1 Introducing Oracle Tuxedo Mainframe Adapter for TCP Gateway
The Oracle Tuxedo Mainframe Adapter for TCP Gateway (hereafter referenced as TMA TCP Gateway) is a domains-based gateway connectivity feature that allows application programs on Oracle Tuxedo systems to perform non-transactional tasks with application programs in other OLTP systems that support TMA TCP, which include:
- CICS on IBM MVS systems
- IMS/TM on IBM MVS systems
The TMA TCP Gateway is designed to provide transparent access to services that reside outside an Oracle Tuxedo region. In addition, TMA TCP Gateway can provide remote application programs with access to local services.
This chapter provides information about the following topics:
1.1 What You Need to Know
This document is intended for system administrators who will configure and administer TMA TCP Gateway. In addition, programmers will find useful pointers for developing client programs and service routines that send data through TMA TCP Gateway.
This document describes the TMA TCP Gateway component and gives instructions for using the tools for building TMA TCP Gateway applications.
This guide explains how to configure and administer TMA TCP Gateway and how TMA TCP Gateway fits into the Oracle Tuxedo environment. In addition, this guide:
- Explains how TMA TCP Gateway processes service requests, those that originate locally and those that originate on remote systems
- Explains how TMA TCP Gateway affects Oracle Tuxedo application programs
- Provides conceptual and procedural information that will help you configure and administer TMA TCP Gateway
1.2 Oracle TMA TCP Gateway and the Oracle Tuxedo Architecture
An Oracle Tuxedo region consists of client and server programs that operate across a network of Oracle Tuxedo systems or compatible systems. Any client program can request services that are offered by any server program running on any computer in the region. The location of server programs is kept transparent through use of a directory that maps services to servers.
The following figure shows, TMA TCP Gateway extends this transparent access by sending requests to and receiving requests from remote regions and systems through TCP/IP network software.
Figure 1-1 Routing Service Calls through Oracle TMA TCP Gateway
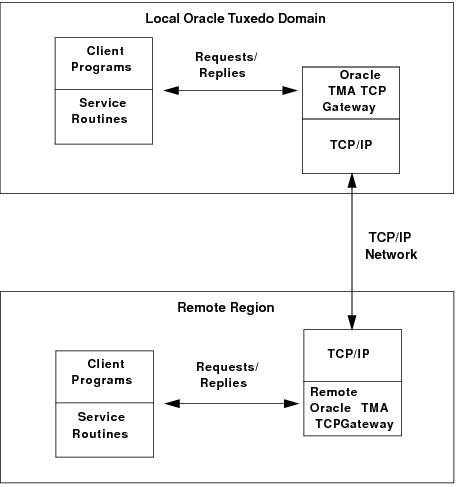
As above figure illustrates, inside a single region, TMA TCP Gateway fits between the Oracle Tuxedo software and TCP/IP.
- When local client programs send requests to remote systems, TMA TCP Gateway transforms those requests into messages formatted appropriately for transmission to the remote system. Also, when remote systems respond, TMA TCP Gateway transforms these responses into replies that local client programs can process.
- When remote client programs send request messages, TMA TCP Gateway transforms those messages into requests that local service routines can process. Also, when local service routines send replies, TMA TCP Gateway transforms those replies into messages that remote services can process.
The TMA TCP Gateway product is implemented as a Tuxedo domain gateway. It accepts standard Oracle Tuxedo service requests and returns standard replies.
One TMA TCP Gateway gateway connects to multiple communications targets, also referred to as gateways. Each communications target, or gateway, is a unique network endpoint.
Although remote systems are identified in the TMA TCP Gateway
configuration, they remain unknown to Oracle Tuxedo software. For
example, remote systems that are accessible through TMA TCP Gateway
are not identified in the MACHINES section of the
UBBCONFIG file.
The TMA TCP Gateway gateway maintains its own control information in shared memory, in much the same way that Oracle Tuxedo software itself maintains the Bulletin Board. Although TMA TCP Gateway accesses the Oracle Tuxedo Bulletin Board, Oracle Tuxedo does not access TMA TCP Gateway control information.
1.3 Operational Considerations
Note:
In the following discussion, a local application program is one that resides within the immediate Oracle Tuxedo administrative region. A remote application program is one that resides outside the immediate Oracle Tuxedo administrative region.- The TMA TCP Gateway software does not support conversational communication.
- The TMA TCP Gateway software supports only nontransactional communication.
- Local client and server programs which use the
tpsprio()function set the priority where service requests are dequeued by TMA TCP Gateway. This process does not affect any prioritization on the remote system. - Local client programs cannot use the
tpbroadcast()function to send unsolicited messages to remote client programs (and the reverse). - Local services cannot use the
tpbroadcast()ortpnotify()functions to send messages to remote client programs (and the reverse). - When local client and server programs use the
tpgprio()function to determine the priority of a remote service, the priority of a local TMA TCP Gateway requester is returned.
For background information about these operational considerations, see Understanding How Oracle TMA TCP Gateway Works
1.4 Oracle TMA TCP Functionality
The following functionality is available in this version of TMA TCP.
1.4.1 Domains-based Gateway Connectivity
The TMA TCP product has a domains-based architecture supporting bidirectional communications, request/response support, and support for MVS Open Transaction Manager Access (OTMA) interfaces.
Parent topic: Oracle TMA TCP Functionality
1.4.2 Security
The TMA TCP Gateway product grants access to Oracle Tuxedo services based on a user name that the remote gateway supplies.
The TMA TCP for CICS product can initiate transactions or link to programs. Oracle Tuxedo security provides the user ID value to the TMA TCP product to test for appropriate security prior to initiating the transactions.
The TMA TCP for IMS product has an OTMA interface that supports enhanced security. This interface allows an Oracle Tuxedo requester to pass a user ID through the OTMA server interface for authorization through a third-party security package, such as RACF.
TMA TCP Gateway supports TLS encryption when communicating with TMA TCP for CICS or TMA TCP for IMS.
Parent topic: Oracle TMA TCP Functionality
1.4.3 Connection Multiplexing
Note:
Each connection is one-directional, which means clients on opposing platforms cannot use the same connection to communicate with remote servers.Parent topic: Oracle TMA TCP Functionality
1.4.4 Domain Name Server Support
The TMA TCP product supports domain name server (DNS) resolution of IP addresses. This support allows you to change the IP address at the Domain Name Server to implement address changes without reconfiguring the TMA TCP gateway.
Parent topic: Oracle TMA TCP Functionality
1.5 GWIDOMAIN Gateway Component
The TMA TCP product consists of a single component, the
GWIDOMAIN gateway. This gateway is responsible for the
mediating both incoming and outgoing requests. It also maintains
connections with all remote gateways.
1.6 How TMA TCP Gateway Affects Oracle Tuxedo Application Programs
The TMA TCP Gateway product preserves the high degree of location transparency that Oracle Tuxedo software provides. In fact, in virtually all cases, programmers do not need to know that particular services are provided by remote systems.
The TMA TCP Gateway product supports the main Oracle Tuxedo communication paradigm: request/reply communications (either synchronous or asynchronous).
All Oracle Tuxedo buffer types can be employed for data exchange. These include:
- X/Open standard XATMI buffer types
X_OCTETX_C_TYPEX_COMMON
- Oracle Tuxedo ATMI buffers
CARRAYSTRINGFMLVIEW
Each of the three X/Open buffer types is equivalent to an Oracle Tuxedo ATMI buffer type. The following information provides these equivalencies.
X_OCTETis equivalent toCARRAYX_C_TYPEis equivalent toVIEWX_COMMONis equivalent toVIEW, but represents only the subset of field types that are common to both the C and COBOL languages
1.6.1 VIEW Definitions
In some circumstances, you must convert typed buffers to formats
that are acceptable to target systems. The standard Oracle Tuxedo
system VIEW definition mechanism is employed for this
purpose.
VIEW definitions make it possible to map input data
and output data between different programming environments (such as
C and COBOL). They also enable TMA TCP Gateway to convert data
representations automatically between different systems.
VIEW definitions can be created by programmers or system administrators. See Configuring Oracle TMA TCP Gateway for Data Mapping for details. For more detailed information about programming considerations, see the Understanding How Oracle TMA TCP Gateway Works.
1.6.2 FML Buffer Support
When communicating with systems or regions that do not support
FML buffers directly, the TMA TCP Gateway can convert FML buffers
to or from user-defined record layouts in a manner transparent to
the FML application. Thus, once a VIEW definition that
describes the remote application’s record layout is created,
it can be used to convert the record to or from an FML buffer. The
GWICONFIG (TMA TCP Gateway configuration file) and
DMCONFIG files contain VIEW
specifications as part of the service description.
Through this conversion between ATMI buffers and record
structures, TMA TCP Gateway supports sending fielded buffers
containing FML data between regions. The TMA TCP Gateway software
converts the data from FML buffers to user-defined records using
the VIEW definitions and field descriptions at the
originating region.
You can use an alternate data mapping tool to map FML buffers to formats that mainframe applications can use. For more information about how to configure TMA TCP Gateway to work with an alternate data mapping tool, see the Configuring Oracle TMA TCP Gateway for Data Mapping and Configuring Oracle TMA TCP Gateway
1.7 How TMA TCP Gateway Affects Oracle Tuxedo Administration
The TMA TCP Gateway administration tools and features are thoroughly integrated with Oracle Tuxedo administration tools and features. Here are some specific examples:
- System administrators define TMA TCP Gateway in the Oracle Tuxedo configuration as a regular Tuxedo domain gateway.
- The TMA TCP Gateway domain configuration file
(
DMCONFIG) specifies how local Oracle Tuxedo service names are mapped to remote service names. Also, theGWICONFIGfile identifiesVIEWdefinitions that TMA TCP Gateway uses to convert and translate input and output data. - At runtime, system administrators use Oracle Tuxedo subcommands to manage TMA TCP Gateway and related processes.
For more detailed information about configuring TMA TCP Gateway, see Configuring Oracle TMA TCP Gateway . For detailed information about commands for administering TMA TCP Gateway, see the Oracle Tuxedo Administrator’s Guide and the Oracle Tuxedo Domain User Guide.