6.3.3.1 Monitoring PMEM Cache Using AWR
Note:
In Oracle Database versions that support Oracle Exadata System Software release 23.1.0 and later, all references to PMEM cache are renamed to XRMEM cache (Exadata RDMA Memory Cache). However, these parts of the AWR report still correspond to PMEM cache when the underlying Oracle Exadata Storage Server contains PMEM cache.
Automatic Workload Repository (AWR) contains information relating to PMEM cache. Following are descriptions and examples of the most commonly used sections in the AWR report that contain information about PMEM cache. By reviewing these sections of the AWR report, administrators can understand the operation of PMEM cache.
Note that because storage servers cannot account for the RDMA I/Os, the
Oracle Database statistics are critical in understanding the use of PMEM cache. The PMEM cache
statistics in the Exadata-specific sections of the AWR report only include I/Os that as
serviced by cellsrv, which are not RDMA I/Os.
Apart from the sections described below, the AWR report also contains sections for PMEM Cache User Writes, and PMEM Cache Internal Reads. These sections are not described in detail because they relate to the use of PMEM cache in Write-Back mode, which is not generally recommended.
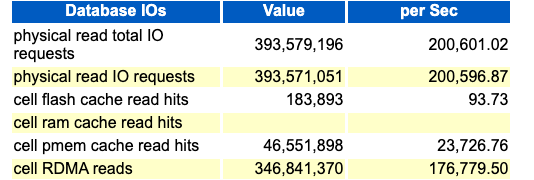
Database IOs
A summary of Database IOs may be found in the Single Block Reads section of the AWR report. This summary contains information about the effectiveness of PMEM cache. The Single Block Reads section is located in the AWR report under Exadata Statistics > Performance Summary.
In the following example, the overwhelming majority of all read I/O
requests (approximately 88%) are serviced using RDMA reads to PMEM cache (cell RDMA reads), at a
rate of more than 176,000 per second. Nearly all of the rest are satisfied using
non-RDMA PMEM cache reads (cell xrmem cache
read hits or cell pmem cache read hits), while the
remaining reads are serviced by using Exadata Smart Flash Cache (cell flash cache read hits). Notice the
massive difference in throughput for each different I/O type, which illustrates the
power of PMEM cache and RDMA.
Figure 6-15 AWR Report: Database IOs
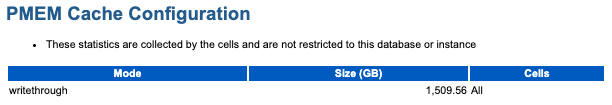
PMEM Cache Configuration and Space Usage
The PMEM Cache Configuration section contains summary information including the caching mode (Write-Through or Write-Back) and overall size. The PMEM Cache Space Usage section provides summary statistics on space usage in PMEM cache.
The following example shows PMEM cache configured in Write-Through mode on all cells, with a total size of approximately 1509 GB.
Figure 6-16 AWR Report: PMEM Cache Configuration
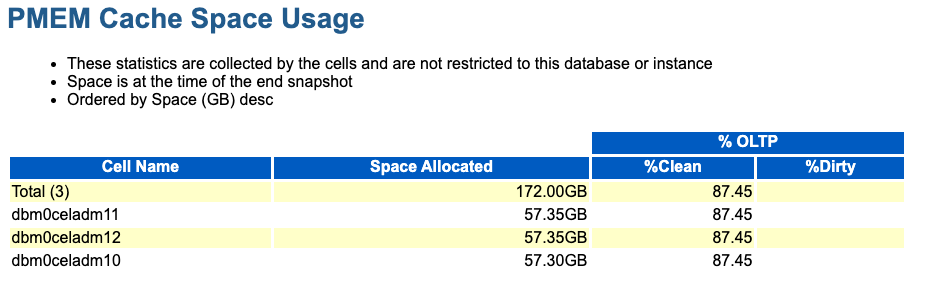
The following example of the PMEM Cache Space Usage section shows 172 GB of PMEM cache spread evenly across 3 cells.
Figure 6-17 AWR Report: PMEM Cache Space Usage
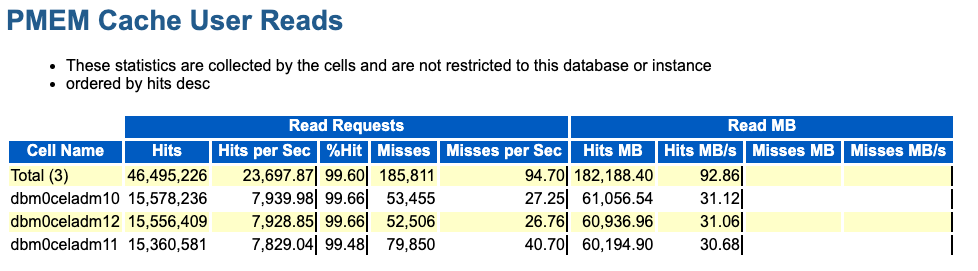
PMEM Cache User Reads
The PMEM Cache User Reads section
shows information about read requests, read throughput, and read efficiency. Because
storage servers cannot account for RDMA I/Os, the statistics only relate to non-RDMA
reads processed by cellsrv. Hits are for I/Os satisfied using PMEM cache, while misses indicate that the data was not
in PMEM cache.
Figure 6-18 AWR Report: PMEM Cache User Reads
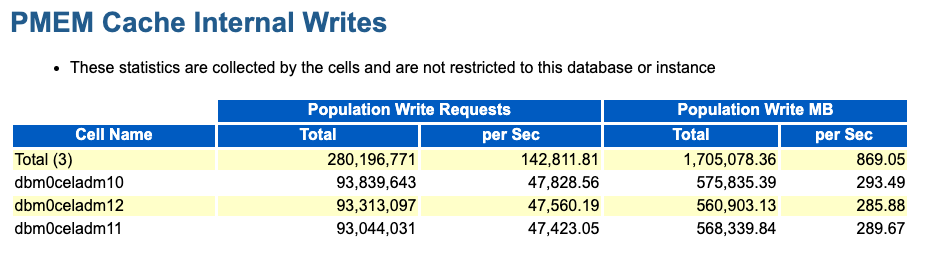
PMEM Cache Internal Writes
The PMEM Cache Internal Writes section shows writes to PMEM cache that are performed by Oracle Exadata System Software. The internal writes are I/Os that populate PMEM cache.
Figure 6-19 AWR Report: PMEM Cache Internal Writes
Parent topic: Monitoring PMEM Cache