6.3.1.1 Monitoring Exadata Smart Flash Cache Using AWR
Automatic Workload Repository (AWR) contains a wealth of information relating to Exadata Smart Flash Cache. Following are descriptions and examples of key sections in the AWR report that contain information about Exadata Smart Flash Cache. By reviewing these sections of the AWR report, administrators can understand how Exadata Smart Flash Cache operates.
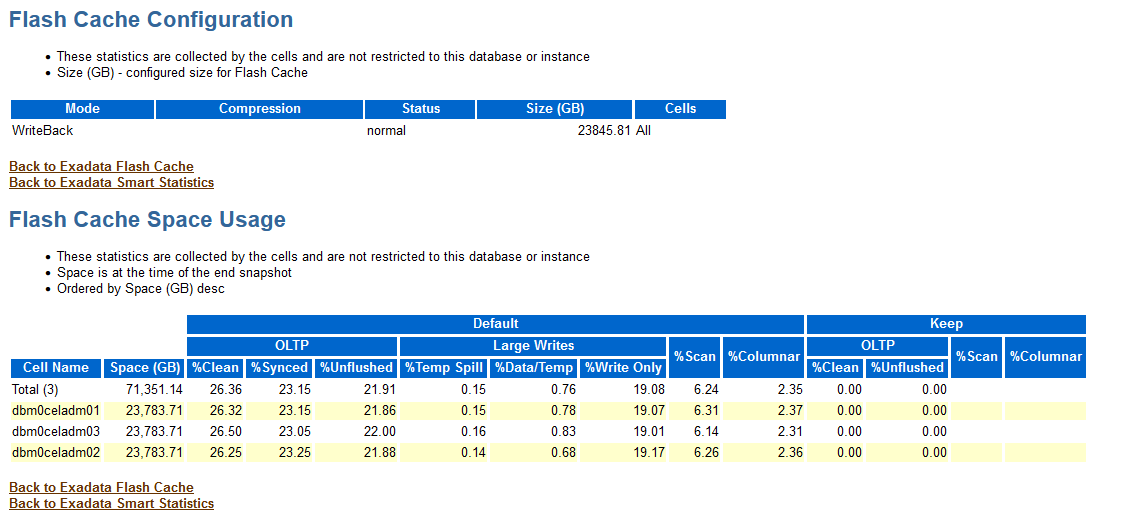
Flash Cache Configuration and Space Usage
The Flash Cache Configuration section contains summary information including the caching mode (Write-Through or Write-Back), status and overall size. The Flash Cache Space Usage section provides summary statistics on space usage in Exadata Smart Flash Cache.
The following example shows Exadata Smart Flash Cache configured in Write-Back mode on all cells, with a size of almost 24 TB on each cell. In the example, the Flash Cache Space Usage section shows that:
-
Practically all of the Exadata Smart Flash Cache space is in use on each cell.
-
Approximately 70% of the allocated space is being used for OLTP, which is typically data that is read into the database buffer cache using block mode reads. The OLTP data is further categorized as follows:
-
Clean data is data that is unchanged since being read into the cache. In the example output, approximately 26% of the space in each cache contains clean OLTP data.
-
If cached OLTP data is updated and the update is written back to the primary storage (usually a hard disk drive), the data is classified as synced. In the example output, approximately 23% of the space in each cache contains synced OLTP data.
-
When cached OLTP data is updated, but the update has not been written to the primary storage, the data is classified as unflushed. In the example output, approximately 22% of the space in each cache contains unflushed OLTP data.
-
-
Approximately 20% of the cache space is being used to absorb large writes.
-
Approximately 6% of the cache supports scan operations.
-
Approximately 2% of the cache is being used to support the columnar cache.
-
In this case, none of the cache space is occupied by keep objects. Keep objects are database segments (tables, partitions, and so on) that override the default caching policy for Exadata Smart Flash Cache by using the
CELL_FLASH_CACHEstorage clause option with theKEEPsetting.
Figure 6-4 AWR Report: Flash Cache Configuration and Space Usage
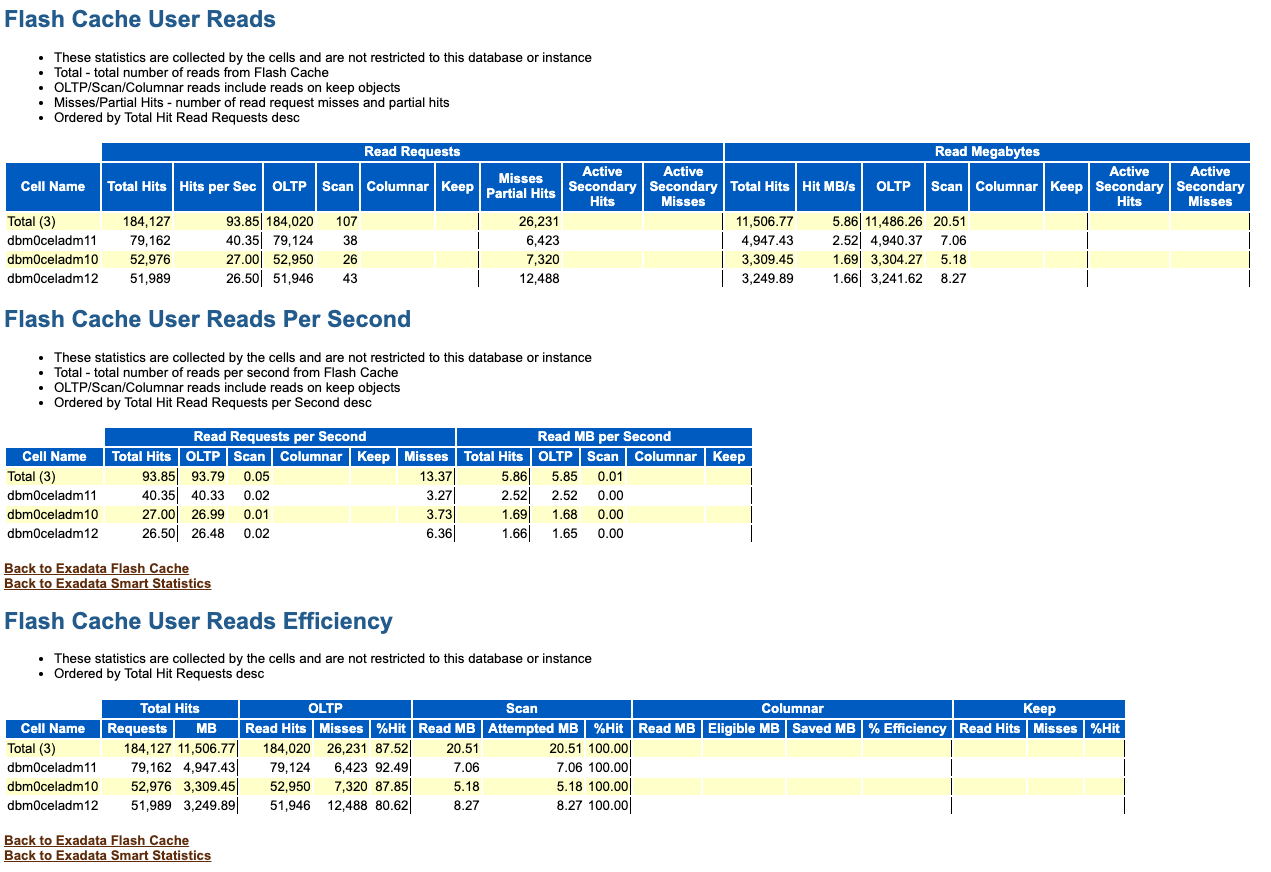
Flash Cache User Reads
The Flash Cache User Reads sections show information about read requests, read throughput, and read efficiency from database clients. The statistics show the I/Os against different areas of Exadata Smart Flash Cache:
- OLTP - relates to block requests
- Scan - relates to scan requests
- Columnar - relates to columnar cache requests
- Keep - relates to read requests against the KEEP pool
Figure 6-5 AWR Report: Flash Cache User Reads
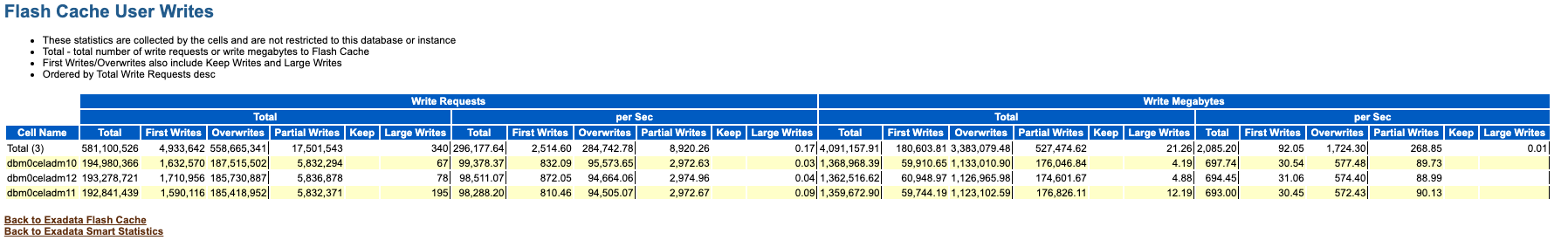
Flash Cache User Writes
The Flash Cache User Writes section shows information about write requests and write throughput for Exadata Smart Flash Cache in Write-Back mode.
In this section, First Writes indicate new data being written to Exadata Smart Flash Cache, while Overwrites indicate data being overwritten in Exadata Smart Flash Cache. First Writes also require writing additional flash cache metadata. Overwrites represents the disk writes that were avoided by using Exadata Smart Flash Cache in Write-Back mode.
Figure 6-6 AWR Report: Flash Cache User Writes
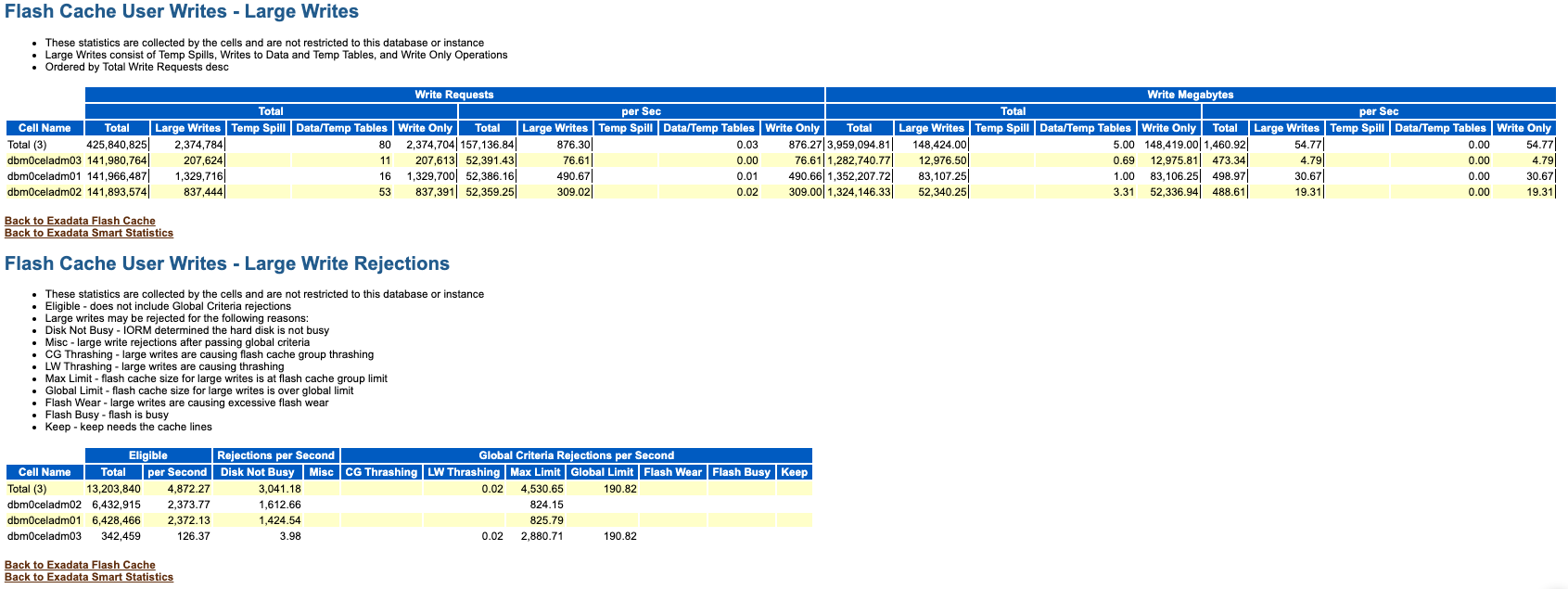
Flash Cache User Writes - Large Writes
The Flash Cache User Writes - Large Writes sections show information about large write requests that are absorbed and rejected by Exadata Smart Flash Cache in Write-Back mode.
Figure 6-7 AWR Report: Flash Cache User Writes - Large Writes
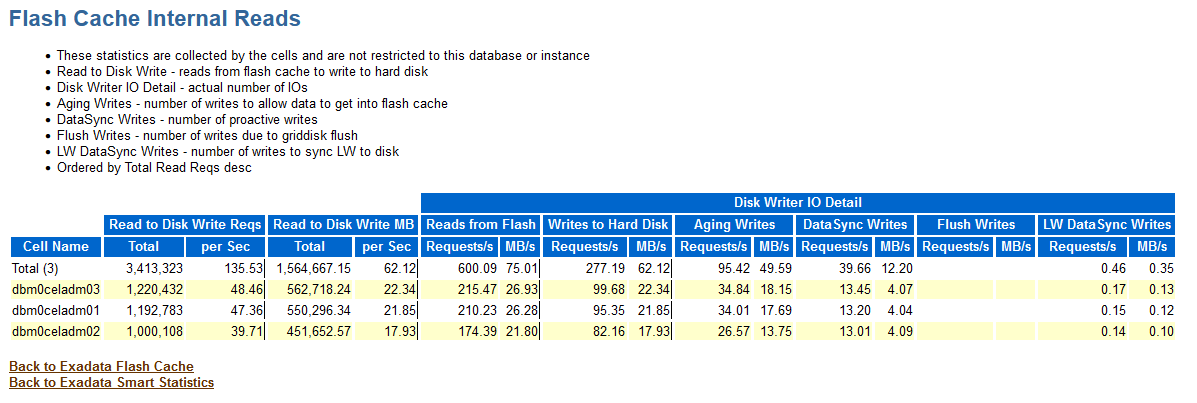
Flash Cache Internal Reads
The Flash Cache Internal Reads section shows reads from Exadata Smart Flash Cache that are performed by Oracle Exadata System Software. These statistics are populated when Exadata Smart Flash Cache is in Write-Back mode.
The Disk Writer IO Detail columns relate to internal I/Os performed to persist data from Exadata Smart Flash Cache to hard disk devices. These columns show the reads from flash and the various categories of writes to hard disk.
Figure 6-8 AWR Report: Flash Cache Internal Reads
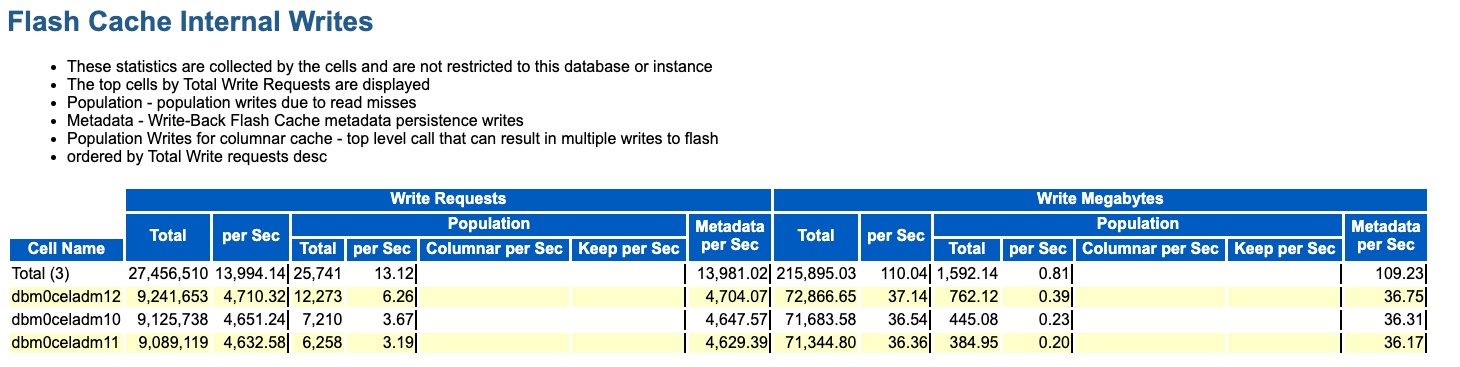
Flash Cache Internal Writes
The Flash Cache Internal Writes section shows writes to Exadata Smart Flash Cache that are performed by Oracle Exadata System Software. The internal writes are I/Os that populate Exadata Smart Flash Cache in response to a cache read miss.
The statistics also include metadata writes that occur when Exadata Smart Flash Cache is in Write-Back mode. Metadata writes occur when a cacheline is used to cache new data.
Figure 6-9 AWR Report: Flash Cache Internal Writes
Parent topic: Monitoring Exadata Smart Flash Cache