Calculate Period-to-Date Values Using Dynamic Time Series Members
In Essbase, you can calculate period-to-date values. To do this, you define Dynamic Time Series members in the outline. For example, to calculate quarter-to-date values, you enable the Q-T-D member and associate it with a particular generation.
A sample use case of dynamic time series is when you want to calculate the sales values for the current quarter up to the current month. If the current month is May, using a standard calendar quarter, the quarter total is the total of the values for April and May.
In Essbase, you can calculate period-to-date values in the following ways:
-
During a batch calculation, using the @PTD function
-
Dynamically, when a user requests the values, using Dynamic Time Series members
-
As part of an MDX query, using the DTS function
This section explains how to use Dynamic Time Series members to dynamically calculate period-to-date values. Using Dynamic Time Series members is almost always the most efficient method. For a detailed example, see Calculate Period-to-Date Values in an Accounts Dimension.
Use Dynamic Time Series Members
To calculate period-to-date values dynamically, enable a Dynamic Time Series member for a period on the time dimension. You do not create the Dynamic Time Series member in the Essbase outline. Instead, you enable a predefined Dynamic Time Series member in the outline properties, and associate it with a generation.
For example, to calculate quarter-to-date values, you enable the Q-T-D member and associate it with the generation that represents quarters.
Dynamic Time Series members are not displayed as members in the outline, but you can access them from the member selection tool in Smart View to add them to your queries.
In Sample Basic, H-T-D (history-to-date) and Q-T-D (quarter-to-date) are enabled. H-T-D is associated with Year (generation 1), and Q-T-D is associated with quarters (generation 2). The Q-T-D member calculates level 0 monthly values limited to the selected quarter, up to the specified month. The H-T-D member calculates level 0 monthly values for the whole year, up to the specified month.
Essbase provides eight predefined Dynamic Time Series members:
-
H-T-D (history-to-date)
-
Y-T-D (year-to-date)
-
S-T-D (season-to-date)
-
P-T-D (period-to-date)
-
Q-T-D (quarter-to-date)
-
M-T-D (month-to-date)
-
W-T-D (week-to-date)
-
D-T-D (day-to-date)
These members provide up to eight levels of period-to-date reporting. How many and which members you use depends on the data and the outline.
For example, if the cube contains hourly, daily, weekly, monthly, quarterly, and yearly data, you can report day-to date (D-T-D), week-to-date (W-T-D), month-to-date (M-T-D), quarter-to-date (Q-T-D), and year-to-date (Y-T-D) information.
If the cube contains monthly data for the last five years, you can report year-to-date (Y-T-D) and history-to-date (H-T-D) information, up to a specific year.
If the cube tracks data for seasonal time periods, you can report period-to-date (P-T-D) or season-to-date (S-T-D) information.
You can associate a Dynamic Time Series member with any generation in the time dimension except the highest generation number, regardless of the data. For example, you can use the P-T-D member to report quarter-to-date information. You cannot associate Dynamic Time Series members with level 0 members of the time dimension.
Note:
Oracle recommends that you avoid assigning time balance properties (First, Last, Average, Skip Missing) to members set for dynamic calculations if you plan to use these members in Dynamic Time Series calculations. Doing so may retrieve incorrect values for the parent members in your accounts dimension.
Enable and Disable Dynamic Time Series Members
To use a predefined Dynamic Time Series member, you must enable the member in the Essbase outline properties, and associate it with an appropriate generation number.
To enable Dynamic Time Series using the Essbase web interface, open the outline for editing and open the outline properties. In the Dynamic Time Series tab, enable one or more of the predefined members and associate it with the correct generation. Only one predefined member per generation number can be mapped.

Note:
The number of generations displayed depends on the number of generations in the time dimension. You cannot associate Dynamic Time Series members with the highest generation (level 0 members).
If you are using an application workbook / Cube Designer to build the cube, enter a generation number next to one or more of the Dynamic Time Series members on the Cube.Settings worksheet, or delete the generation number to disable it. Refer to Understand the Cube.Settings Worksheet: Dynamic Time Series.

If you use REST API to change the outline, enable a Dynamic Time Series member using the enableDtsMbr outline property when performing an update action, or use the disableDtsMbr property to disable it. Refer to documentation for Run Batch Outline Edit.
If required, you can specify aliases for Dynamic Time Series members. See Specify Alias Names for Dynamic Time Series Members.
Specify Alias Names for Dynamic Time Series Members
You can specify alias names for predefined Dynamic Time Series members, such as QtrToDate, for the Q-T-D Dynamic Time Series member. You can then use the alias names to retrieve the Dynamic Time Series members in Smart View or in a report.
To add aliases for Dynamic Time Series members using the Essbase web interface, open the outline for editing and open the outline properties. In the Dynamic Time Series tab, provide an alias name in the Default table, or in any other alias tables currently defined in your cube.

You can create up to eight alias names for each Dynamic Time Series member. Essbase saves each alias name in the Dynamic Time Series alias table that you specify.
In the Smart View query below, the worksheet is set up (using Smart View Options) to display aliases next to member names.

For information on specifying and displaying alias names, see Set Aliases.
Predefined Generation Names for Dynamic Time Series Members
When you enable a Dynamic Time Series member and associate it with a generation number, Essbase creates a predefined generation name for that generation number.
The Dynamic Time Series members and their corresponding generation names are:
- D-T-D: Day
- H-T-D: History
- M-T-D: Month
- P-T-D: Period
- Q-T-D: Quarter
- S-T-D: Season
- Y-T-D: Week
These member and generation names are reserved for use by Essbase.
For example, in Sample Basic, you can enable Dynamic Time Series for a generation named Quarter. Quarter contains quarterly data in the members Qtr1, Qtr2, and so on. If you enable Dynamic Time Series for generation Quarter, Essbase creates a Dynamic Time Series member called Q-T-D.
Retrieve Period-to-Date Values
When you retrieve a Dynamic Time Series member, you must tell Essbase the time period up to which you want to calculate the period-to-date value. This time period, known as the latest time period, must be a level 0 member on the time dimension.
The following examples for specifying the latest time period in a query are based on Sample Basic.
Smart View
-
Connect to a cube in Smart View.
-
From the Essbase ribbon, open the Member Selection tool.
-
Switch to Dynamic Time Series view.

-
Select one of the Dynamic Time Series Members (for example, Q-T-D) and click Add.
-
Select the latest period you want to report on, and click OK twice.

-
Refresh the worksheet to view the value.
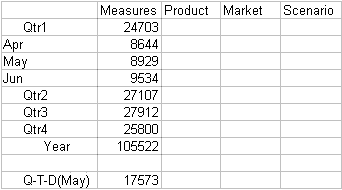
In the example below, Q-T-D(May) displays the period-to-date value for May that is obtained by adding the values for Apr and May (32917 + 33674 = 66591).
Figure 22-2 Spreadsheet Showing Period-To-Date Value for May
Report Writer
The following report script example is based on Sample Basic.
<PAGE (Product, Market, Scenario)
<COLUMN (Measures)
Sales
<ROW (Year)
<ICHILDREN Qtr2
Q-T-D (May)
!The above example produces the following report:
Product Market Scenario Sales
Apr 32,917
May 33,674
Jun 35,088
Qtr2 101,679
Q-T-D(May) 66,591 Optimize Dynamic Time Series Members in Transparent Partitions
To optimize query time across transparent partitions for Essbase outlines containing Dynamic Time Series members, set the application configuration setting TARGETTIMESERIESOPT to TRUE.
To use TARGETTIMESERIESOPT, the time dimensions on the source and target partitions must be identical.