9 Managing Oracle Databases
Manage the Oracle Databases on your Oracle Database Appliance.
- About Administrative Groups and Users on Oracle Database Appliance
Oracle Database Appliance Browser User Interface deployment creates operating system groups and users whose members are granted system administration privileges on the appliance. - About Data Migration Options for Oracle Database Appliance
Oracle Database Appliance supports the use of standard Oracle Database loading and migration tools. - About Standard Edition High Availability for Oracle Database Appliance
Oracle Database Appliance supports Standard Edition High Availability solution with Oracle Grid Infrastructure that provides cluster-based failover for Oracle Database 19c Standard Edition. - About Transparent Database Encryption (TDE) in Oracle Database Appliance
Transparent Data Encryption (TDE) enables you to encrypt sensitive data that you store in tables and tablespaces. - Working with Databases
Use the Browser User Interface to display a list of databases, database details, and create and delete databases. You can use CLI commands to manage your databases. - Working with Database Homes
Use the Browser User Interface to display a list of database homes, details, and create and delete database homes. - Migrating Databases
Review these topics to learn how to prepare for and migrate an entire database to your Oracle Database Appliance. - About Managing Multiple Database Instances Using Instance Caging
Use instance caging to manage your system resources on Oracle Database Appliance. - Oracle EM Express and DB Console
You can use Oracle Enterprise Manager Database Express (EM Express), or the Database Control Console (DB Console) to manage your database.
About Administrative Groups and Users on Oracle Database Appliance
Oracle Database Appliance Browser User Interface deployment creates operating system groups and users whose members are granted system administration privileges on the appliance.
During configuration, two administrative accounts are created for Oracle Database Appliance: the user grid, with a user ID (UID) of 1001, and the user oracle, with a UID of 1000. The user grid is the Oracle Grid Infrastructure installation owner. The user oracle is the Oracle Database installation owner, and the owner of all Oracle Database homes (Oracle homes). By default, these users are members of operating system groups whose members are granted privileges to start up and administer Oracle Database and Oracle Automatic Storage Management.
The following table describes the Oracle system privileges groups, and information about the operating system authentication groups:
Table 9-1 Operating System Groups and Users on Oracle Database Appliance
| Oracle System Privileges | Group Name | Group ID (GID) | grid is a member | oracle is a member |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Oracle Inventory group (OINSTALL) |
|
1001 |
yes (primary group) |
yes (primary group) |
|
OSOPER for dbaoper group |
|
1002 |
yes |
yes |
|
OSDBA group |
|
1003 |
no |
yes |
|
OSASM group for Oracle ASM |
|
1004 |
yes |
no |
|
OSOPER for ASM group |
|
1005 |
yes |
no |
|
OSDBA for ASM group |
|
1006 |
yes |
yes |
To change the Group Name and GID from the default values on Oracle Database Appliance bare metal platforms, change the default values from the Browser User Interface during the deployment. If you create an initial database during deployment, then the password for the SYS and SYSTEM users is the password that you set in the Browser User Interface.
To change the Group Name and GID from the default values on the Oracle Database
Appliance Virtualized Platform, use the -advance parameter with the
command oakcli deploy. If you create an initial database
during deployment, then the password for the SYS and SYSTEM users is the ROOT password
from the Configurator.
Note:
Change the password for both users as soon as possible after configuration to prevent unauthorized access to your database using these privileged accounts.Parent topic: Managing Oracle Databases
About Data Migration Options for Oracle Database Appliance
Oracle Database Appliance supports the use of standard Oracle Database loading and migration tools.
If you are loading data or migrating data from an existing database to Oracle Database Appliance, then you can use the standard Oracle Database loading and migration tools. These tools include the following:
-
Oracle GoldenGate
-
SQL*Loader
-
Oracle Data Pump
-
transportable tablespaces
-
RMAN
You can also use the RMAN utility to back up and recover databases on Oracle Database Appliance.
Parent topic: Managing Oracle Databases
About Standard Edition High Availability for Oracle Database Appliance
Oracle Database Appliance supports Standard Edition High Availability solution with Oracle Grid Infrastructure that provides cluster-based failover for Oracle Database 19c Standard Edition.
About Standard Edition High Availability for Oracle Database 19c
With Standard Edition High Availability, when there is an instance or a node failure, the database automatically fails over to the other node, after attempting to restart on the local node. The database is restarted on the surviving node, thereby providing high availability for Oracle Standard Edition databases.
If your Oracle Database deployment contains Standard Edition 2 Oracle Real Application Cluster (Oracle RAC) databases of releases earlier than 19c, then they must be converted to a Standard Edition High Availability configuration as part of the upgrade to Oracle Database 19c.
For more details about this feature, refer to the Oracle Database Documentation Library at https://docs.oracle.com/en/database/oracle/oracle-database/index.html.
About Standard Edition High Availability for Oracle Database Appliance Release 19.9
Standard Edition High Availability for Oracle Database 19c is supported on Oracle Database Appliance for high availability deployments, that is, deployments that have two server nodes, shared storage, and server interconnects.
Oracle Database Appliance enables automatic configuration for failover at deployment time for Oracle Database 19c Standard Edition single-instance databases. Both nodes have Oracle Homes for Standard Edition single-instance databases.
Single-instance Oracle Database 19c Standard Edition databases created using the ODACLI commands or the Browser User Interface (BUI) have Standard Edition High Availability enabled by default. You can also choose to disable the High Availability option. To enable Standard Edition High Availability for existing Standard Edition Oracle RAC databases of releases earlier than 19c, you must convert these Oracle RAC databases to single-instance databases, and then upgrade to single-instance Oracle Database 19c Standard Edition database with Standard Edition High Availability enabled by default.About Provisioning, Upgrading, and Relocating Standard Edition High Availability Oracle Database
To create a single-instance Oracle Database 19c with Standard Edition High Availability, use the following command:
odacli create-database -u db_unique_name -n db_name -dh db_home -y SI -g target_nodeTo upgrade a Standard Edition Oracle RAC Database to Oracle Database 19c Standard Edition, convert the Oracle RAC Database to a single-instance Oracle Database:
odacli modify-database -in db_name -y single-instanceThen, upgrade the single-instance database to Oracle Database 19c with Standard Edition High Availability as follows:
odacli upgrade-database -i db_id -to destination_dbhome -shTo relocate a Standard Edition High Availability Oracle Database from one node to another outside of a failover, use the following command:
odacli modify-database -in db_name -g target_node | -th target_hostFor detailed information about these ODACLI command options, see the Oracle Database Appliance Command Line Reference chapter in this guide.
About Transparent Database Encryption (TDE) in Oracle Database Appliance
Transparent Data Encryption (TDE) enables you to encrypt sensitive data that you store in tables and tablespaces.
After the data is encrypted, this data is transparently decrypted for authorized users or applications when they access this data. TDE helps protect data stored on media (also called data at rest) in the event that the storage media or data file is stolen.
Oracle Database uses authentication, authorization, and auditing mechanisms to secure data in the database, but not in the operating system data files where data is stored. To protect these data files, Oracle Database provides Transparent Data Encryption (TDE).
TDE encrypts sensitive data stored in data files. To prevent unauthorized decryption, TDE stores the encryption keys in a security module external to the database, called a keystore.
Note:
To enable Transparent Data Encryption (TDE), you must deploy Enterprise Edition Oracle Database 18c or later.See Also:
Using Transparent Data Encryption in the Oracle Database Advanced Security GuideCaution:
When you enable TDE, you are prompted to set a password for the TDE wallet. Provide a strong password for security compliance. Set the password carefully, and ensure that this password is available to you at all times for database management operations. Failure to provide the TDE wallet password when prompted, will cause an error in accessing encrypted data.Parent topic: Managing Oracle Databases
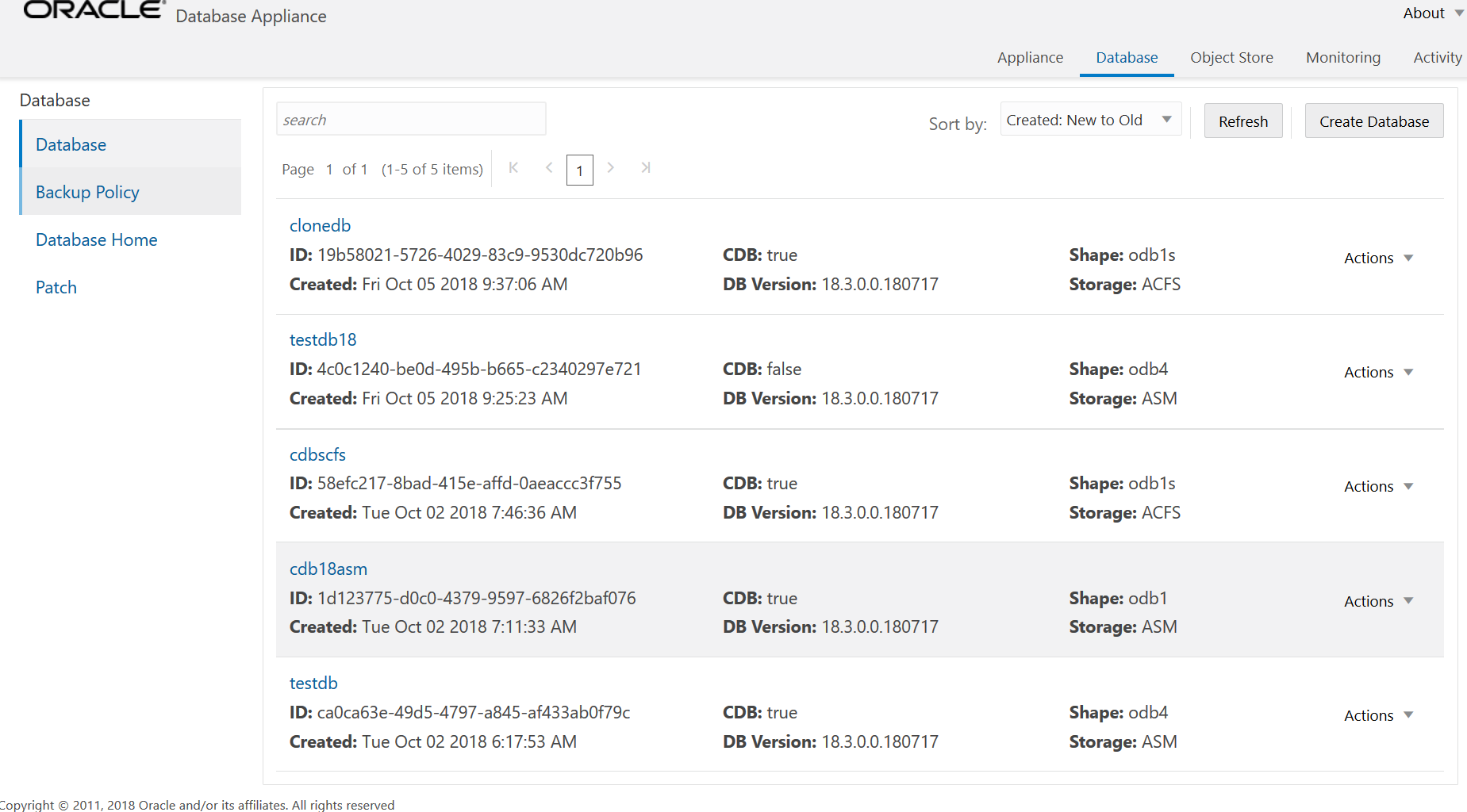
Working with Databases
Use the Browser User Interface to display a list of databases, database details, and create and delete databases. You can use CLI commands to manage your databases.
Note:
Oracle Database Appliance enables unified auditing for databases created in new database homes. Unified audit trail captures audit information and places them in one location and in one format. This consolidated view enables auditors to co-relate audit information from different components. Having a single audit trail also improves management and security of the audit trail. For more information about unified audit trail for Oracle Database, see Oracle Database Security Guide.- Viewing Databases
Use the Oracle Appliance Manager Browser User Interface to display a list of Oracle databases and database details, create, upgrade, and delete a database in Oracle Database Appliance. - Creating a Database Using the Browser User Interface
Use the Oracle Appliance Manager Browser User Interface to create a database in Oracle Database Appliance. - Creating a Database Using ODACLI Commands
Create a database from the command-line interface. - Cloning a Database from Backup
Use the Browser User Interface to clone a database from a backup. - Cloning an Oracle ACFS Database Using the Browser User Interface
Create a database from an existing Oracle ACFS database using the Browser User Interface. - Cloning an Oracle ACFS Database Using Command Line Interface
Create a database from an existing Oracle ACFS database using CLI commands. - Modifying a Database
Use the Oracle Appliance Manager Browser User Interface or ODACLI commands to modify a database in Oracle Database Appliance. - Moving a Database from One Oracle Home to Another
Use the Oracle Appliance Manager Browser User Interface or ODACLI commands to move a database from one Oracle home to another of the same database version. - Upgrading a Database
Use the Oracle Appliance Manager Browser User Interface to upgrade an Oracle database to a different database home version. - Deleting a Database
Use the Oracle Appliance Manager Browser User Interface to delete an Oracle database.
Parent topic: Managing Oracle Databases
Viewing Databases
Use the Oracle Appliance Manager Browser User Interface to display a list of Oracle databases and database details, create, upgrade, and delete a database in Oracle Database Appliance.
oakcli list databases.
Parent topic: Working with Databases
Creating a Database Using the Browser User Interface
Use the Oracle Appliance Manager Browser User Interface to create a database in Oracle Database Appliance.
Note:
For Standard Edition Oracle Database 19c or later, you cannot create Oracle RAC Or Oracle RAC One Node Database. You can only create single-instance Oracle Database. For Standard Edition Oracle Database 19.6 or later, you can choose to enable high availability for single-instance database.The Browser User Interface provides a quick and easy method of creating new databases. The Create New Database page in the Browser User Interface is populated with default options for most of the configuration options. Drop-down lists enable you to quickly view and select from a list of available options. You can use the drop-down list to create a new database Oracle Database Home (ORACLE_HOME) for the database or select an existing ORACLE_HOME that you created earlier.
Oracle Database 19.9 is
supported on both Oracle Automatic Storage Management (Oracle ASM) and Oracle ASM
Cluster file system (Oracle ACFS). When databases are created in Oracle ACFS, each
database is configured with its own Oracle ACFS file system for the datafiles and
uses the following naming convention: /u02/app/db
user/oradata/db unique
name. The default size of this mount point is 100 GB.
Follow these steps to create a database:
After you close the Job confirmation page, you can click the Activity tab to monitor the job progress. Click the job number to view the tasks and status details. Click Refresh to refresh the page.
Parent topic: Working with Databases
Creating a Database Using ODACLI Commands
Create a database from the command-line interface.
Note:
If you provisioned the appliance without creating an initial database, then you must create a Oracle home. If the version of the database home is different from the migrated database, create a database home for the migrated database. You might want to create a database home specifically for the migrated database.Caution:
When you create a database with Transparent Data Encryption (TDE) enabled, you are prompted to set a password for the TDE wallet. Provide a strong password for security compliance. Enter this password carefully when setting it for the first time, and ensure that this password is available to you at all times for database management operations. Failure to provide the TDE wallet password when prompted, will cause an error in accessing encrypted data.This example creates a new database named PRODDB with database
version 19.9, and a new database home, if a database
home does not exist.
Parent topic: Working with Databases
Cloning a Database from Backup
Use the Browser User Interface to clone a database from a backup.
-
The source database backup location must be Object Store or External FRA (Network File System).
-
If you use Object Store backup location, then obtain Object Store Credentials for the host.
-
If you use an External FRA (Network File System) backup location, then obtain the Network File System (NFS) mount point location.
-
Create a backup policy using the object store credentials or NFS mount point as the backup destination.
-
Attach the backup policy to the database that you want to backup. If the source database does not have TDE enabled, then providing the Backup Encryption password is mandatory when attaching Objectstore backup policy. However, the Backup Encryption password is optional when attaching the NFS backup policy. If the source database has TDE enabled, then you must specify the TDE password, and not the Backup Encryption password.
-
Create a manual backup of the database and save the backup report generated when the backup completes.
Parent topic: Working with Databases
Cloning an Oracle ACFS Database Using the Browser User Interface
Create a database from an existing Oracle ACFS database using the Browser User Interface.
-
Create a database from another database without bringing down the source database
-
Create multiple databases from a gold image, thus ensuring standardized mass deployments
-
Optimize space utilization, by use of Oracle ACFS snapshots in cloning
-
Create different types of databases, from a single source database type. For example, you can create single-instance databases, Oracle RAC databases, or Oracle RAC One Node databases from any type of source database
-
Depending on the available memory and CPU cores, specify a supported database shape such as
odb1s,odb2, and so on, to create any class of database from any source database.
Note:
Cloning a Transparent Database Encryption (TDE) enabled database is not supported.Parent topic: Working with Databases
Cloning an Oracle ACFS Database Using Command Line Interface
Create a database from an existing Oracle ACFS database using CLI commands.
-
Create a database from another database without bringing down the source database
-
Create multiple databases from a gold image, thus ensuring standardized mass deployments
-
Optimize space utilization, by use of Oracle ACFS snapshots in cloning
-
Create different types of databases, from a single source database type. For example, you can create single-instance databases, Oracle RAC databases, or Oracle RAC One Node databases from any type of source database
-
Depending on the available memory and CPU cores, specify a supported database shape such as
odb1s,odb2, and so on, to create any class of database from any source database. - The ability to create clone databases on a standby system enables you to set up test or development environments based on your standby databases. Since standby systems are not production systems, they are a better choice for seeding test or development environments.
-
Ensure that Oracle Clusterware is running on all nodes, and the source database is up and running.
-
The source database must use Oracle ACFS storage.
-
The source database must not be a multitenant container databases (CDBs)
-
The source database must be in the OPEN state.
-
The source database must not be in backup mode.
-
The source database must be in archive mode.
- The source database must not have Transparent Database Encryption (TDE) enabled.
Note:
For Standard Edition Oracle Database 19c or later, you cannot clone Oracle RAC or Oracle RAC One Node Database. You can only clone an single-instance Oracle Database. For Standard Edition Oracle Database 19.6 or later, you can choose to enable high-availability for single-instance database.Follow this procedure to clone a database:
Related Topics
Parent topic: Working with Databases
Modifying a Database
Use the Oracle Appliance Manager Browser User Interface or ODACLI commands to modify a database in Oracle Database Appliance.
Modifying a Database Using the Browser User Interface
- Log into the Browser User Interface:
https://host-ip-address:7093/mgmt/index.html
- Click the Database tab.
- For the database that you want to modify, select Modify in the Actions drop down list.
- In the Modify Database page, you can attach or detach associated networks and backup policy, and modify database shape and class.
- To modify the Database Class or Database Shape, select the new value in the drop down list.
- To attach or detach networks, modify the values in the Attach Networks and Detach Networks fields.
- To remove the associated backup policy from the database, do not select any value in the Select Back up Policy drop down list.
- If you configured Oracle Flex disk group when you created the database, you can also modify the database redundancy. If the database you are modifying is an Oracle ACFS Database, then the database redundancy for all cloned Oracle ACFS databases is modified.
- You can choose to change the Backup Encryption Password. If the database has TDE enabled, then the RMAN Backup Encryption password is not used.
- Click Modify. When prompted, click Yes to confirm that you want to start the job to modify the database.
Modifying a Database Using ODACLI Commands
- Use the
odacli modify-databasecommand to modify the configuration of a database, such as backup configuration, database class, database type, TDE key.# odacli modify-database -s database_shape -cl database_class -i dbidFor example:# odacli modify-database -i 1941d594-c777-4eca-9fce-18b778d5c153 -s odb2 -cl DSSFor example, the following command re-keys the TDE master encryption key of the database after accepting the current TDE Wallet password.
# odacli modify-database -in testdb -rkt Current password for TDE wallet:For more information about the
odacli modify-databasecommand options, see the Oracle Database Appliance Command Line Reference chapter in this guide.
Related Topics
Parent topic: Working with Databases
Moving a Database from One Oracle Home to Another
Use the Oracle Appliance Manager Browser User Interface or ODACLI commands to move a database from one Oracle home to another of the same database version.
Moving a Database Using the Browser User Interface
- Log into the Browser User Interface:
https://host-ip-address:7093/mgmt/index.html
- Click the Database tab.
- For the database that you want to modify, select Move in the Actions drop down list.
- Select the Destination Database Home where you want to move the database. The destination database home must be of the same base version.
- Click Move. When prompted, click Yes to confirm that you want to start the job to move the database.
Moving a Database Using ODACLI Commands
- Use the
odacli move-databasecommand to move a database from one Oracle home to another home of the same database version.# odacli move-database -i database_ID -dh destination_database_home_IDFor more information about the
odacli move-databasecommand options, see the Oracle Database Appliance Command Line Reference chapter in this guide.
Related Topics
Parent topic: Working with Databases
Upgrading a Database
Use the Oracle Appliance Manager Browser User Interface to upgrade an Oracle database to a different database home version.
Note:
You cannot upgrade Oracle RAC or Oracle RAC One Node Database to a destination database home of Standard Edition Oracle Database 19c or later. You must first convert Oracle RAC Or Oracle RAC One Node Database to single-instance Oracle Database using theodacli
modify-database command and then upgrade the
single-instance Oracle Database to a destination database home of
Standard Edition 19c or later.
Parent topic: Working with Databases
Deleting a Database
Use the Oracle Appliance Manager Browser User Interface to delete an Oracle database.
Parent topic: Working with Databases
Working with Database Homes
Use the Browser User Interface to display a list of database homes, details, and create and delete database homes.
- About Managing Multiple Oracle Homes on Oracle Database Appliance
Create and manage one or more Oracle home directories and Oracle databases on Oracle Database Appliance. - Viewing Database Homes
Use the Browser User Interface to display a list of database homes and database home details, including databases associated with a DB home. - Creating a Database Home
Use the Browser User Interface to create database homes in Oracle Database Appliance. - Deleting a Database Home
Use the Browser User Interface to delete an Oracle database home.
Parent topic: Managing Oracle Databases
About Managing Multiple Oracle Homes on Oracle Database Appliance
Create and manage one or more Oracle home directories and Oracle databases on Oracle Database Appliance.
Oracle home is the directory in which you install Oracle Database binaries, and from which Oracle Database runs. Oracle Database Appliance supports multiple Oracle homes, including support of different release Oracle Database homes. You can create multiple Oracle databases on a given Oracle home. Use Oracle Appliance Manager Browser User Interface to create and manage multiple Oracle homes and databases on Oracle Database Appliance. Oracle Database Appliance Manager automatically creates an Oracle Database Oracle home that is compliant with Oracle’s Optimal Flexible Architecture (OFA) standards.
Check the Oracle Database Appliance Release Notes to obtain information about the specific Oracle software releases supported for your Oracle Database Appliance platform.
When you use ODACLI commands to create multiple homes on Oracle Database Appliance, the commands start the Oracle Home cloning process. In Oracle Database Appliance deployments, the user oracle is the default software installation owner.
You can use the Browser User Interface or the command-line interface to create and manage databases.
Use ODACLI commands to create, list, describe, and delete databases on Oracle Database Appliance. The odacli create-database command enables you to create a database with minimal user input. When you run this command without any additional options, the command creates a new database home (ORACLE_HOME). You can create a database in an existing home by using the --dbhomeid option. To find the dbhomeid, use the odacli list-dbhomes command.
Alternatively, you can use the Browser User Interface to create list, describe and delete databases and database homes. You can display a list of all Database Homes that includes the database home name, ID, version, the date and time that the database home was created and the location on the same page. You can also create and delete database homes on the Browser User Interface.
Caution:
Do not apply Oracle Database patches directly to Oracle Databases on Oracle Database Appliance. Only use Oracle Database Appliance patch bundles, which are tested to work across the whole software stack. If a one-off database patch is required, it may be applied to the Oracle Home. When you apply the Oracle Database Appliance patch bundle, it may cause a conflict during future patching events and you might need to roll back and then re-apply the patch.
Parent topic: Working with Database Homes
Viewing Database Homes
Use the Browser User Interface to display a list of database homes and database home details, including databases associated with a DB home.
Parent topic: Working with Database Homes
Creating a Database Home
Use the Browser User Interface to create database homes in Oracle Database Appliance.
Parent topic: Working with Database Homes
Deleting a Database Home
Use the Browser User Interface to delete an Oracle database home.
Parent topic: Working with Database Homes
Migrating Databases
Review these topics to learn how to prepare for and migrate an entire database to your Oracle Database Appliance.
- About Migrating Databases
You can migrate an entire active container database (CDB) or non-CDB database to an Oracle Database Appliance machine by using the RMAN duplicate command. - Configuring a Static Listener
Configure a static listener before you duplicate a database. - Migrating a Database
Use theRMAN Duplicatecommand to migrate the entire database to the appliance. - Registering a Database
Use theodacli register-databasecommand to register the migrated database with the appliance.
Parent topic: Managing Oracle Databases
About Migrating Databases
You can migrate an entire active container database (CDB) or non-CDB database to an Oracle Database Appliance machine by using the RMAN duplicate command.
When using RMAN Duplicate, ensure to have network connectivity from source and target databases:
-
Source database: The existing database to be migrated.
-
Target database: The new database created on an Oracle Database Appliance environment.
If you do not have network connectivity between the source and the target environments, you can use the offline migration method. Offline migration uses RMAN backup sets for duplication, which does not require connectivity to the primary database.
At a high level, the procedure involves the following steps:
-
Deploy or update Oracle Database Appliance to the latest version.
Confirm that the provisioning completed successfully. On bare metal systems, use the command
odacli list-jobsand the commandodacli describe-jobto verify the status. -
Create an instance only database from the command-line interface.
-
On bare metal systems, use the command
odacli create-databasewith theinstanceonlyflag on an Oracle Database Appliance machine. The new database is the target database.
Creating an instance only database also creates the following:
-
ACFS Filesystem used to store the database files
-
Directory structures that are required by the database instance/rman duplicate command
-
Password file for the SYS user
-
-
Configure a static listener.
-
Migrate the existing database to the target database using the backup and restore operations.
-
Register the migrated database with the appliance.
Note:
You can only migrate and register a database of the same storage type. For example, to migrate and register an Oracle ACFS database, you must create an Oracle ACFS database and then migrate and register it. Similarly, to to migrate an Oracle ASM database, you must create an Oracle ASM database and then migrate it.Parent topic: Migrating Databases
Configuring a Static Listener
Configure a static listener before you duplicate a database.
The static listener is only required when using RMAN Duplicate command.
Perform the following steps to manually configure the listener.ora file:
Parent topic: Migrating Databases
Migrating a Database
Use the RMAN Duplicate command to migrate the entire database to the appliance.
Parent topic: Migrating Databases
Registering a Database
Use the odacli register-database command to register the migrated database with the appliance.
The dbclass, dbshape, servicename and password are mandatory for registering the database. The dbclass and dbshape determine the sga_target and pga_target settings. The database init.ora parameters are reset as part of the odacli register-database command. Review the init.ora parameters after registration and ensure that the parameters set correctly.
Note:
Theodacli register-database
command is supported only for primary database of type single-instance.
Follow these steps to register a database:
Parent topic: Migrating Databases
About Managing Multiple Database Instances Using Instance Caging
Use instance caging to manage your system resources on Oracle Database Appliance.
Oracle Database provides a method for managing CPU allocations on a multi-CPU server that runs multiple database instances. This method is called instance caging. Instance caging uses an initialization parameter to limit the number of CPUs that an instance can use simultaneously.
Instance caging and Oracle Database Resource Manager (the Resource Manager) work together to support your desired service levels across multiple instances. Consolidation can minimize idle resources, maximize efficiency, and lower costs.
Oracle Database Appliance templates are already tuned for the size of each database instance workload. They are designed to run on a specific number of cores. Instance caging ensures that each database workload is restricted to the set of cores allocated by the template, enabling multiple databases to run concurrently with no performance degradation, up to the capacity of Oracle Database Appliance. You can select database template sizes larger than your current needs to provide for planned growth.
Note:
Oracle strongly recommends that you use the Oracle Database Appliance templates, because they implement best practices and are configured specifically for Oracle Database Appliance.
The Oracle Database Appliance Manager interface refers to the database sizing templates as database classes.
By default, instance caging is not enabled on Oracle Database Appliance. To enable instance caging, set the initialization parameter, RESOURCE_MANAGER_PLAN, for each database on Oracle Database Appliance. The parameter specifies the plan to be used by the Resource Manager for the current instance. Setting this parameter directs the Resource Manager to allocate core resources among databases. If a plan is not specified with this parameter, then the Resource Manager and instance caging are not enabled.
Instance caging allocation of core resources is enabled in accordance with the Oracle Database Appliance database template size that you select for each database. The CPU_COUNT initialization parameter is set in the template. Use the CPU_COUNT setting that matches the size of each database to consolidate, and follow the standard instructions for configuring instance caging.
Parent topic: Managing Oracle Databases
Oracle EM Express and DB Console
You can use Oracle Enterprise Manager Database Express (EM Express), or the Database Control Console (DB Console) to manage your database.
The EM Express console is available for Oracle Database 18c, 12.2.0.1, and 12.1.0.2. The DB Console is available for Oracle Database 11.2.0.4. Both consoles are web-based tools for managing Oracle Databases.
The EM Express console provides the following features:
-
Support for basic administrative tasks, such as storage and user management
-
Comprehensive solutions for performance diagnostics and tuning
-
Performance advisors in a graphic user interface
-
Oracle Database utilities in a graphic user interface, such as SQL*Loader and Oracle Recovery Manager (RMAN)
EM Express is built inside the database server and cannot perform actions outside the database.
Parent topic: Managing Oracle Databases