local files into existing tables.
To refresh the objects or worksheets list, click the ![]() icon. To create a new object, click the
icon. To create a new object, click the ![]() icon.
icon.
For context-related help, click the ![]() icon.
icon.
You can drag objects from the Navigator and drop them into the worksheet editor in the right pane:
-
If you drag and drop a table or view, you are prompted to select one of the following SQL statements: Insert, Update, Select, or Delete. For example, if you choose Select, a Select statement is constructed with all columns in the table or view. You can then edit the statement, for example, modifying the column list or adding a WHERE clause.
If you choose Object Name, the name of the object prefixed by the schema name is added to the worksheet.
-
If you drag and drop a function or procedure, you can choose to insert the name or the PL/SQL code of the function or procedure in the worksheet. If you select the PL/SQL code, you can enter the parameters before inserting the code into the worksheet.
5.2 Executing SQL Statements in the Worksheet Editor
The worksheet editor in the right pane enables you to enter the SQL statements that you intend to execute. You can use SQL and PL/SQL statements to specify actions such as creating a table, inserting data, selecting data or deleting data from a table. For multiple statements, each non-PL/SQL statement must be terminated with either a semicolon or (on a new line) a slash (/), and each PL/SQL statement must be terminated with a slash (/) on a new line. SQL keywords are automatically highlighted.
For a list of the SQL*Plus statements that are supported by the SQL Worksheet, see Supported SQL*Plus Statements.
If you press Ctrl+Space, the worksheet provides you with a list of possible completions at the insertion point that you can use to autocomplete code that you are editing. This list is based on the code context at the insertion point. Also, you can select multiple options in the list using Ctrl+Click.
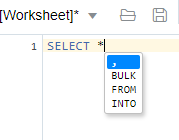
Description of the illustration autocomplete_wrksheet.png
An error in the code is signified by a red dot or squiggle line. When you hover over it, you see a pop-up displaying possible fixes for resolving the error.
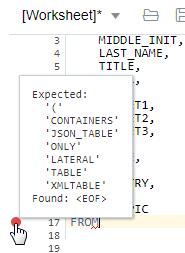
Description of the illustration error_wrksheet.png
The SQL Worksheet toolbar contains icons for the following operations:
-
Worksheet enables you to create a worksheet, open or delete an existing worksheet, and save a worksheet.
Note:
The worksheets are saved in the browser. Therefore, if you do sensitive work on a computer in a public network, remember to clear the browser cache before you leave. Additionally, the saved worksheets will only be displayed in the browser that was used at the time of creating the worksheet.
-
Run Statement executes the selected statements or the statement at the mouse pointer in the worksheet editor. The SQL statements can include bind variables and substitution variables of type VARCHAR2 (although in most cases, VARCHAR2 is automatically converted internally to NUMBER if necessary). A dialog box is displayed for entering variable values.
-
Run Script executes all statements in the worksheet editor using the Script Runner. The SQL statements can include bind variables (but not substitution variables) of type VARCHAR2 (although in most cases, VARCHAR2 is automatically converted internally to NUMBER if necessary). A dialog box is displayed for entering bind variable values.
-
Explain Plan generates the execution plan for the statement (internally executing the EXPLAIN PLAN statement). The execution plan is automatically displayed in the Explain Plan tab in the worksheet output pane.
-
Autotrace runs the statement and collects runtime statistics and the actual execution plan. The Autotrace output is displayed in the Autotrace tab in the worksheet output pane. Currently, there are no preferences available.
-
Download Editor Content downloads the content of the worksheet as a SQL file to the local system.
-
Format formats the SQL statement in the editor, such as capitalizing the names of statements, clauses, keywords, and adding line breaks and indentation.
-
Clear removes the statements from the editor.
-
Tour provides a guided tour of the worksheet highlighting salient features and providing information that is useful if you are new to the interface.
-
Help provides context-related help and provides a link to the help documentation.
For a list of shortcuts used in the worksheet, see Shortcut Keys in the Worksheet.
5.2.1 Shortcut Keys in the Worksheet
The following table lists the shortcut keys for various user actions in the worksheet.
Table 5-1 Shortcut Keys for User Actions in the Worksheet
| Shortcut | Action |
|---|---|
|
Ctrl+Enter/ Cmd+Enter |
Runs the code as query. |
|
Ctrl+Down Arrow/ Cmd+Down Arrow |
Moves to the next SQL code from history. |
|
Ctrl+Up Arrow/ Cmd+Up Arrow |
Moves to the previous SQL code from history. |
|
Ctrl+D/ Cmd+D |
Clears the editor. |
|
Ctrl+S/ Cmd+S |
Saves the current worksheet. |
|
Ctrl+O/ Cmd+O |
Opens the worksheet browser dialog. |
|
Ctrl+I/ Cmd+I |
Downloads the content of the editor. |
|
F1 |
Opens the help topic. |
|
F5 |
Runs code as script. |
|
F6 |
Shows Autotrace. |
|
F10 |
Shows Explain Plan. |
|
Ctrl+F7/ Cmd+F7 |
Formats code in the editor. |
|
Ctrl+Space/ Cmd+Space |
Autocompletes code (shows hints). |
|
Windows+Esc/ Cmd+Esc |
Focuses outside the editor and navigates to the rest of the application using the Tab key. |
5.3 Viewing the Worksheet Output
The bottom right pane of the Worksheet screen has tabs that display the following panes:
-
Query Result: Displays the results of the most recent Run Statement operation in a display table.
-
Script Output: Displays the text output from your statements executed as a script using SQL Developer Web's script engine.
-
DBMS Output: Displays the output of DBMS_OUTPUT package statements.
-
Explain Plan: Displays the plan for your query using the Explain Plan command.
-
Autotrace: Displays the session statistics and execution plan from
v$sql_planwhen executing a SQL statement using the Autotrace feature. Displays the output if you clicked the Autotrace icon. -
SQL History: Displays the SQL statements and scripts that you have executed. To re-enter a previously executed query in the worksheet, double-click the query in the history list. You can search for specific statements by clicking the Search icon. The Search functionality is case-sensitive, retrieves all entries that contain the search text, and does not require wildcard characters.
The icons in this pane are:
-
Clear output: Clears the output.
-
Show info: Displays the SQL statement for which the output is displayed.
-
Open in new tab: Opens the query result or explain plan in a new window.
-
Download: This is applicable only for Query Result. Enables you to download the query result to your local computer in CSV, JSON, XML, or TEXT (.tsv) format.
In the Query Result tab, in the display table, the context menu (right-click) for the row header consists of the following:
-
Columns enables you to select columns to hide.
-
Sort displays a dialog box for selecting columns to sort by. For each column, you can specify ascending or descending order, and you can specify that null values be displayed first.
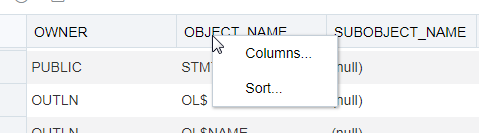
Description of the illustration contmenu_rowheader.png
The context menu for the rest of the display table consists of the following commands:
-
Count Rows displays the number of rows in the result set for your query.
-
Single Record View enables you to view data for a table or view, one record at a time.
-
Export generates the file for download based on the format selected, which can be XML, CSV (comma-separated values including a header row for column identifiers), Insert , Delimited, Fixed, HTML, JSON, or TEXT.
Note:
If a popup blocker is enabled, it will prevent the file from downloading.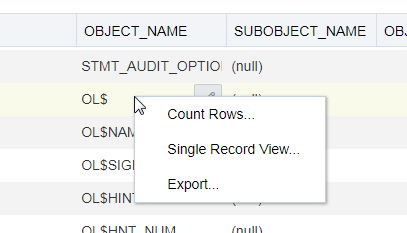
Description of the illustration contmenu_table.png