Search Condition General Syntax
A search condition is a single predicate or several predicates connected by the logical operators AND or OR. A predicate is an operation on expressions that evaluates to TRUE, FALSE, or UNKNOWN. If a predicate evaluates to TRUE for a row, the row qualifies for further processing. If the predicate evaluates to FALSE or NULL for a row, the row is not available for operations.
SQL syntax
[NOT]
{BetweenPredicate | ComparisonPredicate | InPredicate |
LikePredicate | NullPredicate | InfinitePredicate | NaNPredicate |
QuantifiedPredicate |(SearchCondition)}
[{AND | OR} [NOT]
{BetweenPredicate | ComparisonPredicate | InPredicate |
LikePredicate | NullPredicate | QuantifiedPredicate | (SearchCondition)}
] [...]Parameters
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Logical operators with the following functions:
|
|
|
Determines whether an expression is within a certain range of values. For example: |
|
|
Compares two expressions or list of two expressions using one of the operators |
|
|
Determines whether an expression or list of expressions matches an element within a specified set. |
|
|
Determines whether a subquery returns any row. |
|
|
Determines whether an expression contains a particular character string pattern. |
|
|
Determines whether a value is |
|
|
Determines whether an expression is infinite (positive or negative infinity). |
|
|
Determines whether an expression is the undefined result of an operation ("not a number"). |
|
|
Determines whether an expression or list of expressions bears a particular relationship to a specified set. |
|
( |
One of the above predicates, enclosed in parentheses. |
Description
-
Predicates in a search condition are evaluated as follows:
-
Predicates in parentheses are evaluated first.
-
NOTis applied to each predicate. -
ANDis applied next, left to right. -
ORis applied last, left to right.
Figure 5-1 shows the values that result from logical operations. A question mark (
?) represents theNULLvalue. -
Figure 5-1 Values that result from logical operations
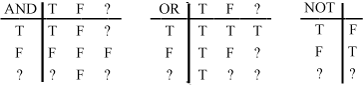
Description of "Figure 5-1 Values that result from logical operations"
-
When the search condition for a row evaluates to
NULL, the row does not satisfy the search condition and the row is not operated on. -
You can compare only compatible data types.
-
TT_TINYINT,TT_SMALLINT,TT_INTEGER,TT_BIGINT,NUMBER,BINARY_FLOATandBINARY_DOUBLEare compatible. -
CHAR,VARCHAR2,BINARY, andVARBINARYare compatible, regardless of length. -
CHAR,VARCHAR2,NCHAR,NVARCHAR2,TT_TIME,DATEandTIMESTAMPare compatible.
-
-
See "Expressions" for information on value extensions during comparison operations.
-
See "Numeric Data Types" for information about how TimesTen compares values of different but compatible types.