Flow for Archive-to-Cloud Storage
All backup objects archived to cloud storage are encrypted using a random Data Encryption Key (DEK). A Transparent Data Encryption (TDE) master key for each protected database is used to encrypt the DEK; the encrypted DEK is stored in the backup piece. The Oracle Key Vault (OKV) contains the TDE master keys; it does not contain the individual DEKs used to encrypt backups written to tape or cloud. A protected database may acquire many TDE master keys with time, so restoration of an individual archived object requires the protected database's master key in use at time of backup.
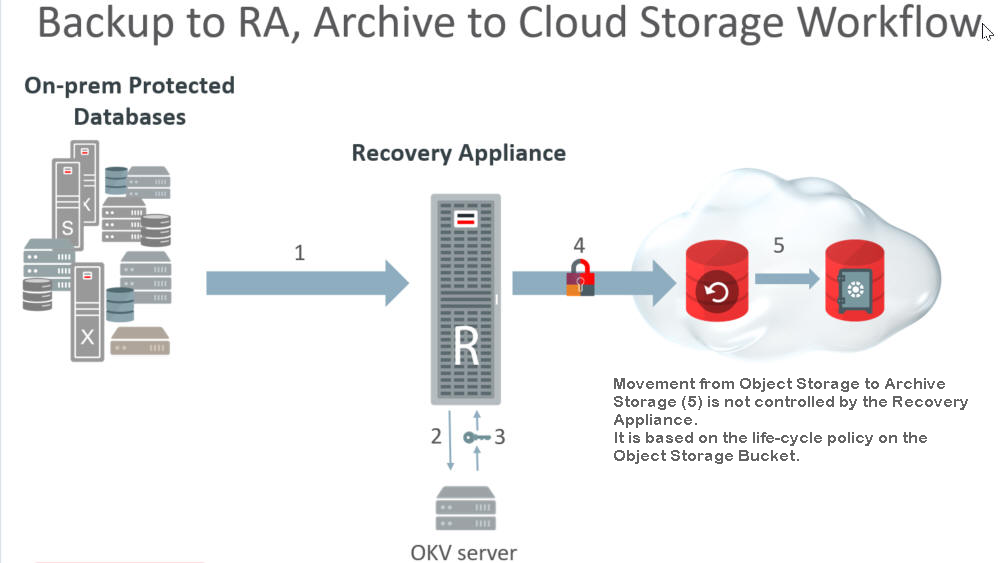
The following image shows the flow for backing up to a Recovery Appliance that archives to cloud storage. The restore operations are predicated on this backup and archive flow.
Figure 10-1 Flow for Backups to Cloud Storage
Description of "Figure 10-1 Flow for Backups to Cloud Storage"
-
Incremental backups of the database are performed regularly to the Recovery Appliance. This happens at a different interval than the following archive operations.
-
When the scheduled archive-to-cloud operation starts, the Recovery Appliance requests a master key for the protected database from the OKV Server.
-
The OKV returns the protected database's master key. If one doesn't exist for the protected database, a new master key is generated. (A new master key can be generated whenever desired.)
-
A DEK is generated for the backup object(s).
-
The backup objects are encrypted using the DEK.
-
Using the master key, the Recovery Appliance encrypts the DEK and stores this with the backup object.
-
-
The life-cycle policy for a given database determines if and when its backup objects are written to tape or cloud storage.
-
The life-cycle policy of the object storage bucket determines if and when a backup object in cloud storage moves from object storage to archive storage. The Recovery Appliance does not control this.