7.9 The Real Time SQL Monitoring Page
![]() Available only if you signed in as a database user with
DBA and PDB_DBA roles for Oracle
Database 18c and previous releases.
Available only if you signed in as a database user with
DBA and PDB_DBA roles for Oracle
Database 18c and previous releases.
To navigate to the Real Time SQL Monitoring page, do either of the following:
-
In the Database Actions page, click Real Time SQL Monitor.
-
Click Selector
 to display the left navigation pane. Expand the
Monitoring menu and select Real Time SQL
Monitor.
to display the left navigation pane. Expand the
Monitoring menu and select Real Time SQL
Monitor.
In the Auto Refresh drop-down list, you can select the time (in seconds) to
periodically refresh the data. Select 0 seconds to disable the
auto-refresh.
This tool helps identify run-time issues for SQL statements by providing two major functions:
-
General view of monitored statements
-
View of SQL execution details
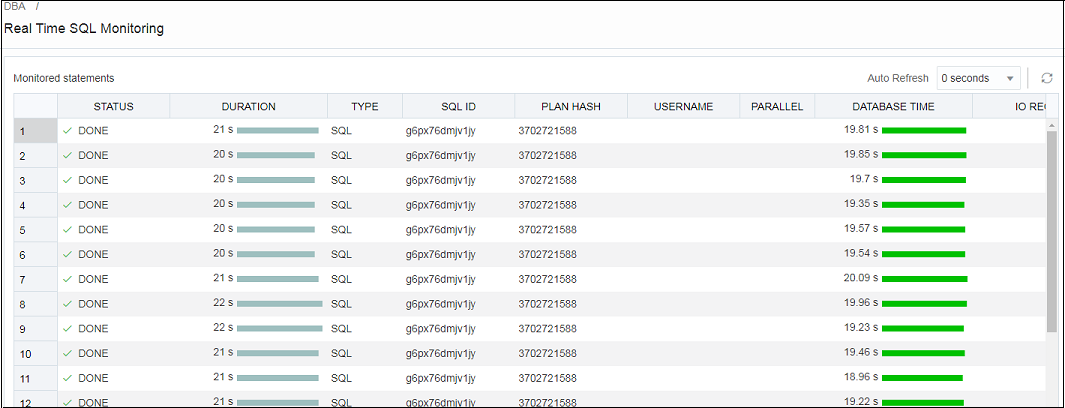
General View of Monitored Statements
The page contains a table of SQL statements currently running. This table shows the following information:
-
Status: Current state of the SQL statement execution. For example, a SQL statement that has already finished its execution will show a status of "DONE".
-
Duration: Amount of time a SQL statement is taking, or has taken, to execute.
-
SQL ID: SQL identifier of the statement being monitored.
-
Session ID: Session identifier that is executing, or has executed, the SQL statement.
-
Session Serial Number: Uniquely identifies a session's objects.
-
Instance Degree of Parallelism: This Degree of Parallelism (DOP) column shows how many instances and parallel execution servers are allocated. It is shown in the form of “number of instances” | “number of parallel servers”.
-
Database Time: Place the cursor over the database time to see a breakdown of the time and wait events.
-
CPU Time: CPU time consumed by the execution of the query.
-
I/O Time: I/O time consumed by the execution of the query.
-
Start Time: Time in which the execution of the SQL statement started.
-
SQL Statement: SQL statement being monitored.
View of SQL Execution Details
When a SQL statement is drilled down from the main monitor table, a detailed view is shown. The SQL ID, Start Time and the SQL Execution ID represent the execution key that uniquely identify this SQL statement. A detail view consists of the general characteristics that integrate the execution of a SQL statement.
General information about the query execution is provided:
-
Execution Plan: Degree of Parallelism of the SQL statement
-
Execution Started: Time that the SQL statement execution started
-
Last Refresh Time: Last update time of the SQL monitor registry for the SQL statement
-
Execution ID: Execution identifier
-
User: User in the format USER@CONTAINER
-
SQL Text: Formatted view of the SQL statement that is being executed.
Figure 7-5 SQL Execution Details in Real Time SQL Monitor
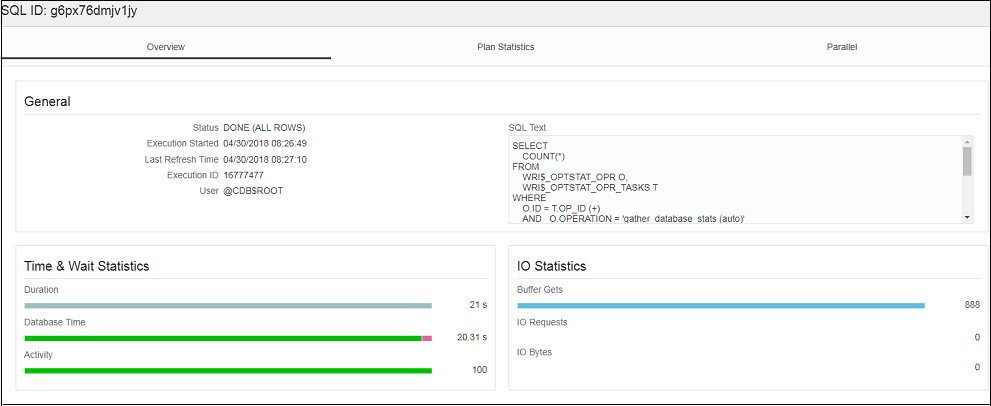
Description of "Figure 7-5 SQL Execution Details in Real Time SQL Monitor"
General statistics of the SQL statement are provided: total duration of execution, the number of buffered gets, number of Input/Output requests and bytes.
Detailed information of the statement: This space holds the information corresponding to the explain plan, parallel behavior and CPU activity involved in the execution of the statement:
-
Plan Statistics: Explain plan of the execution of the SQL statement in the form of a table. Each row is a different operation involved in the execution of the SQL statement and it shows hierarchy dependency by adding a space at the beginning of the text in the Operation column.
-
Parallelism Details for the SQL statement: Each execution consists of a parallel coordinator and one or more parallel sets. Each set can have one or more processes. When a row has dependents, each of its columns will be the sum of the values of its dependants. When this happens, a sigma symbol will appear to show that a value consists of the sum of others.
Note:
For more information, see "Monitoring the Database" in the Oracle Database Administrator’s Guide.