Creating a File System, Mount Target, and Export
This section describes how to perform all the tasks that are required to create a file system and make it available for instances.
Task Flow
| No. | Description | Links to Procedures |
|---|---|---|
| 1. |
Ensure that a mount target exists for the subnet that the instance where you want to mount a file system will use and the backing store pool that the file system will use. NoteThe file system and mount target must be in the same compartment and the same backing store pool when you create an export. |
|
| 2. |
Create the file system. |
|
| 3. |
Create a file system export in the mount target. |
|
| 4. |
Enable Security Rules for File Storage. |
|
| 5. |
Change NFS export options to control access to the file system. |
After the file system is exported, on the NFS client, perform these tasks to mount the file system:
-
(If needed) Install NFS client software.
-
Create a mount point.
-
On the client, mount the file system to the mount point.
-
On the client, add whatever files, directories, and data that you want in the file system.
For more information about mounting file systems, see Mounting File Systems on UNIX-Based Instances.
Creating a Mount Target
A mount target is an NFS endpoint assigned to a subnet of your choice. The mount target provides the IP address or DNS name that is used in the mount command when connecting NFS clients to a file system.
For an instance to mount a file system, the instance's VCN must have a mount target.
You can create at most two mount targets per VCN: at most one mount target per pool type. Pool type refers to the backing store pool for the file system, which can be either the default pool of the attached ZFS Storage Appliance or a high performance pool. See the poolName property (the OraclePCA.poolName defined tag) in Creating a File System. Two mount targets in a VCN are counted as one with regard to resource limits (see Tenancy Resource Configuration Limits in the Oracle Private Cloud Appliance Release Notes).
You can reuse a mount target to make many file systems available on the network. To reuse the same mount target for multiple file systems, create an export in the mount target for each file system. The file system and mount target must be in the same compartment and the same backing store pool when you create an export.
Caution:
Do not use /30 or smaller subnets for mount target creation because they might not have sufficient available IP addresses.
Important:
When exporting file systems to overlapping CIDRs in a VCN, exports to the longest CIDR (smallest network) must be done first. For more information and an example, see My Oracle Support article PCA File system as a Service Exports (Doc ID 2823994.1).
Before you can create a mount target, ensure that these items are configured:
-
At least one Virtual Cloud Network (VCN) and subnet is configured. See Managing VCNs and Subnets.
- (Required for cross appliance mounting) A Dynamic Routing Gateway (DRG) with a route rule in the VCN. See Connecting to the On-Premises Network through a Dynamic Routing Gateway.
-
(Optional) Security rules for the file system mount target. Security rules can be created in the security list for the mount target subnet, or in a Network Security Group (NSG) that you add the mount target to. See Controlling Access to File Storage.
You don't need security rules to create a mount target, but you do need security rules to eventually mount file systems that are associated with this mount target.
Using the Compute Web UI
-
In the navigation menu, under File Storage, click Mount Targets.
In the compartment drop-down menu above the mount targets list, select the compartment where you plan to create the file system.
If a mount target is listed, click the name of the mount target to open the details page and check the following parameters:
-
The mount target must be on the same subnet as the instance where you want to mount the file system.
-
Click the Tags tab. The mount target must be in the same backing store pool that is specified for the file system. If the value of the OraclePCA.poolName tag is PCA_POOL_HIGH, then the mount target is in the high performance pool. If the value of the OraclePCA.poolName tag is PCA_POOL, or if there is no OraclePCA.poolName tag, then the mount target is in the default pool of the attached ZFS Storage Appliance.
If the mount target meets your needs, skip this procedure and go to Creating a File System.
-
-
Click Create Mount Target.
-
Enter the mount target information:
-
Name: It doesn't have to be unique. An Oracle Cloud Identifier (OCID) uniquely identifies the mount target. Avoid entering confidential information.
Note:
The mount target name is different than the DNS hostname.
-
Create in Compartment: Specify the compartment.
-
VCN: Select the VCN for the new mount target.
-
Subnet: Select a subnet to attach the mount target to.
-
IP Address:(Optional) You can specify an unused IP address in the subnet you selected for the mount target. If left blank, an IP address is automatically assigned.
-
Host Name:(Optional) You can specify a hostname you want to assign to the mount target.
Note:
The File Storage service constructs a fully qualified domain name (FQDN) by combining the hostname with the FQDN of the mount target subnet.
For example,
myhostname.subnet123.dnslabel.examplevcn.com. -
Enable Network Security Groups: Select this option to add this mount target to an existing NSG.
Important:
Rules for the NSG that you select must be configured to allow traffic to the mount target's VNIC using specific protocols and ports. For more information, see Controlling Access to File Storage Configuring VCN Security Rules for File Storage.
-
Tagging:(Optional) Add defined or free-form tags for this mount target as described in Adding Tags at Resource Creation. Tags can also be applied later.
By default, the mount target is for the default pool of the attached ZFS Storage Appliance. To create a mount target for a high performance pool, select the OraclePCA tag namespace, the poolName tag key, and the value PCA_POOL_HIGH. For more information, see "Block Volume Performance Options" in the Block Volume Storage Overview chapter in the Oracle Private Cloud Appliance Concepts Guide. Before you specify PCA_POOL_HIGH, check with an appliance administrator to verify that a high performance pool is available. The poolName property can be set only when the mount target is created. You cannot set or change this property value after the mount target is created.
-
-
Click Create Mount Target.
Next, create a file system. See Creating a File System.
Using the OCI CLI
-
Gather the information that you need to run the command:
-
OCID of the compartment where you plan to create the file system (
oci iam compartment list) -
OCID of the subnet of the instance where you want to mount a file system (
oci network subnet list)
-
-
Run the create mount target command.
Syntax:
oci fs mount-target create \ --availability-domain AD-1 \ --compartment-id compartment_OCID \ --subnet-id subnet_OCID
By default, the mount target is for the default pool of the attached ZFS Storage Appliance. To create a mount target for a high performance pool, specify the
OraclePCA.poolNametag with a value ofPCA_POOL_HIGHas shown in the following example. For more information, see "Block Volume Performance Options" in the Block Volume Storage Overview chapter in the Oracle Private Cloud Appliance Concepts Guide. Before you specifyPCA_POOL_HIGH, check with an appliance administrator to verify that a high performance pool is available. ThepoolNameproperty can be set only when the mount target is created. You cannot set or change this property value with theupdatecommand.Example:
oci fs mount-target create --availability-domain AD-1 \ --compartment-id ocid1.compartment.uniqueID --subnet-id ocid1.subnet.uniqueID \ --defined-tags '{"OraclePCA":{"poolName":"PCA_POOL_HIGH"}}' \ --display-name HighPerfPoolMT { "data": { "availability-domain": "AD-1", "compartment-id": "ocid1.compartment.uniqueID", "defined-tags": { "Oracle-Tags": { "CreatedBy": "pca_user", "CreatedOn": "2024-07-03T14:56:29.92Z" }, "OraclePCA":{ "poolName":"PCA_POOL_HIGH" } }, "display-name": "HighPerfPoolMT", "export-set-id": "ocid1.exportset.uniqueID", "freeform-tags": {}, "id": "ocid1.mounttarget.uniqueID", "lifecycle-details": null, "lifecycle-state": "CREATING", "nsg-ids": [], "private-ip-ids": [], "subnet-id": "ocid1.subnet.uniqueID", "time-created": "2024-07-03T14:56:29.921587+00:00" }, "etag": "2d278b37-a74a-4fec-b74a-fd9e9a1c72de"
-
Next, create a file system. See Creating a File System.
Creating a File System
You can set values for the file system quota, the database record size, and the pool to use for the backing store by using OraclePCA defined tags. If you use the OCI CLI or API, you can specify the OraclePCA tag namespace, tag key, and values for the parameters that you want to set. You do not need to first create the OraclePCA tag namespace and tag keys.
Note:
If you use the Compute Web UI to set these parameters, you must first create the OraclePCA tag namespace, tag keys, and value choices. See Creating OraclePCA Tags for instructions.
Using the Compute Web UI
-
On the Dashboard, click the File Storage/View File Systems button.
Ensure that the correct compartment is selected in the compartment drop-down menu above the file systems list. The file system and mount target must be in the same compartment and the same backing store pool when you create an export.
-
Click the Create File System button.
-
In the Create File System dialog, enter the following information:
-
Name: It doesn't have to be unique. An Oracle Cloud Identifier (OCID) uniquely identifies the file system. Avoid entering confidential information.
-
Create in Compartment: Select the compartment where the file system is created.
-
Tagging: (Optional) Add defined or free-form tags for this file system as described in Adding Tags at Resource Creation. Tags can also be applied later.
See the OCI CLI procedure for descriptions of the file system quota (OraclePCA.quota), database record size (OraclePCA.databaseRecordSize), and backing store pool (OraclePCA.poolName) defined tags. Note that databaseRecordSize and poolName must be set in Create File System. The database record size and backing store pool cannot be set or updated after the file system is created. For more information about backing store pools, see "Block Volume Performance Options" in the Block Volume Storage Overview chapter in the Oracle Private Cloud Appliance Concepts Guide. Before you specify the high performance backing store pool, check with an appliance administrator to verify that a high performance pool is available.
-
-
Click Create File System.
The file system is created.
Next, create an export for the file system. See Creating an Export for a File System.
Using the OCI CLI
-
Gather the information that you need to run the command:
-
Compartment OCID (
oci iam compartment list) -
File System Name: The display name you want assigned to this file system
-
-
Decide whether you need to set certain optional properties.
The following properties are set by using defined tags. For the syntax to specify a defined tag, see Adding Tags at Resource Creation.
Specify the
OraclePCAtag namespace to set values for the following properties:-
File system quota. Specify
quotafor the tag key. The default value ofquotais 0, which means no quota is set. A quota that you set includes the data in the file system and all snapshots created under the file system. You can specify a quota value in gigabytes from 0 to 8000000 (8 petabytes). Any fractional portion of the gigabyte value is rounded to the next larger megabyte. The file system quota can be reset with the file systemupdatecommand. -
Database record size. Specify
databaseRecordSizefor the tag key. The default database record size is 131072 bytes. You can specify one of the following values (in bytes) for the value ofdatabaseRecordSize: 512, 1024, 2048, 4096, 8192, 16384, 32768, 65536, 131072, 262144, 524288, 1048576. ThedatabaseRecordSizeproperty can be set only when the file system is created. You cannot set or change this property value with theupdatecommand. -
Backing store pool. Specify
poolNamefor the tag key. By default, the backing store of a file system instance is the default pool of the attached ZFS Storage Appliance, specified asPCA_POOL. You can specifyPCA_POOL_HIGHfor the value ofpoolNameto indicate that you want to use a high performance pool for the backing store. For more information about backing store pools, see "Block Volume Performance Options" in the Block Volume Storage Overview chapter in the Oracle Private Cloud Appliance Concepts Guide. Before you specifyPCA_POOL_HIGH, check with an appliance administrator to verify that a high performance pool is available. ThepoolNameproperty can be set only when the file system is created. You cannot set or change this property value with theupdatecommand.
See the following step for an example of setting these values.
-
-
Run the create file system command.
Syntax:
oci fs file-system create --availability-domain AD-1 \ --compartment-id compartment_OCIDExample:
oci fs file-system create --availability-domain AD-1 \ --compartment-id ocid1.compartment.unique_ID --display-name MyFileSystem { "data": { "availability-domain": "AD-1", "compartment-id": "ocid1.compartment.unique_ID", "defined-tags": { "Oracle-Tags": { "CreatedBy": "pca_user", "CreatedOn": "2024-07-05T13:15:11.19Z" } }, "display-name": "MyFileSystem", "freeform-tags": {}, "id": "ocid1.filesystem.unique_ID", "is-clone-parent": false, "is-hydrated": true, "is-targetable": null, "kms-key-id": "", "lifecycle-details": "", "lifecycle-state": "CREATING", "metered-bytes": 0, "source-details": { "parent-file-system-id": "", "source-snapshot-id": "" }, "time-created": "2024-07-05T13:15:11.234434+00:00" }, "etag": "58dec47e-4732-4730-9e18-6b5db1ac30d6" }
Example using defined tags to set additional properties:
To set a quota for the file system, change the default database record size, or specify a high performance pool for the file system backing store, use
OraclePCAdefined tags as shown in the following example.oci fs file-system create --availability-domain AD-1 \ --compartment-id ocid1.compartment.unique_ID --display-name myfilesystem \ --defined-tags '{"OraclePCA":{"quota":100000,"databaseRecordSize":8192,"poolName":"PCA_POOL_HIGH"}}'Alternatively, you can specify these properties in a JSON file.
{ "OraclePCA": { "quota": 100000, "databaseRecordSize": 8192, "poolName": "PCA_POOL_HIGH" } }Then specify the file as the argument of the
--defined-tagsoption.--defined-tags file://./fs_options.json
-
Next, create an export for the file system. See Creating an Export for a File System.
Creating an Export for a File System
Exports control how NFS clients access file systems when they connect to a mount target.
A file system must have at least one export in one mount target for instances to mount the file system.
Important:
When exporting file systems to overlapping CIDRs in a VCN, exports to the longest CIDR (smallest network) must be done first. For more information and an example, see My Oracle Support article PCA File system as a Service Exports (Doc ID 2823994.1).
Using the Compute Web UI
-
On the Dashboard, click the File Storage/View File Systems button.
-
If the file system that you want to export is not listed, use the Compartment drop-down menu above the file systems list to select the correct compartment.
-
Click the name of the file system that you plan to create an export for.
-
Scroll down to the Resources section, click Exports, and click Create Export.
-
Enter the following information:
-
Mount Target: Select a mount target from the list.
-
Source CIDR: Enter the longest CIDR (smallest network) in the CIDR range. Starting with the smallest CIDR range (largest network) will result in an error later in the process because CIDR ranges larger than existing ones will not be accepted. For example, 10.0.0.0/29 is a longer CIDR than 10.0.0.0/28, so add 10.0.0.0/29 first.
-
-
Click Create Export.
The file system export is created and the export details page is displayed.
-
In the export details page, note the export path as shown in the following screen capture. The export path is used to mount the file system on an instance.
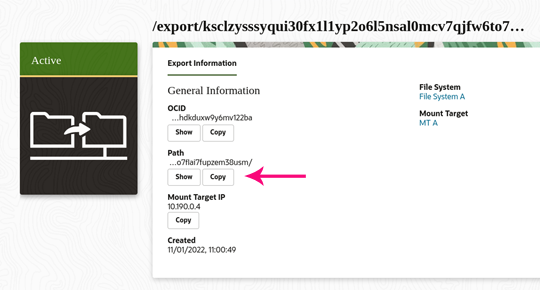
-
Scroll down to the Resources section and review the NFS Export Options.
The NFS export options for that file system are set to the default values, which allow full access for all NFS client source connections. These defaults must be changed if you want to restrict access.
-
Consider your next action:
-
Mount the file system from an NFS client. See Mounting File Systems on UNIX-Based Instances.
-
Configure NFS options to secure the exported file system. See Setting NFS Export Options.
-
Using the OCI CLI
-
Gather the information that you need to run the command:
-
Export set OCID (
oci fs export-set list) -
File system OCID (
oci fs file-system list)
-
-
Run the export create command.
Important:
The
pathoption is required and its value must beAUTOSELECT. The value must be given in all uppercase letters. Providing any other value will cause theexport createcommand to fail.The export path is always automatically generated. See the
pathproperty in the command output for the export path.Syntax:
oci fs export create --export-set-id export_set_OCID \ --file-system-id file_system_OCID --path AUTOSELECT
Example:
oci fs export create --export-set-id ocid1.exportset.uniqueID \ --file-system-id ocid1.filesystem.uniqueID --path AUTOSELECT { "data": { "export-options": [ { "access": "READ_WRITE", "anonymous-gid": 65534, "anonymous-uid": 65534, "identity-squash": "NONE", "require-privileged-source-port": false, "source": "0.0.0.0/0" } ], "export-set-id": "ocid1.exportset.uniqueID", "file-system-id": "ocid1.filesystem.uniqueID", "id": "ocid1.export.uniqueID", "lifecycle-state": "ACTIVE", "path": "/export/18lt6v4drhddiz2mn7vwmqt7mjiz3kfbw4reqaew33y50pdrj35p4ef5p04x", "time-created": "2023-06-06T04:34:28.829547+00:00" }, "etag": "a0842b0b-b27b-4c98-a1ff-da85ae4bf150" }
-
In the command output, note the value of
path. The path value is used to mount the file system. To reprint this information, use the following command:oci fs export get --export-id ocid1.export.uniqueID -
In the output, review the export options.
In this example, the NFS export options for the file system are set to the default values, which allow full access for all NFS client source connections. These defaults must be changed if you want to restrict access
-
Next, control access to the file system.
Mounting File Systems Across Private Cloud Appliances
You can create a file system on one Private Cloud Appliance, and mount the file system from an instance that is on another Private Cloud Appliance. To achieve this scenario, you must configure certain network parameters on each appliance.
Restriction
The appliance hosting the file system and the instance on the remote appliance that mounts the file system can't have overlapping VCN CIDR blocks.
On the Appliance Hosting the File System
-
Configure these network parameters:
-
Create a Dynamic Routing Gateway (DRG).
See Connecting to the On-Premises Network through a Dynamic Routing Gateway.
-
For the VCN subnet that will be used by the mount target, attach the VCN to the DRG.
-
For the VCN subnet, add a route rule with the DRG as the target, and assign a destination CIDR that matches the remote appliance VCN CIDR.
For example, if the remote appliance instance that will mount the file system has a VCN with a 10.11.0.0/16 CIDR, the set the route rule destination CIDR to 10.11.0.0/16.
Important:
Don’t specify 0.0.0.0/0 as the destination. Doing so causes serious internal network issues.
Note:
This route rule configuration is only required for mounting file systems across appliances. This configuration is not required for file system mounts within the same appliance.
-
- Create a mount target. See Creating a Mount Target.
- Create a file system. See Creating a File System.
-
Create an export that exports to both the source and remote appliance VCN CIDR.
The export CIDR must be big enough to cover both appliance VCN subnet CIDRs. For example, if the host VCN CIDR is 10.10.0.0/16, and the remote appliance instance VCN is 10.11.0.0/16, you can configure the export to use 10.10.0.0/15. This requirement only applies to the appliance hosting the file system.
On the Remote Appliance
-
Configure these network parameters:
-
Create a Dynamic Routing Gateway (DRG).
See Connecting to the On-Premises Network through a Dynamic Routing Gateway.
-
For the VCN subnet, attach the VCN to the DRG.
-
For the VCN subnet, add a route rule with the DRG as the target, and assign a destination CIDR that matches the host appliance VCN CIDR.
For example, if the host appliance mount target has a VCN 10.0.0.0/16 CIDR, set the route rule destination CIDR to 10.0.0.0/16.
Important:
Don’t specify 0.0.0.0/0 as the destination. Doing so causes serious internal network issues.
Note:
This route rule configuration is only required for mounting file systems across appliances. It is not required for file system mounts within the same appliance.
-
-
Log in to the instance and mount the file system.
See: